Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Chapter 3 Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Exercise 3.2 Properties Of Parallel Lines
Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Chapter 3 Exercise 3.2 Properties Of Parallel Lines Solutions Page 152 Exercise 1 Problem 1
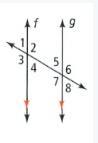
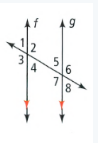
Given that: The given two parallel lines with angles
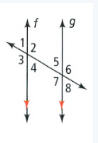
To find – Identify two pairs of supplementary angles.
f,g are parallel lines with 8 angles.
These are vertical, alternate, corresponding angles, supplementary angles.
The given two parallel lines with angles
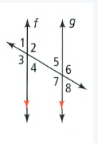
Have two lines pairs of supplementary angles are (2,40)(1,3).
The two pairs of supplementary angles are (2,40), (1,3) for the parallel lines with angles
Read and Learn More Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Solutions
Exercise 3.2 Properties Of Parallel Lines Savvas Geometry Answers Page 152 Exercise 2 Problem 2
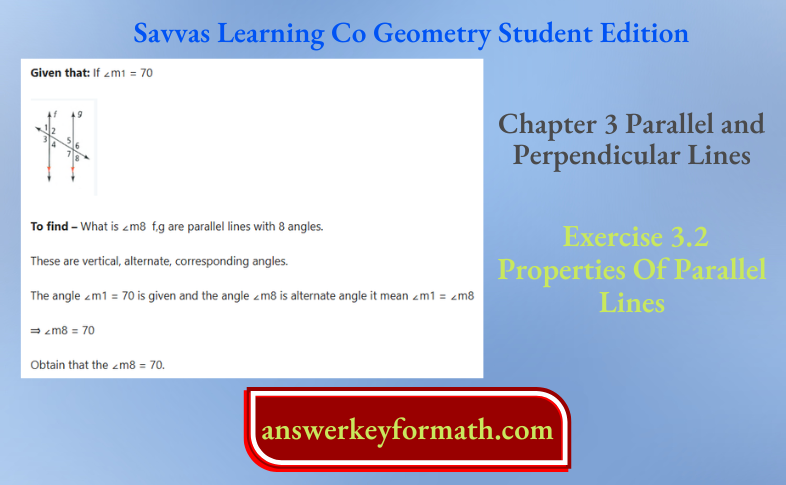
The value of ∠m8 = 70 because of alternate angles. for the given parallel lines and ∠m1 = 70.
Properties Of Parallel Lines Solutions Chapter 3 Exercise 3.2 Savvas Geometry Page 152 Exercise 3 Problem 3
Given: Alternate Interior Angles Theorem and the Alternate Exterior Angles Theorem
To Find – The similarity and difference between the given theorems.
The alternate interior angles are nonadjacent interior angles that lie on the opposite side of the transversal.
The Alternate Interior Angles Theorem states that “If a transversal intersects two parallel lines, then the alternate interior angles are congruent.
“The alternate exterior angles are nonadjacent exterior angles that lie on the opposite side of the transversal.
The Alternate Exterior Angles Theorem states that “If a transversal intersects two parallel lines, then the alternate exterior angles are congruent.
“The two theorems are alike in the fact that both of them deal with a transversal intersecting two parallel lines and that the alternate angles are congruent.
The two theorems differ from each other by the fact that the alternate interior angles are nonadjacent angles that lie within the parallel lines and the alternate exterior angles are nonadjacent angles that lie outside the parallel lines.
The similarity between the Alternate Interior Angles Theorem and the Alternate Exterior Angles Theorem is that two parallel lines are cut by a transversal and the angles are congruent. The difference between the Alternate Interior Angles Theorem and the Alternate Exterior Angles Theorem is that the interior angles are between the parallel line whereas the exterior angles are not between the parallel lines.
Properties Of Parallel Lines Solutions Chapter 3 Exercise 3.2 Savvas Geometry Page 152 Exercise 4 Problem 4
Given that: The problem is
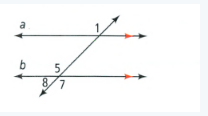
To find – You proved that ∠1 and ∠8, in the diagram below, are supplementary.
What is a good name for this pair of angles? Explain.
The lines a,b are parallel with each other and one line intersect both these parallel lines.
The angles ∠1,∠8 are supplementary angles because these are alternate same side exterior angles.
And the sum of two alternate same side angles is 180.
If the sum of two angles is 180 called supplementary angles.
The ∠1,∠8 are supplementary angles because these are alternate same side exterior angles. the good name of the pair of angle is alternate same side exterior angles. for the problem
Chapter 3 Exercise 3.2 Properties Of Parallel Lines Savvas Learning Co Geometry Explanation Page 153 Exercise 5 Problem 5
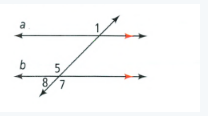
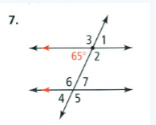
Given that: The given problem is
To find – Identify all the numbered angles that are congruent to the given angle.
Justify your answers the given one angle is 65 degree and the congruent angles are ∠1,∠7,∠4.
The angle ∠1 is vertical opposite angle of 65 , the angle ∠7 is alternate angle with 65 and the angle ∠4 is correspondence angle with angle 65.
The congruent angles are ∠1,∠7,∠4 for the given problem is
Chapter 3 Exercise 3.2 Properties Of Parallel Lines Savvas Learning Co Geometry Explanation Page 153 Exercise 6 Problem 6
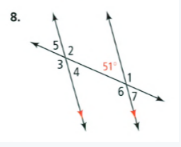
Given that: The given problem is
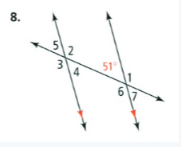
To find – Identify all the numbered angles that are congruent to the given angle.
Justify your answers the given one angle is 51 degree and the angles ∠7,∠5,∠4
are congruent angles.
The ∠7 angle is vertical opposite angle of 51, the ∠4 angle is alternate angle with 51 and the angle ∠5 is correspondence angle with angle 51.
The congruent angles are ∠7,∠5,∠4 for the problem is
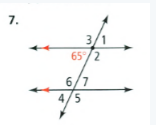
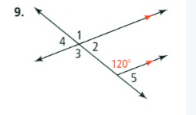
Solutions For Properties Of Parallel Lines Exercise 3.2 In Savvas Geometry Chapter 3 Student Edition Page 153 Exercise 7 Problem 7
Given that: The given problem is
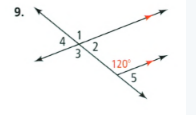
To find – Identify all the numbered angles that are congruent to the given angle.
Justify your answers.The given one angle is 120 degree and the angles ∠3,∠1 are congruent angles.
The angle ∠3 is alternate angle with angle 120 and the angle ∠1 is correspondence angle with 120.
The congruent angles are ∠1,∠3 for the problem is
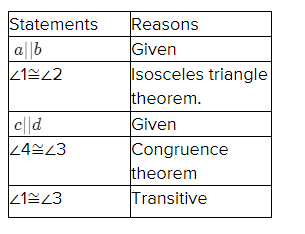
Solutions For Properties Of Parallel Lines Exercise 3.2 In Savvas Geometry Chapter 3 Student Edition Page 153 Exercise 8 Problem 8
Given: The angle 2
To Find – Write a two-column proof.
Given a ∣∣ b
Two-column proof:
The two-column theorem:
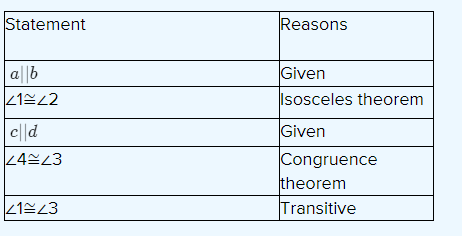
Exercise 3.2 Properties Of Parallel Lines Savvas Learning Co Geometry Detailed Answers Page 153 Exercise 9 Problem 9
Given: Figure in which two lines a∥b and q is transversal.
To find: m∠1 and m∠2 m∠1 is equal to 120°, because they are corresponding angles.
m∠1 and m∠2 are interior angles on same-side.
Therefore, they are supplementary angles.
⇒ m∠1 + m∠2 = 180°
⇒ 120° + m∠2 = 180°
⇒ m∠2 = 180° −120°
⇒ m∠2 = 60°
According to the given figure, m∠1 = 120° and m∠2 = 60°
Exercise 3.2 Properties Of Parallel Lines Savvas Learning Co Geometry Detailed Answers Page 153 Exercise 10 Problem 10
Given: Figure in which two lines AB∥CD and BC and AD are transversal.
To find – m∠1 and m∠2 = 70° since they are alternate interior angles.
m∠1 and 80° are interior angles on same side.
Therefore, they are supplementary angles.
⇒ m∠1 + 80° = 180°
⇒ m∠2 = 180°− 80°
⇒ m∠2 = 100°
According to the given figure, m∠1 = 100° and m∠2 = 70°
Geometry Chapter 3 Properties Of Parallel Lines Savvas Learning Co Explanation Guide Page 153 Exercise 11 Problem 11
Given: A figure in which two lines are parallel.
To find – value of x and to find the measure of each labeled angle.
5x° and 4x° are angles on same side.
Therefore, they are supplementary.
Value of x is 20° Measure of labeled angle 5x° = 100°, 4x° = 80°
Geometry Chapter 3 Properties Of Parallel Lines Savvas Learning Co Explanation Guide Page 154 Exercise 12 Problem 12
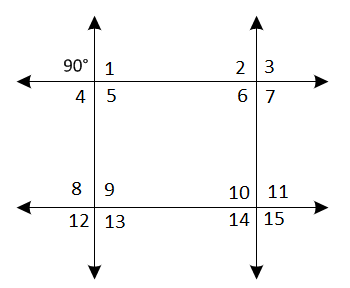
Given: Etchings on floors and walls in Rome suggest that the game required a grid of two intersecting pairs of parallel lines, similar to the modern game tick-tack-toe.
The measure of one of the angles formed by the intersecting lines is 90 degrees
To Find – Find the measure of each of the other 15 angles. Justify your answers.
The diagram: Draw a diagram with two intersecting pairs of parallel lines where one angle is ninety degrees.
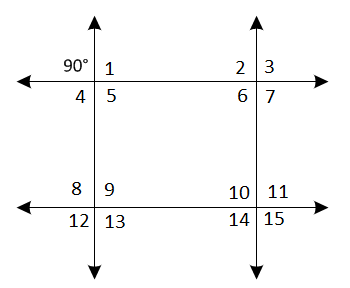
The 90 degrees angle forms a linear pair with ∠1 and ∠ 4.
Since linear pairs are supplementary, then the sum of their measure is 180degree.
It means both the angles are equal to 90 degrees.
The 90 degrees angle and ∠5 are also vertical angles so they are congruent by the vertical angles theorem.
Hence, ∠5 is equal to 90 degrees
Each of these four angles we found is corresponding angles to angles 2,3,6,7,8,9,12,13 in no particular order so by the corresponding angles theorem, these eight angles also measure 90 degrees.
Using the angles set 2,3,6,7 or8,9,12,1 they are corresponding angles with angles10,11,14,15 so they are also congruent.
So, these four angles are measures 90 degrees
Hence, all 15 angles are measures 90 degrees.
All 15 angles are measure 90 degrees, the diagram
Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Chapter Page 154 Exercise 13 Problem 13
Given: Camper pulls the rope taut between the two parallel trees.
The figure:
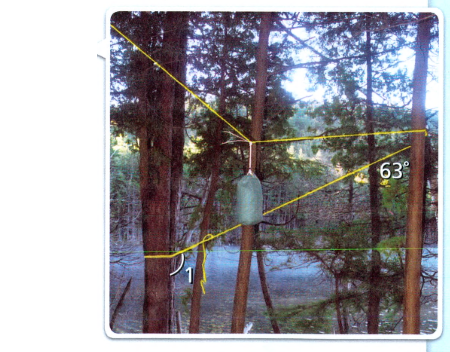
To Find – What is m∠1.
Given
Camper pulls the rope taut between the two parallel trees.
The given figure forms a triangle.
Given one angle: 63
We can see from the figure that the triangle is a right angle triangle so
The second angle is: 90 degree
Now, we know the sum of all three angles is 180 so
The third angle is:
⇒ 90 + 63 = 153
⇒ 180 − 153 = 27
Now the 1 point is perpendicular to 27degrees
And the sum of the perpendicular is180
So,∠1 180 − 27 = 153
The answer is 153 degrees
The answer is 153 degrees
Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Chapter 3 Page 155 Exercise 13 Problem 14
Given: The diagram
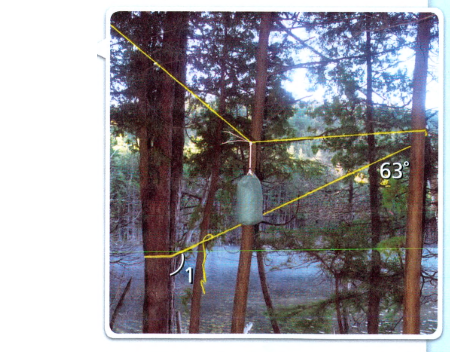
To Find – Are∠1 the given angle alternate interior angles, same-side interior angles, or corresponding angles?
Given , ∠1
If two parallel lines are transected by a third line, the angles which are inside the parallel lines and on alternate sides of the third line are called alternate interior angles.
The angles which are inside the parallel lines and on the same side of the third line are called opposite interior angles.
In the given figure there is no alternate interior angle so, it is not an alternate angle.
Same side interior angles are two angles that are on the interior of (between) the two lines and specifically on the same side of the transversal.
The same-side interior angles sum up to 180 degrees.
Let check:
⇒ 153 + 63 = 216
So, it is not the same side interior angle.
Corresponding angles are the angles that are formed when two parallel lines are intersected by the transversal. These are formed in the matching corners or corresponding corners with the transversal.
Yes, it is a corresponding angle.
The given figure is a corresponding angle.
The answer is the corresponding angle.
Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Chapter 3 Page 155 Exercise 14 Problem 15
Given: l ∥ m
To find – To prove ∠3 and ∠6 are supplementary.
Line l and m are Parallel ∠2 and ∠3 from a linear pair and linear pair are supplementary.
⇒ m∠2 + m∠3 = 180
⇒ ∠2 ≅ ∠6 are congurent
From congruence m∠2 = m∠6
By using substutition property
m∠6 + m∠3 = 180
∠3 and ∠6 are supplementary.
∠3 and ∠6 are supplementary proved.
Page 155 Exercise 15 Problem 16
Given: a ∥ b, ∠1 ≅ ∠4
To find – To prove ∠2 ≅ ∠3
In geometry, two figures or objects are congruent if they have the same shape and size, or if one has the same shape and size as the mirror image of the other.
Line l and m are Parallel.
∠1 and∠2, ∠3 and ∠4 both are supplementary.
⇒ m∠1 + m∠2 = 180
⇒ m∠3 + m∠4 = 180
Both have same value
⇒ m∠1 + m∠2 = m∠3 + m∠4
⇒ ∠1 ≅ ∠4 (given)
Which means
⇒ m∠1 = m∠4
By using substutition property
m∠4 + m∠2 = m∠3 + m∠4
Subtract
⇒ m∠2 = m∠3
By the defination of congruence
⇒ ∠2 ≅ ∠3
∠2 and ∠6 are congurent peoved.
Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Chapter 3 Page 155 Exercise 16 Problem 17
Given: The Diagram
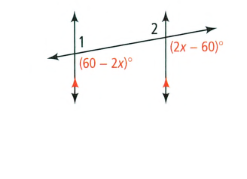
To find – To error analysis the diagram contain.
(60−2x)° and (2x−60)° are corresponding angles formed by tranversal,so they must be congruent.
We write it as
⇒ 60 − 2x = 2x − 60
⇒ −4x =−120
⇒ x = 30°
Subsittuting x = 30°
We get
⇒ 60 − 2(30) = 0°
⇒ 2(30) − 60 = 0°
We get 0° in both the expression which contradict the diagram and the tranversal must have form angle with parallel lines.
We get 0° in both the expression which contradict the diagram and the tranversal must have form angle with parallel lines.
Page 155 Exercise 17 Problem 18
Given: ∠1 and ∠2 are same-side interior angles formed by two parallel lines and ∠1 = 115.
To find – To find∠2
The theorem for the “same side interior angle theorem” states.
If a transversal intersects two parallel lines, each pair of same-side interior angles are supplementary.
Because ∠1 and∠2 are same-side interior angles formed by two parallel lines.
By using same-side interior angle theorem
⇒ m∠1 + m∠2 = 180
⇒ m∠2 = 180 − m∠1
⇒ m∠2 = 180 − 115
⇒ m∠2 = 65
The valuse of m∠2 is 65°
Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Chapter 3 Page 155 Exercise 18 Problem 19
Given: A rectangular swimmimg pool area 1500 ft 2 surround by the walkway.
To find – Length of fencing to surround the walkway.
Length of fencing to surround the walkway is equal to the perimeterof the larger rectangle.
Let l and w are the length and width of the smaller rectangle respectively
Area
lw = \(\frac{1500}{l}\)
w = \(\frac{1500}{50}\)
Let L and W are the length and width of the larger Rectangle respectively
⇒ L = 50 + 2(4)
⇒ L = 59ft
⇒ W = 20 + 3(4)
⇒ W = 38ft
Perimeter of the bigger reactangle
⇒ P = 2(L) + 2(W)
⇒ P = 2(59) + 2(38)
⇒ P = 192 ft
Length of fencing to surround the walkway is 192 ft
Page 155 Exercise 19 Problem 20
Given: The sum of measure angle and two times of measure angle is complement.
To find – To find measured angle.
An angle and its complement add up to
This means we have x + 2x = 90
⇒ 3x = 90
⇒ x = 30
The measure of the angle is 30°
Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Chapter 3 Page 155 Exercise 20 Problem 21
Given: ∠1 and ∠2 are vertical angles, m∠1 = 4x and m∠2 = 56
To find – To find value of x
Because ∠1 and ∠2 are vertical angles
By vertical angle theorem
⇒ m∠1 = m∠2
Subsitutin property
⇒ 4x = 56
⇒ x = \(\frac{56}{4}\)
The value of x is 46°
Page 155 Exercise 21 Problem 22
Given: The statement “Skew lines are coplanar.”
To find: The given statement is always, sometimes, or never true.
Skew lines are two or more lines that do not intersect, are not parallel, and are not coplanar.
The only way that two non parallel can never be intersect is if they are not coplaner.
The given statement is never ture.
Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Chapter 3 Page 155 Exercise 22 Problem 23
Given: The statement “Skew lines intersect.”
To find – The given statementis always, sometimes, or never true.
Skew lines are two lines that do not intersect and are not parallel.
By the definaton we can conclude that skew line never intersect.
This statement is never be ture.
Page 155 Exercise 23 Problem 24
Given: The statement “Parallel planes intersect.”
To find – The given statement is always, sometimes, or never true.
Parallel lines are coplanar straight lines that do not intersect at any point.
By the defination we can conclude that Parallel planes intersect.
This statement is never be true.
Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Chapter Page 155 Exercise 24 Problem 25
Given: The statement ” If a triangle is a right triangle, then it has a 90°”
To find – To Write the converse of the statement.
Converse of the satement is if triangle has 90° then it is a right angle triangle.
The converse of the given statement is if triangle has 90° then it is a right angle triangle.
