Core Connections Course 1 Student 1st Edition Chapter 2 Arithmetic Strategies and Area
Core Connections Course 1 Student 1st Edition Chapter 2 Exercise 2.2 Solutions Page 62 Problem 1 Answer
Given- The top of the desk is a flat space. We have to determine the units that can be used to measure the area without gaps or overlaps.
We will use square units to determine the area.
As two quantities measured in the same units have been multiplied together gives square units that help us to find the area that helps in accurately without leaving gaps.
Hence we would use square units to determine the area of the top of the desk.
Core Connections Course 1 Student 1st Edition Chapter 2 Exercise 2.2 Solutions Page 62 Problem 2 Answer
Given- The top of the desk is a flat space.
We have to determine the number of units to cover the area of the desk.space.
We will use the concept of the area of the square which is side × side.
Let’s assume that our desk is in a square shape.
The area of my table as measured with the squares is 3×3, i.e. 9 square units are needed to cover the area of my desk because area of the square is equal to side ×side
Read and learn More Core Connections Course 1 Student 1st Edition Solutions
For 3×3 square units desk, a total of 9 units are needed to cover the area of the desk.
Core Connections Course 1 Chapter 2 Page 63 Problem 3 Answer
Given-

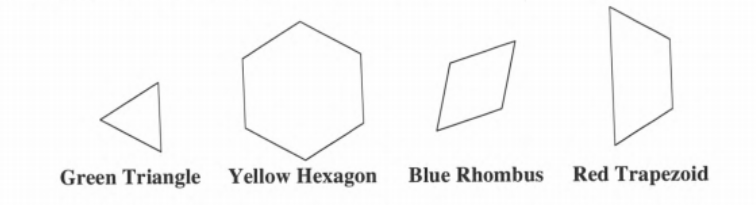
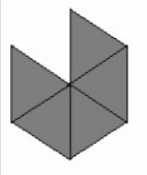
Maureen decides that the green triangle represents one unit of area.
We need to determine the area of the blue rhombus, red trapezoid and yellow hexagon.
We divide each figure into equal parts to find out the area.
If Green Triangle represents one unit area, then,
The Area of Blue Rhombus will be 2 unit areas because Rhombus is equal to two triangles.
The Area of the Red Trapezoid will be 3 unit areas because Trapezoid is equal to 3 triangles.
The Area of the Yellow Hexagon will be 6 unit areas because the hexagon is equal to 6 triangles.
Hence
Area of rhombus =2 units,
Area of Trapezoid = 3 units ,
Area of Hexagon =6 units.
Chapter 2 Exercise 2.2 Arithmetic Strategies And Area Solutions Core Connections Course 1 Page 63 Problem 4 Answer
Given-
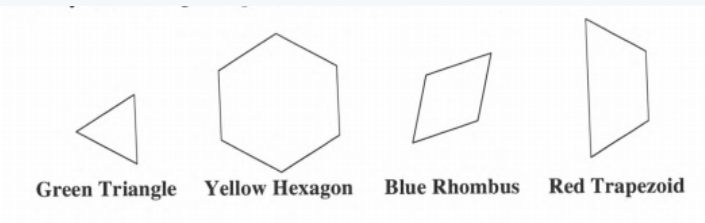
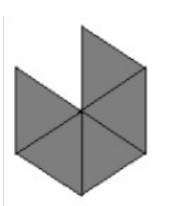
We have to explain what if, instead of the green triangle, Maureen decides the blue rhombus represents one unit of area. What would the area of the green triangle be? The red trapezoid?
The yellow hexagon? We will use the concepts of triangle, trapezoid and hexagon.
If Blue Rhombus represents one unit area, then,
The Area of Green Triangle will be 1/2 unit areas.
The Area of Red Trapezoid will be 11/2 unit areas.
The Area of Yellow Hexagon will be 3 unit areas.
Area of triangle =1/2 units, Area of trapezoid =3/2 units and area of hexagon =3 units
Core Connections Course 1 Chapter 2 Page 63 Problem 5 Answer
Given-
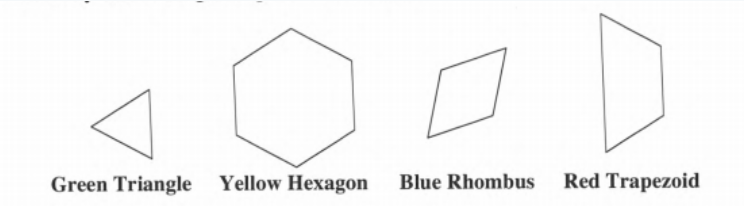
Maureen decides that the red trapezoid represents an area of one unit.
We have to determine the area of the green triangle, blue rhombus and yellow hexagon.
We divide each figure into equal parts to find out the area.
If Red Trapezoid represents one unit area, then,
The Area of Green Triangle will be 1/3 of unit area because Trapezoid is equal to three triangles.
The Area of Blue Rhombus will be 2/3 unit area because Rhombus is equal to two triangles and Trapezoid is equal to three triangles.
The Area of Yellow Hexagon will be 2 unit areas because Hexagon is equal to two trapezoids.
Area of triangle =1/3 units,
Area of rhombus =2/3 units and
Area of hexagon =2 units
Core Connections Course 1 Chapter 2 Exercise 2.2 Step-By-Step Solutions Page 63 Problem 6 Answer
Given-
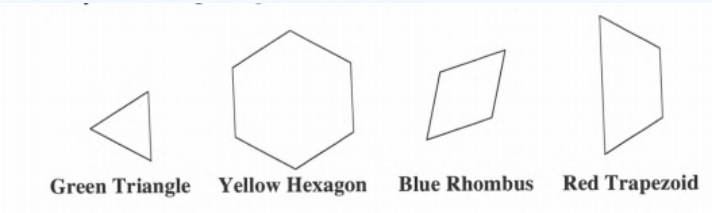
Maureen has finally decided that she should use the biggest block and will make the yellow hexagon represent an area of one unit.
We need to determine the area of the green triangle, The blue rhombus and the red trapezoid.
We divide each figure into equal parts to find out the area.
If Yellow Hexagon represents one unit area, then,
The Area of Green Triangle will be 1/6 of unit area because Hexagon is equal to six triangles.
The Area of Blue Rhombus will be 1/3 unit area because Rhombus is equal to two triangles.
The Area of Trapezoid will be 1/2 unit areas because Trapezoid is equal to three triangles.
Area of triangle =1/6 units,
Area of rhombus=1/3 units and
Area of hexagon =1/2 units
Core Connections Course 1 Chapter 2 Page 63 Problem 7 Answer
Given-:
Assume that the area of the blue rhombus is 1/4 unit
We have to Build a shape that has an area of 5/8
What would be the area of a shape built using one of each color of block?
we see from the above figure that rhombus is a combination of two triangles and so the triangle must have an area of 1/8।
Given that the area of the blue rhombus is 1/4 unit Also we see from the above figure that rhombus is a combination of two triangles and so the triangle must have an area of 1/8.
Now we need to build a shape that has an area of5/8. We can see that
5/8=1/4+1/4+1/8
So, we basically need two rhombus and a triangle shaped figure or five triangles for an area of 5/8.
It can be the one as shown below.
Since blue rhombus is a combination of two triangles, area of one triangle is1/8units as mentioned in the above part
From the above figures, we saw that a hexagon has 6 triangles and a trapezoid has 3 triangles.
So, if a shape is built using one of each color of block, there will be a total of 12 triangles, i.e.
6 from hexagon, 2 from rhombus, 3 from trapezoid and 1 triangle itself.
Thus the total area of that shape will be 12 times the area of one triangle, i.e.
12×1/8=3/2 units
The shape having an area of 5/8 is shown below
The area of the shape built using one of each color of block is 3/2 units .
Core Connections Course 1 Chapter 2 Page 63 Problem 8 Answer
In our Learning Log, we need to describe area. What makes area different from length ?
What can you use to measure area? Label this entry “Area” and include today’s date.
29/09/2021 Area
An area is a space enclosed within a curve forming a closed shape.
Line is a linear object, that is we can move only in two directions on a line, whereas area is a two-dimensional object and allows movement in all six directions.
Area can be measured using another piece of object taken as a reference for unit area.
Hence , An area is a space enclosed within a curve forming a closed shape.
Solutions for Core Connections Course 1 Chapter 2 Exercise 2.2 Arithmetic Strategies And Area Page 65 Problem 9 Answer
Given-
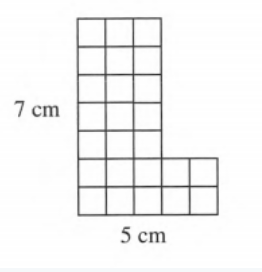
We have to find the area of the shape at right that was cut from graph paper.
We will use the area of rectangle which is l×b and area of the square which is (side)2
The shape can be divided into two parts with one part (yellow) covered by using 21 squares of 1×1 centimeters and the other part (blue) by using 4 squares of 1×1centimeters.
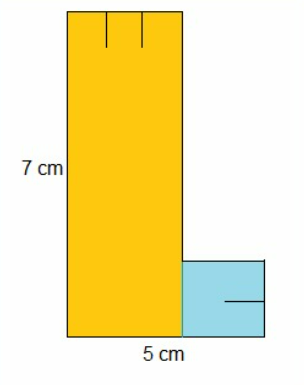
So the area of the shape is 25 square centimeters.
Core Connections Course 1 Chapter 2 Page 65 Problem 10 Answer
Given-
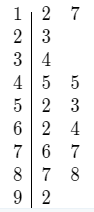
We have to copy and complete the stem-and-leaf plot at right for the following set of data:64,87,52,12,17,23,45,88,45,92,62,76,77,34,and53.
We will make the table of stem and leaf plot.
We will make the stem and leaf plot by using the following steps
(1) On the left hand side of the page, write down the thousands, hundreds or tens (all digits but the last one). These will be your stems.
(2) Draw a line to the right of these stems.
(3) On the other side of the line, write down the ones (the last digit of a number)
The Stem and Leaf Plot
The stem-and-leaf plot at right for the following set of data: 64,87,52,12,17,23,45,88,45,92,62,76,77,34,and 53 is
Solutions For Core Connections Course 1 Chapter 2 Exercise 2.2 Arithmetic Strategies And Area Page 65 Problem 11 Answer
Given-9.67+49.7+5.22
We have to add the given expression.
We will convert unlike decimal numbers into like numbers.
We will arrange the given terms according to the decimals and then add them.
The given expression is 9.67+49.7+5.22
Converting then to like decimals, we get
49.7=49.70
Thus, now all digits are having equal numbers on the right side of the decimal.
Thus, the additions of given numbers can be performed as,
49.70
9.67
+ 5.22
−−−−−−−−−−−−−
= 64.59
Hence , value of 9.67+49.7+5.22 is 64.59
Core Connections Course 1 Chapter 2 Page 65 Problem 12 Answer
Given-4.2+1.903
We have to add the given expression.
We will convert unlike decimal numbers into like numbers and then add them
The given expression is 4.2+1.903
Converting then to a like decimals, we get
4.2=4.200
Thus, now both digits have equal numbers in the right side of decimal.
Thus, to additions of given numbers can be perform as,
4.200
+ 1.903
−−−−−−−−−−−−
=6.103
The solution is 6.103.
Hence, the value of 4.2+1.903 is 6.103
Core Connections Course 1 Student 1st Edition Chapter 2 Exercise 2.2 Guide Page 65 Problem 13 Answer
Given-97.1−35.04
We have to subtract the given expression.
97.1 − 35.04
= 62.06
97.10
−35.04
Hence , the value of 97.1−35.04 is 62.06
Core Connections Course 1 Chapter 2 Page 67 Problem 14 Answer
We have given a rectangle that is 5 centimeters by 3 centimeter.
We need to find how many square centimeter will this rectangle will fill.
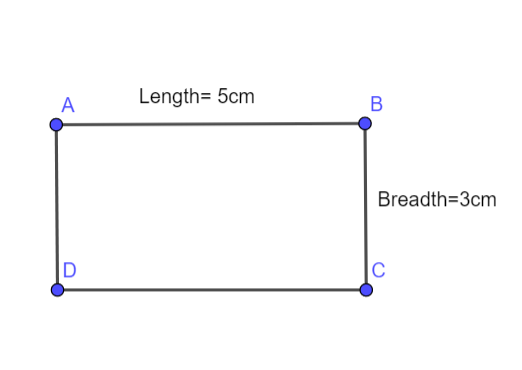
We will use formula of area of rectangle to find the answer.
Given rectangle that is 5 centimeters by 3 centimeters can be drawn as following
Area of rectangle = product of length and breadth
=l∗b
=5cm∗3cm
=15 square centimeters
So the area of rectangle is 15 square centimeters.
The area filled by rectangle is 15 square centimeters.
Chapter 2 Exercise 2.2 Arithmetic Strategies And Area Explained Core Connections Course 1 Page 67 Problem 15 Answer
We have given a rectangle that is 6 inches by 2 inches.
We need to find how many square inches will this rectangle will fill.
We will use formula of area of rectangle to find the answer.
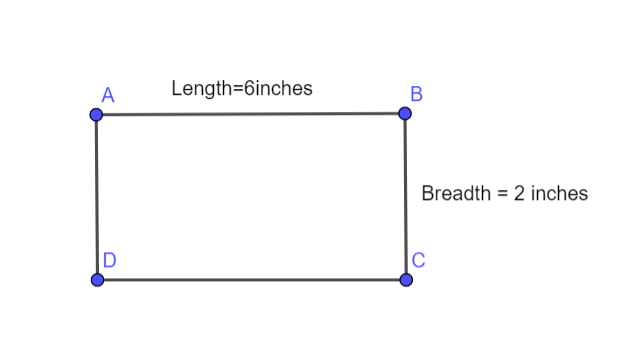
Given rectangle is 6inches by 2 inches that can be drawn as following
Area of rectangle = product of length and breadth
Area of given rectangle =l∗b =6inches ∗2inches
=12 square inches
So, the area of rectangle is 12 square inches.
Area of given rectangle is 12 square inches.
Core Connections Course 1 Chapter 2 Page 67 Problem 16 Answer
We have given a rectangle that is 60 feet by 20 feet.
We need to find how many square inches will this rectangle will fill.
We will use formula of area of rectangle to find the answer.
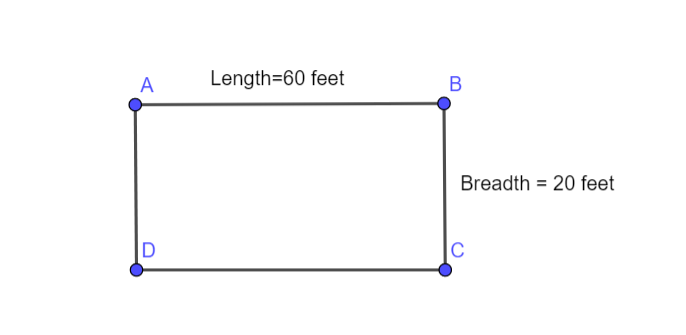
Given rectangle is 60 feet by 20 feet, which can be drawn as following.
Area of rectangle = product of length and breadth
Area of given Rectangle =l∗b
=60 feet ∗20 feet
=1200 square feet
So, Area of given rectangle is 1200 square feet.
Area of the given rectangle is 1200 square feet.
Chapter 2 Exercise 2.2 Arithmetic Strategies And Area Explained Core Connections Course 1 Page 67 Problem 17 Answer
We need to find Area of rectangular garden whose length is 60 feet, breadth is 40 feet.
We will use formula of area of rectangle to find answer.
Given rectangular garden will be as follows
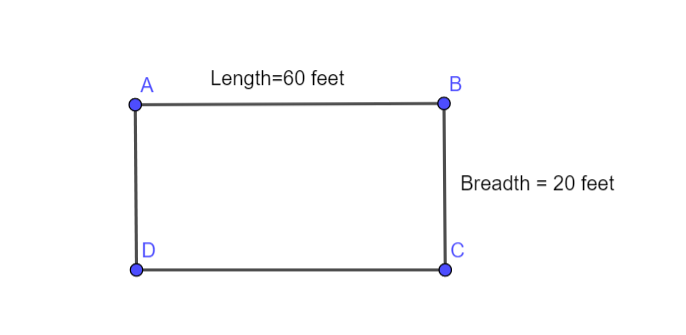
Area of rectangular garden=Length∗Breadth
=l∗b⇒60 feet∗20 feet
=1200 square feet
so , the Area is 1200 square feet.
Area of given Rectangular garden is 1200 square feet.
Core Connections Course 1 Chapter 2 Page 68 Problem 18 Answer
Given: Frank’s pattern for the desktops is on the Lesson 2.2.2C Resource Page that our teacher will provide.
It is asked to find the area of the kidney-bean desktop pattern twice, using each of the two different square units once.
We will calculate the figure with the help of a Square Grip Paper.
At first, we will take a Square Grip Paper, which have the area of one square be 1 sq. cm.
After, placing the paper on the table, we count the complete squares as 1 and colour the complete squares green.
Then, count the squares which are exactly covered half as 1/2 and colour them pink.
After that, count the squares which are covered more than half as 1 and colour them yellow.
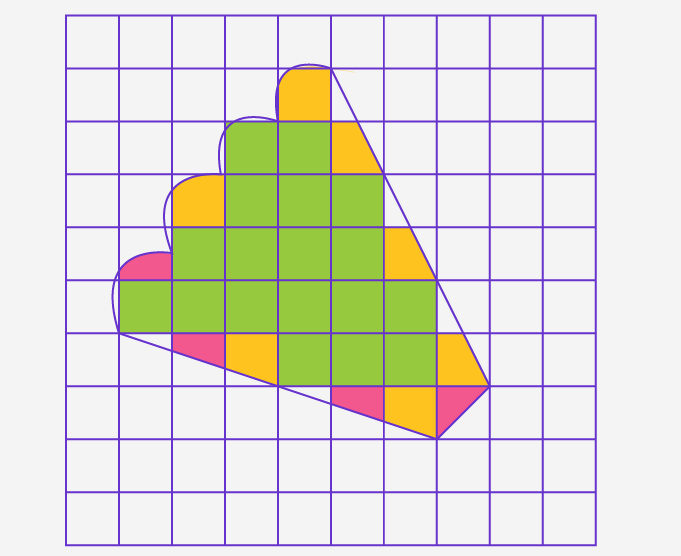
Lastly, ignore the squares that are covered less than half.
Let, take a irregular figure to give a example of this method-
Now, let this irregular figure be the kidney-bean desktop, which covered 18 full squares, 4 half squares and 7 more than a half squares.
Then the area will be (18⋅1+4⋅1/2+7⋅1)=27 unit sq.cm(approx.)
Again, we will take a Square Grip Paper, which have the area of one square be 1 sq. m. and follow the above method to find the area.
Let, the desktop covered x full squares, y half squares and z more than a half squares.
Then the area will be (x⋅1+y⋅1/2+z⋅1)=(x+y/2+z) unit sq.m(approx.)
Hence, from the above step, the area of kidney bean bag will be-
(x+y/2+z) unit sq.m(approx.) and 27 unit sq.cm(approx.)
Core Connections Course 1 Chapter 2 Page 68 Problem 19 Answer
Given: Frank’s pattern for the desktops is on the Lesson 2.2.2C Resource Page that our teacher will provide.
It is asked to compare the two areas from part(a).
From part (a), we know that, the area of kidney bean bag are (x+y/2+z) unit sq.m(approx.) and 27 unit sq.cm(approx.).
Since the area of kidney-bean desktop is constant, so the above two areas will also be same.
They look different because they are in the form of two different square units.
As, we know that, 1 unit sq.cm.=0.0001 unit sq.m.; That’s why they looks different.
Hence, from the above explanation, we can conclude that, the area of kidney-bean desktop is constant, so the two areas from part(a) will also be same.
They look different because they are in the form of two different square units.
As, we know that, 1 unit sq.cm.=0.0001 unit sq.m.; That’s why they looks different.
Worked Examples for Core Connections Course 1 Chapter 2 Exercise 2.2 Arithmetic Strategies And Area Page 68 Problem 20 Answer
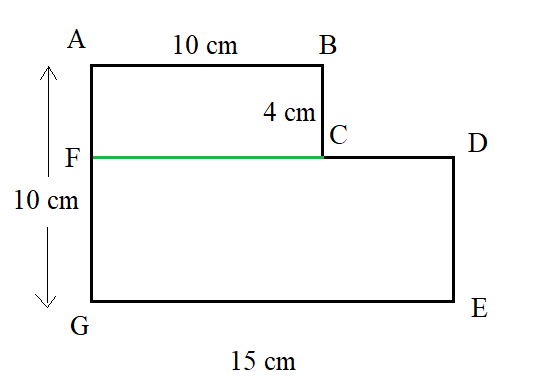
Given a figure where all corner angles are right angles:
To find the area of the above figure in at least two different ways.
Since all corner angles are right angles, we will use formula for area of a rectangle.
Let’s first label the figure and join CF as below.
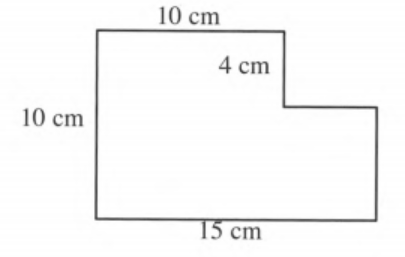
We have, AB=AG=10 cm,
BC=4 cm and GE=15 cm.
Since all corner angles are right angles, ABFG and CDEF are two rectangles.
Therefore, in rectangle ABFG, BF=GF=10 cm and in rectangle CDEF, CD=FE=(15−10) cm
i.e., CD=FE=5 cmand CF= DE=(10−4) cm
i.e., CF=DE=6 cm.
Area of rectangle ABFG = AB×AG
=10×10
=100cm2
Area of rectangle CDEF= CD×CF
=5×6
=30cm2
Area of the given figure= Area of rectangle ABFG + Area of rectangle CDEF
i.e., are of the given figure=(100+30)
=130cm2
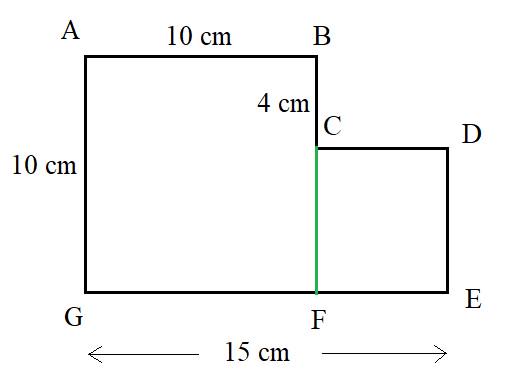
Consider the figure below:
Since all corner angles are right angles, ABCF and GEDF are two rectangles.
In rectangle GEDF, FG= AG − AF
= AG − BC
=(10−4) cm
=6 cm
Area of rectangle ABCF= AB×BC
=10×4
=40cm2
Area of rectangle GEDF=GE×FG
=15×6
=90cm2
Area of the given figure= Area of rectangle ABCF + Area of rectangle GEDF
i.e., are of the given figure=(40+90)cm2
=130cm2
The area of the given figure is 130cm2.
Core Connections Course 1 Chapter 2 Page 68 Problem 21 Answer
Given a figure where all corner angles are right angles.
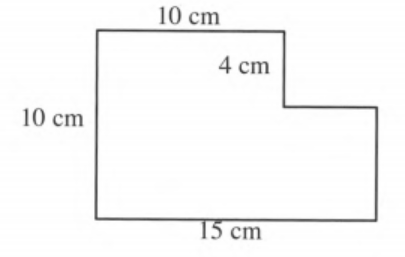
To find the perimeter of the figure.
We will calculate the distance around the figure or length of the boundary of the given figure.
Let’s first label the figure and join CF as below.
Perimeter of the given figure= AB+BC+CD+DE+EG+GA
Since all corner angles are right angles, ABFG and CDEF are two rectangles.
Hence, AB=GF, AG=
BF, CD=
FE and DE=CF.
Thus, GF=10 cm
Therefore, CD=FE
⇒ CD = GE − GF
⇒ CD =(15−10) cm
or, CD=5 cm
Similarly,DE=CF
⇒ DE=BF−BC
= AG−BC
=(10−4) cm
⇒ DE =6 cm.
So, perimeter of the given figure=10+4+5+6+15+10
=50 cm.
The perimeter of the figure is 50 cm.
Core Connections Course 1 Chapter 2 Page 70 Problem 22 Answer
The shaded tiles in the large square each have an area of one square foot.
To find the total area of the shaded squares.
We will count the number of shaded squares in the big square and then multiply by the area of 1 shaded square.
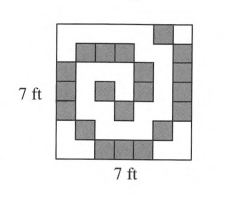
Area of 1 shaded square=1 square foot.
Number of shaded squares=20.
Total area of the shaded squares=20×1 square foot
=20 square foot
Total area of the shaded squares=20 square foot.
Core Connections Course 1 Chapter 2 Exercise 2.2 Detailed Answers Page 70 Problem 23 Answer
The shaded tiles in the large square each have an area of one square foot and side of the big square is 7 ft.
To find the total area of the un-shaded squares.
We will subtract the total area of shaded squares from the area of the big square.
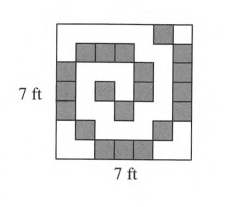
Total area of the shaded squares=20 square foot
Side of the big square=7 ft
Area of the big square=side× side
=7×7 square foot
=49 square foot
Now, total area of the un-shaded squares= area of the big square−total area of the shaded squares
Hence, total area of the un-shaded squares=49−20 =29 square foot
The total area of the un-shaded squares is 29 square foot.
Core Connections Course 1 Chapter 2 Page 70 Problem 24 Answer
The shaded tiles in the large square each have an area of one square foot and side of the big square is 7 ft.
To find the total number of square feet of area in the figure in two different ways.
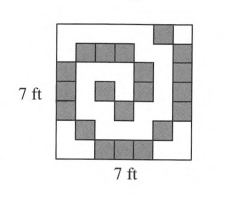
We can find the total number of square feet of area in the figure by following ways: Add the answers from part (a) and part (b). Multiply the dimensions of the big square.
From part (a) and (b),
Total area of the shaded squares =20 square foot.
The total area of the un-shaded squares =29 square foot.
Hence, total are of the square=20+29 =49 square feet.
Side of the big square=7 ft
Hence, area of the big square=7×7 =49 square feet.
Hence, total area of the big square=49 square feet.
Core Connections Course 1 Chapter 2 Exercise 2.2 Detailed Answers Page 70 Problem 25 Answer
We are given that Hector measured the area of his desktop by covering it with quarters ( coins which are circular in shape).
We need to check if he can find the area using these circular units of measure exactly, or will he have to estimate.
A coin is round in shape and he wants to measure the area of his desktop which is rectangular.
So, he will have to estimate the area of his desktop because when the coins are placed side by side, there will be some area that will be left unmeasured.
If Hector uses squares instead of coins, he can exactly measure the area as squares will cover the entire desktop.
Hector cannot use circular units to get an exact answer because when using the coins there will be some gap left in between them.
Core Connections Course 1 Chapter 2 Page 70 Problem 26 Answer
Given the numbers 2,3 and 4.
We need to use the mathematical operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division to create three different numerical expressions with three different values out of which one should have a value of 14.
We will use the four operations on the given numbers.
On using the operations +,×,we get :
2+3⋅4=2+12
=14
On using the operations ×,+, we get :
2⋅4+3=8+3
=11
On using the operations ×,−, we get :
2⋅3−4=6−4
=2
So three different numerical expressions with three different values are :
2+3×4=14
2×4+3=11
2×3−4=2
Core Connections Course 1 Chapter 2 Page 70 Problem 27 Answer
Given: Daily high temperature for Honolulu, Hawaii in December of 2009:83,83,81,82,80,83,81,82,79,83,84,82,81,81,
80,81,84,80,80,81,81,82,80,79,78,80,84,82,82,81,83
To find the best way to display the data given. We also need to explain the reason behind choosing that way and display the data using the method we chose.
We will plot the given data using histogram.
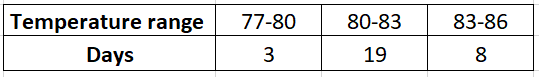
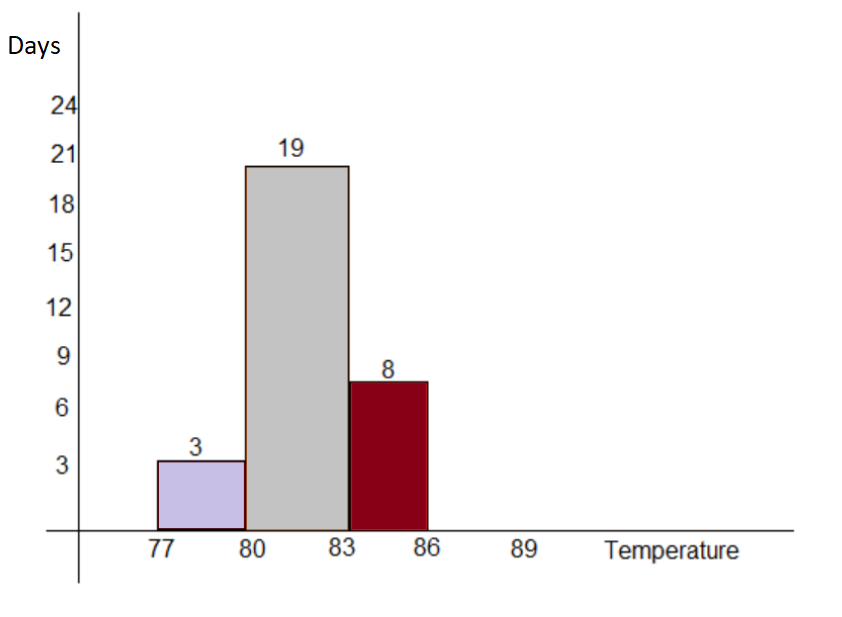
We can see that there are 30 values corresponding to each day of the month, and most of the values share a same stem so stem and leaf plot will be very big and single lined for this case, in this case a Histogram will be efficient and since there is not so much variation in data values we can reduce the bin size to make more accurate predictions from the data.
The table and the histogram are shown below:
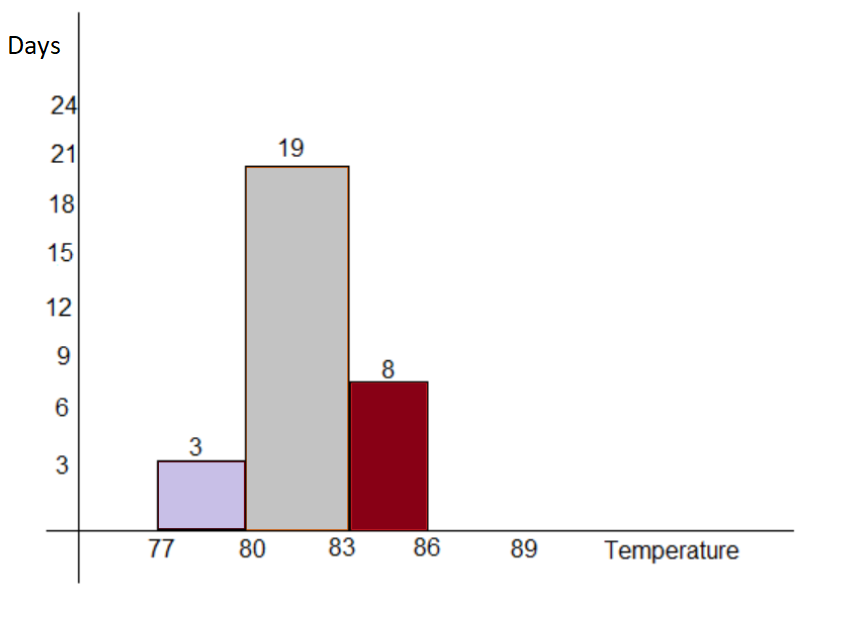
The best way to display data is using a histogram.
