Geometry Student Text 2nd Edition Chapter 3 Perimeter and Area
Carnegie Learning Geometry Student Text 2nd Edition Chapter 3 Exercise 3.3 Solution Page 161 Problem 1 Answer
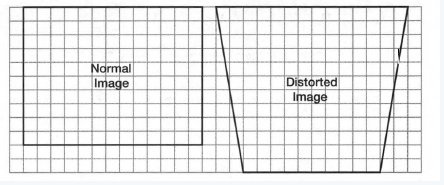
We have to Describe how the normal image has been distorted.
The keystone effect is the apparent distortion of an image caused by projecting it onto an angled surface.
It is the distortion of the image dimensions, such as making a square look like a trapezoid, the shape of an architectural keystone, hence the name of the feature. In the typical case of a projector sitting on a table, and looking upwards to the screen, the image is larger at the top than on the bottom.
Some areas of the screen may not be focused correctly as the projector lens is focused at the average distance only.
The effect is usually corrected for by either using special lenses in Tilt–shift photography or in post-processing using modern image editing software.
Hence, The keystone effect is the apparent distortion of an image caused by projecting it onto an angled surface.
Read and learn More Carnegie Learning Geometry Student Text 2nd Edition Solutions
Solutions For Perimeter And Area Exercise 3.3 In Carnegie Learning Geometry Page 161 Problem 2 Answer
Given: The normal image and distorted image are shown.
To find: Describe the shapes formed by the normal image and the distorted image.
The shape of the normal image is square and the shape of the distorted image is trapezoidal.
Hence the shape of the normal image is square and the shape of the distorted image is trapezoidal.
Page 162 Problem 3 Answer
Given:
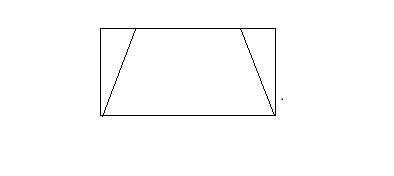
Normal and distorted image.
We have to tell which image has a larger area.
The shape of a normal image is a rectangle while the shape of a distorted image is a trapezoid.
We can see the normal and distorted image has the same big base and height.
A rectangle is divided into a trapezoid and two triangles as shown.
So, the rectangle has a larger area than the trapezoid, or we can say the normal image has a larger area.
Hence, the normal image has a larger area as it can be divided into trapezoid and two triangles.
Carnegie Learning Geometry Chapter 3 Page 162 Problem 4 Answer
Given:
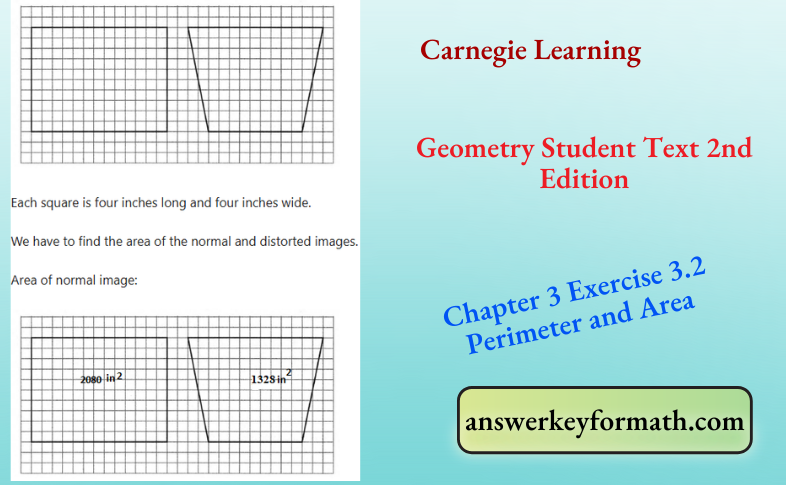
Given Normal image is a rectangle, its area is;
Base is 13×4=52 as it extends across 13 squares on grid.
Height is 10×4=40 as it extends across 10 squares on grid.
Area =40×52=2080 in2
Area of distorted image:
Given distorted image is a trapezoid.
The trapezoid is divided into two triangles and a rectangle.
Base of triangle is 2×4=8 inches
Height of a triangle is 10×4=40 inches
Area of rectangle =l×w
=4(9)×4(10)
=36×40
=1440in2
Area of each triangle=1/2b×h
=1/2[8+40]
=1/2[48]
=24in2
Area of trapezoid =1440+2(24)=1488in2
The area of the normal image is 2080 in2 and area of the distorted image is 1488 in2.
Carnegie Learning Geometry 2nd Edition Exercise 3.3 Solutions Page 162 Problem 5 Answer
Given: From the previous part we have,
Area of the normal image is 2080.in2
Area of distorted image is 1328 in2.
We have to compare the area of images.
The shape of a normal image is a rectangle while the shape of a distorted image is a trapezoid.
A rectangle is divided into a trapezoid and two triangles as shown.
So, the rectangle has a larger area than the trapezoid, or we can say the normal image has a larger area.
Also, it is proved in the previous part as the area of the normal image is 2080 in2 and the area of the distorted image is 1328in2.
Hence, the area of the distorted image is lesser than the area of a normal image.
Hence, We can compare the area of images by comparing the shapes of images.
Carnegie Learning Geometry Chapter 3 Page 162 Problem 6 Answer
Given: Distorted image
We have to find the area of the distorted image.
Base b1 extends to 13 squares on grid and each square is four inches long and four inches wide.
So, b1
=13×4=52 and b²
=9×4=36
as it extends across 9 squares on grid.
Height is 10×4=40 as it extends across 10 squares on grid.
Area of distorted image(Trapezoid):
A=1/2(52+36)×40
=1/2(88)×40
=44×40
=1760in2
The exact area of the distorted image using formula is 1760in2.
Perimeter And Area Solutions Chapter 3 Exercise 3.3 Carnegie Learning Geometry Page 163 Problem 7 Answer
Given: Distorted image
We have to find the area of the distorted image.
Base b1 extends to 13 squares on grid and each square is four inches long and four inches wide.
So, b1
=13×4
=52 and b2
=9×4
=36 as it extends across 9 squares on grid.
Height is10×4=40 as it extends across 10 squares on grid.
Area of distorted image(Trapezoid):
A=1/2(52+36)×40
=1/2(88)×40
=44×40
=1760in2
The exact area of the distorted image using formula is 1760 in2.
Carnegie Learning Geometry Chapter 3 Page 163 Problem 8 Answer
Given:
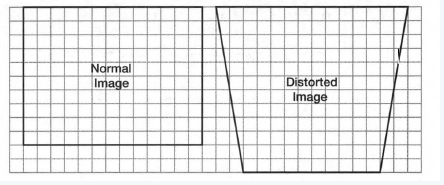
We need to write how does the area of the distorted image compares to the area of the normal image.
Here the normal image is a rectangle and the distorted image is a trapezoid.
Therefore, we can calculate the area of the trapezoid by using the formula and compare it with the area of the rectangle.
Therefore, we can calculate the area by using the formula of the area of the trapezoid and rectangle and compare it.
Page 163 Problem 9 Answer
The given image is
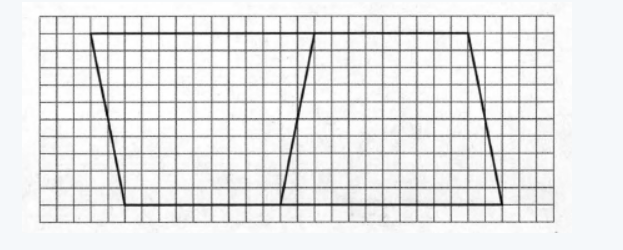
We need to flip it vertically and move it. next to the image as shown.
We need to write the geometric figure that is formed from this image.
The given image is
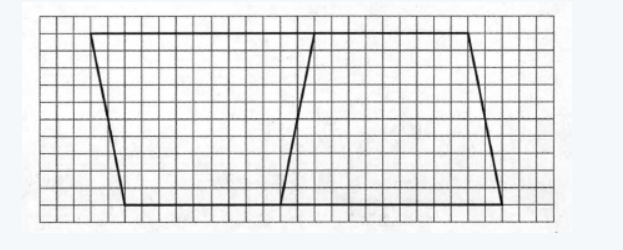
When we fit the image it vertically and move it to the next to the image we found that a quadrilateral with no sides parallel.
Therefore, the new figure is a trapezoid.
Hence, the new figure is Trapezoid.
Step-By-Step Solutions For Carnegie Learning Geometry Chapter 3 Exercise 3.3 Page 163 Problem 10 Answer
The given image is.
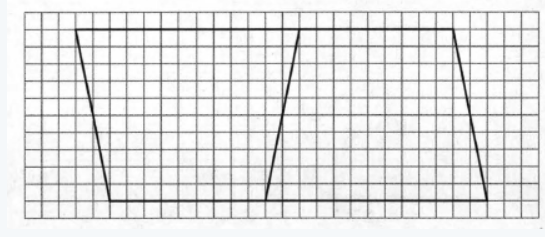
We need to calculate the area of a geometric figure in question 1.
Also, we need to calculate the area of the distorted image.
The given image is
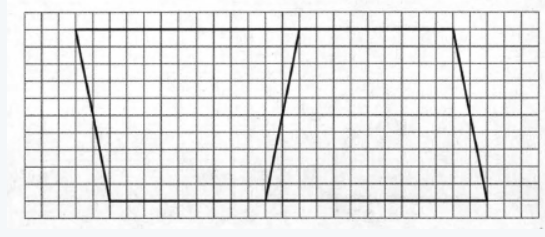
The geometric area in question 1 is a trapezoid.
and the area of a trapezoid is a+b/2h units.
Here a is the base b is the base and h is the height.
The distorted image is a parallelogram and the area of a parallelogram is bh units.
Here b is the base and h is the height.
The area of the geometric figure is a+b/2h units. and the area of the distorted image is b⋅h units.
Carnegie Learning Geometry Chapter 3 Exercise 3.3 Free Solutions Page 164 Problem 11 Answer
the given image is
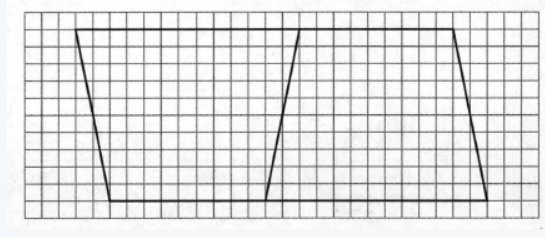
It is given that the distorted image is a trapezoid. parallel sides of the trapezoid are called the bases of the trapezoid.
non-parallel sides are the legs of the trapezoids.
on the arcade of the trapezoid is a line segment drawn from the vertex perpendicular to a line containing the opposite sides.
We need to calculate the area of a trapezoid.
The given image is
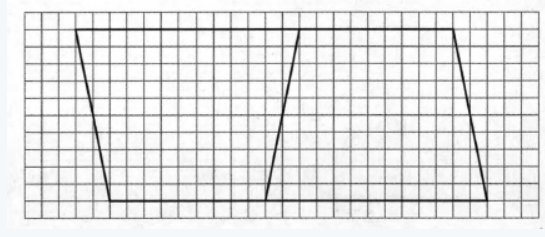
Let b1 is the length of one base,b2 is the length of another base and h is the length of the altitude.
We know that, area of the trapezoid can be evaluated by multiplying the sum of the bases (parallel sides) by the altitude and then divided by 2.
Hence, the area of the distorted image is 1/2(b1+b2)h units.
Hence, the area of the distorted image is 1/2(b1+b2)h units.
Carnegie Learning Geometry Chapter 3 Page 165 Problem 12 Answer
From the given image
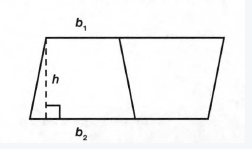
We need to write the formula of the entire figure.
The area of a parallelogram is base on height.
The above figure is a simple quadrilateral with two pairs of parallel sides.
and the opposite or facing sides are equal hence the given figure is a parallelogram.
and we know that area of a parallelogram is base multiplied by the height.
Hence the area of the entire figure is (b1+b2)h units.
Hence, the area of the entire figure is (b1+b2)h.
Carnegie Learning Geometry Exercise 3.3 Student Solutions Page 165 Problem 13 Answer
The given image is
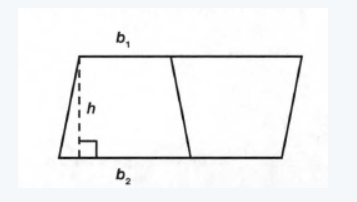
We need to suppose that we make an exact copy of this trapezoid, flip it vertically and move it next to the trapezoid.
We need to write the formula for the area of one of the trapezoid and explain it.
The given image is
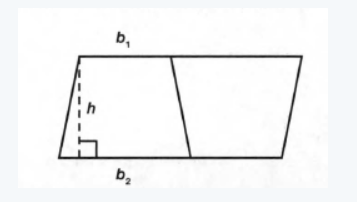
when we flip it vertically, then we make it a trapezoid.
To find the area of the trapezoid, multiply the sum of the bases (the parallel sides) by the height (the perpendicular distance between the bases) and then double by 2. i.e 1/2(b1+b2)h unit square meter.
Hence, the area of the trapezoid is 1/2(b1+b2)h.
Carnegie Learning Geometry Chapter 3 Page 166 Problem 14 Answer
The given trapezoid is
Here either the height, the length of one base, or the area of the trapezoid is unknown.
We need to determine the value of the unknown measure.
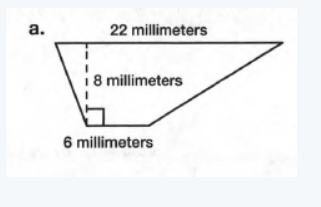
The given trapezoid is
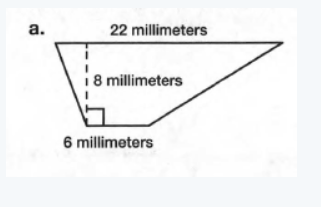
Here the height h is 8 millimeter.
The length of one base is b1 is 6 millimeter.
The length of another base b2 is 22 millimeter.
Hence we need to determine the area of the trapezoid.
We know that=1/2(b1+b2)h
=1/2(6+22)×8
=1/2(28)×8
=28×4
=112 square milimeter
Hence, the area of the trapezoid is 112 square milimeter.
Page 166 Problem 15 Answer
The given figure is
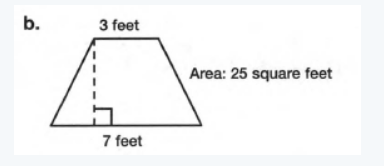
We need to find the value of the unknown measure.
In the given figure height is unknown And the given are is 25 square feet, b1 and b2 are the length of the bases i.e 7 feet and 3 feet respectively.
We need to determine the length of the given figure
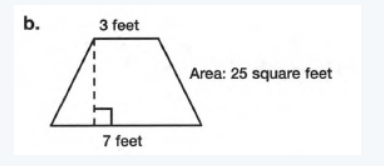
The area of the given figure is,
25=1/2(b1+b2)h
25=1/2(7+3)h
25×2=(10)h
50=(10)h
h=5
Hence, the height of the trapezoid is 5 feet.
Carnegie Learning Geometry Chapter 3 Page 166 Problem 16 Answer
Here the length of one base is unknown.
We need to determine the unknown measure.
From the given image,
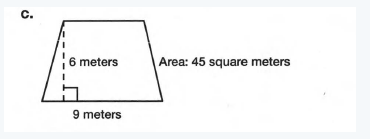
The height, length of one base b1 and area of the trapezoid is 6 meter,9 meters and 45 square meter.
We need to determine the length of another base(b2).
We know that,
Area=1/2(b1+b2)h
⇒45=1/2(b1+b2)h
⇒45=1/2(9+b2)6
⇒90=(9+b2)6
⇒15−9=b2
⇒b2
=6
Hence, the length of another base is 6 meter.
Perimeter And Area Exercise 3.3 Carnegie Learning 2nd Edition Answers Page 167 Problem 17 Answer
Here, the projection in problem 1 was tilted differently to create the distorted image shown.
each square on the grid represents a square that is 4 inches long and 4 inches wide.
We need to determine the area of the distorted image.
from the given image
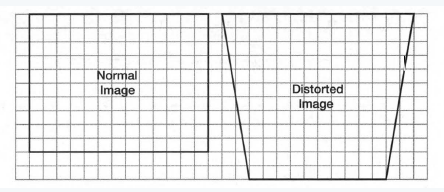
The distorted image of the figure is a trapezoid.
The area of the trapezoid is 1/2(b1+b2)h square unit.
here, b1 and b2 are the length of the bases and h is the length of the height of the trapezoid.
Hence, the length of the trapezoid is 1/2(b1+b2)h square units.
Carnegie Learning Geometry Chapter 3 Page 167 Problem 18 Answer
From the given image
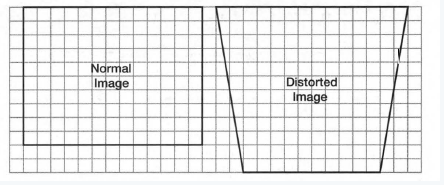
The projection in problem 1 is tilted differently to create a distorted image.
We need to write how does the area of the distorted image compares to the area of the normal image.
The given image is
Here the normal image is a rectangle and the distorted image is a trapezoid.
We know that a trapezoid is composed of two triangles and one rectangle.
therefore, we can calculate the area of the trapezoid by taking the sum of the areas of two triangles and one rectangle.
Therefore, we can calculate the area of the trapezoid by taking the sum of the areas of two triangles and one rectangle.
Page 168 Problem 19 Answer
Given AB is the perimeter of the trapezoid. Hence, fold this line to form a quadrilateral with at least a pair of two opposite sides parallel.
To draw the trapezoid,
Draw two parallel lines of different lengths.Join the corresponding starting points and the finishing points of the parallel lines to obtain the required figure.
The drawn trapezoid is
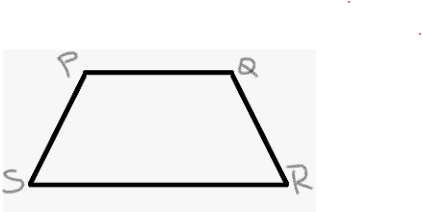
The drawn trapezoid is
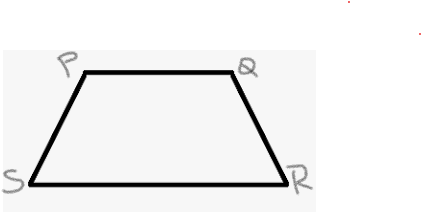
Carnegie Learning Geometry Chapter 3 Page 168 Problem 20 Answer
I drew a trapezoid previously with the given perimeter AB.
All classmates drew different trapezoid. Because, as the perimeter is given, it is same for everyone.
The length of the sides differ but are adjusted when the final perimeter that is the sum of the lengths of the sides is constant for individual students.
As a result the trapezoids are different.
All classmates drew different trapezoid. Because, as the perimeter is given, it is same for everyone.
The length of the sides differ but are adjusted when the final perimeter that is the sum of the lengths of the sides is constant for individual students.
As a result the trapezoids are different.
