Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Chapter 6 Polygons And Quadrilaterals Exercise 6.1 The Polygon – Sum Theorems
Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Chapter 6 Exercise 6.1 The Polygon-Sum Theorems Solutions Page 356 Exercise 1 Problem 1
Given: We have given a regular decagon.
To find – Measures of an interior angle and an exterior angle of a regular decagon.
We will be using the concept of finding the sum of interior angles of the polygon with a given number of sides and the polygon exterior angle sum theorem.
We are given a regular decagon, that is the number of sides are n = 10.
The measure of the exterior angle of a decagon is given by
\(\frac{360^{\circ}}{10}\) = 36°
The sum of interior angles is given by:
⇒ S = 180 (n − 2)
⇒ S = 180 (10 − 2)
⇒ S = 180 (8)
⇒ S = 1440°
So, we have the measure of an interior angle as
\(\frac{1440^{\circ}}{10}\) = 144°
The measures of an interior angle is 144° and an exterior angle is 36° of a regular decagon
Read and Learn More Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Solutions
Exercise 6.1 The Polygon-Sum Theorems Savvas Geometry Answers Page 356 Exercise 2 Problem 2
An equiangular polygon means a polygon with the same measure of each interior angle.
Yes, we can draw an equiangular polygon that is not equilateral. For example we may draw a rectangle, that has all the angles as right angles but not all the sides of same measure.
Exercise 6.1 The Polygon-Sum Theorems Savvas Geometry Answers Page 356 Exercise 3 Problem 3
We have the given figure as
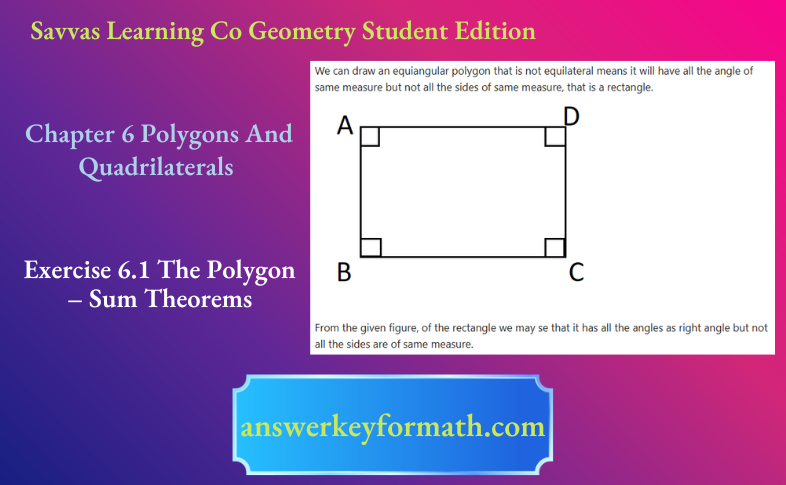
We know that an exterior angle is an angle which is formed by one of the sides of any closed shape structure such as polygon and the extension of its adjacent side.
From the given figure, we may see that the exterior angle of ∠1 can be given by ∠2,∠4
We see that ∠1,∠2 makes a linear pair and ∠1,∠4 also make linear pair. So the measure of the exterior angle ∠2, ∠4 can be given by 180° −∠1.
The exterior angles of ∠1 are given by ∠2, ∠4.
The measure of these angles can be given by 180° −∠1 as both the exterior angle makes a linear pair with the given interior angle.
Exercise 6.1 The Polygon-Sum Theorems Savvas Geometry Answers Page 356 Exercise 4 Problem 4
Given: We have given a 35 – polygon.
To find – The sum of interior angles.
We will be using the concept of finding the sum of interior angles of the polygon with a given number of sides.
We have the given polygon with total number of sides as n = 35.
The sum of interior angles of a polygon can be given by
S = 180 (n − 2), where n is the number of sides.
So, we have
⇒ S = 180 (35 − 2)
⇒ S = 180 (33)
⇒ S = 5940°
The sum of the interior angle measures of the given polygon is 5940°.
The Polygon-Sum Theorems Solutions Chapter 6 Exercise 6.1 Savvas Geometry Page 356 Exercise 5 Problem 5
Given: A 14 − polygon.
To find – The sum of interior angles.
We will be using the concept of finding the sum of interior angles of the polygon with a given number of sides.
We have the given polygon with total number of sides as n = 14.
The sum of interior angles of a polygon can be given by
S = 180 (n−2), where n is the number of sides.
So, we have
⇒ S = 180 (14 − 2)
⇒ S = 180 (12)
⇒ S = 2160°
The sum of the interior angle measures of the given polygon is 2160°.
The Polygon-Sum Theorems Solutions Chapter 6 Exercise 6.1 Savvas Geometry Page 356 Exercise 6 Problem 6
Given: The regular polygon as

To find – The measure of one interior angle in regular polygon.
We will be using the concept of finding the sum of interior angles of the polygon with a given number of sides.
From the given figure, we have the number of sides of the given regular polygon as n = 8.
The sum of all interior angles is given by:
⇒ S = 180 (n − 2)
⇒ S = 180 (8 − 2)
⇒ S = 180 (6)
⇒ S = 1080°
Measure of one interior angle is given by
= \(\frac{1080^{\circ}}{8}\)
= 135°
The measure of one interior angle is 135° in the given regular polygon.
The Polygon-Sum Theorems Solutions Chapter 6 Exercise 6.1 Savvas Geometry Page 356 Exercise 7 Problem 7
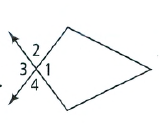
Given: The figure as showing a quadrilateral as follows
To find – The missing angles.
We will be using the concept of sum of all interior angles to find the measure of missing angle.
We are given a quadrilateral with angle measures as – 2h°, 2h°, h°, h°.
By angle sum property of quadrilateral, we have:
⇒ 2h + h + 2h + h = 360°
⇒ 6h = 360°
⇒ h = 60°
So we have
⇒ 2h = 2 (60°)
⇒ 2h = 120°
⇒ h = \(\frac{120^{\circ}}{2}\)
⇒ h = 60°
The angle measure of the given quadrilateral are 120°,120°,60°, 60.
Chapter 6 Exercise 6.1 The Polygon-Sum Theorems Savvas Learning Co Geometry Explanation Page 356 Exercise 8 Problem 8
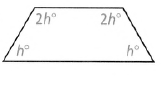
Given: The figure representing a pentagon as follows
To find – The missing angles.
We will be using the concept of sum of all interior angles to find the measure of missing angle.
We are given a pentagon with some angle measures as – 117°,100°,105°,115°,x°.
By angle sum property of a pentagon, we have:
⇒ 117° + 100° + 105° + 115° + x = 540°
⇒ x + 437° = 540°
⇒ x = 540° − 437°
⇒ x = 103°
The measure of missing angle is 103° for the given pentagon.
Solutions For The Polygon-Sum Theorems Exercise 6.1 In Savvas Geometry Chapter 6 Student Edition Page 356 Exercise 9 Problem 9
Given: We have given a pentagon.
To find – The measure of an exterior angle of the given regular polygon.
We will be using the concept of polygon exterior angle-sum theorem.
We are given a pentagon, that means the number of sides are n = 5.
By polygon exterior angle sum theorem, we have that the measure of an exterior angle of a regular polygon is the ratio of the whole angle by the number of sides of the polygon.
So, we have the measure of an exterior angle of given polygon as
\(\frac{360^{\circ}}{5}\) = 72°
The measure of an exterior angle is 72° of the given pentagon.
Exercise 6.1 The Polygon-Sum Theorems Savvas Learning Co Geometry Detailed Answers Page 356 Exercise 10 Problem 10
Given: We have given a 36 −polygon.
To find – The measure of an exterior angle of the given regular polygon.
We will be using the concept of polygon exterior angle-sum theorem.
We are given a 36 − polygon, that means the number of sides are n = 36.
By polygon exterior angle sum theorem, we have that the measure of an exterior angle of a regular polygon is the ratio of the whole angle by the number of sides of the polygon.
So, we have the measure of an exterior angle of given polygon as
\(\frac{360^{\circ}}{36}\) = 10°
The measure of an exterior angle is 10o of the given 36 – polygon.
Exercise 6.1 The Polygon-Sum Theorems Savvas Learning Co Geometry Detailed Answers Page 356 Exercise 11 Problem 11
Given: We have given a 100 − polygon.
To find – The measure of an exterior angle of the given regular polygon.
We will be using the concept of polygon exterior angle-sum theorem.
We are given a 100 − polygon, that means the number of sides are n = 100.
By polygon exterior angle sum theorem, we have that the measure of an exterior angle of a regular polygon is the ratio of the whole angle by the number of sides of the polygon.
So, we have the measure of an exterior angle of given polygon as
\(\frac{360^{\circ}}{100}\) = 3.6°
The measure of an exterior angle is 3.6° of the given 100 − polygon.
Geometry Chapter 6 The Polygon-Sum Theorems Savvas Learning Co Explanation Guide Page 356 Exercise 12 Problem 12
Given: The sum of interior angles of a polygon is given as 180°.
To find – The number of sides of the polygon.
We will be using the concept of finding the sum of interior angles of the polygon with a given number of sides.
We are given the sum of interior angles of the polygon as S = 180°
By using the formula for finding the sum, we have:
S = 180 (n−2), where is n the number of sides.
So we have
⇒ 180 = 180 (n − 2)
⇒ 1 = n − 2
⇒ n = 2 + 1
⇒ n = 3
The number of sides are 3 when the sum of interior angles is given as 180° for a polygon.
Geometry Chapter 6 The Polygon-Sum Theorems Savvas Learning Co Explanation Guide Page 356 Exercise 13 Problem 13
Given: The sum of interior angles of a polygon is given as 1080°.
To find – The number of sides of the polygon.
We will be using the concept of finding the sum of interior angles of the polygon with a given number of sides.
We are given the sum of interior angles of the polygon as S = 1080°.
By using the formula for finding the sum, we have:
S = 180 (n − 2), where n is the number of sides.
So we have
1080 = 180 (n − 2)
\(\frac{1080}{180}\) = n − 2
⇒ 6 = n − 2
⇒ n = 6 + 2
⇒ n = 8
The number of sides are 8 when the sum of interior angles is given as 1080° for a polygon.
Solutions For The Polygon-Sum Theorems Exercise 6.1 In Savvas Geometry Chapter 6 Student Edition Page 356 Exercise 14 Problem 14
Given: The sum of interior angles of a polygon is given as 1980°.
To find – The number of sides of the polygon.
We will be using the concept of finding the sum of interior angles of the polygon with a given number of sides.
We are given the sum of interior angles of the polygon as 1980°.
By using the formula for finding the sum, we have:
S = 180 (n − 2), where nis the number of sides.
So we have
⇒ 1980 = 180 (n − 2)
\(\frac{1980}{180}\) = n − 2
⇒ 11 = n − 2
⇒ n = 11 + 2
⇒ n = 13
The number of sides are 13 when the sum of interior angles is given as 1980° for a polygon.
Solutions For The Polygon-Sum Theorems Exercise 6.1 In Savvas Geometry Chapter 6 Student Edition Page 356 Exercise 15 Problem 15
Given: The sum of interior angles of a polygon is given as 2880°.
To find – The number of sides of the polygon.
We will be using the concept of finding the sum of interior angles of the polygon with a given number of sides.
We are given the sum of interior angles of the polygon as 2880°.
By using the formula for finding the sum, we have:
S = 180 (n − 2), where n is the number of sides.
So we have
2880 = 180 (n − 2)
\(\frac{2880}{180}\) = n − 2
⇒ 16 = n − 2
⇒ n = 16 + 2
⇒ n = 18
The number of sides are 18 when the sum of interior angles is given as 2880° for a polygon.
Exercise 6.1 The Polygon-Sum Theorems Savvas Learning Co Geometry Detailed Answers Page 357 Exercise 16 Problem 16
We know that Polygon is a representation of the surface and is formed using a collection of lines.
An polygon that can is equilateral but not equiangular can be given by a rhombus.
As a rhombus have all equal sides, but the angles of the rhombus are not equal.
We may sketch the rhombus as follows:
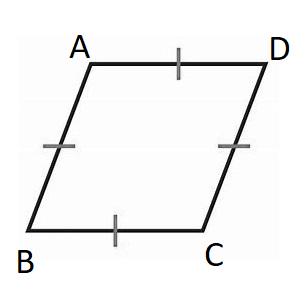
The sketch of an equilateral polygon that is not equiangular is a rhombus that is given below:
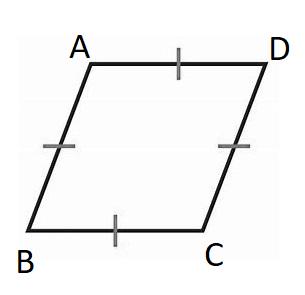
Exercise 6.1 The Polygon-Sum Theorems Savvas Learning Co Geometry Detailed Answers Page 357 Exercise 17 Problem 17
We are given that a triangle has two congruent interior angles and an exterior angle that measures 100°.
So, we may draw the diagram for the triangle as:
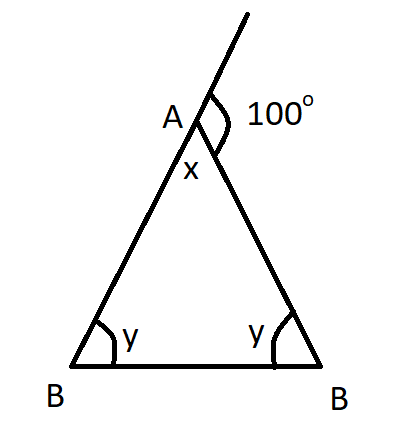
Now, here we see that the two interior angles that are congruent to each other are given by y, and other interior angle is given by x.
Diagram thus helps us to find the values of the missing angle in any polygon.
The diagram helps us to find the missing angles in a polygon, which is only possible if we have the diagram with the given values of angles and the missing values as variables.
Exercise 6.1 The Polygon-Sum Theorems Savvas Learning Co Geometry Detailed Answers Page 357 Exercise 17 Problem 18
We are given a triangle has two congruent interior angles and an exterior angle that measures 100°
Also, we have the diagram for the given triangle as follows:
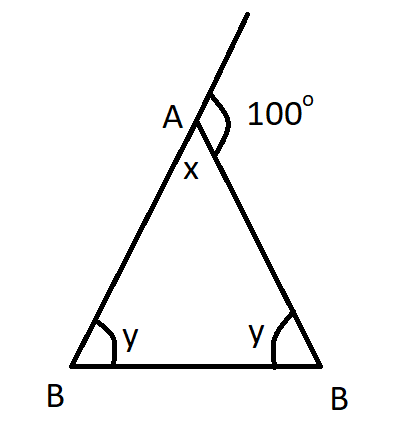
Now by angle sum property of a triangle we know that the sum of all the interior angles of a triangle is always 180°.
We can also verify this by the formula S = 180(n − 2), where n is the number of sides and we will get :
⇒ S = 180 (3 − 2)
⇒ S = 180° (1)
⇒ S = 180°
The sum of the angle measures in a triangle is always 180°.
Exercise 6.1 The Polygon-Sum Theorems Savvas Geometry Answers Page 357 Exercise 18 Problem 19
Given: The figure as
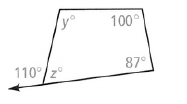
To find – The value of each variable.
We will be using the angle sum property of the polygon and the linear pair property to find the missing values.
From the given figure as, we see that z,110o form a linear pair, so we have :
⇒ z +110° = 180°
⇒ z = 180° − 110°
⇒ z = 70°
Now by angle sum property of a quadrilateral, we have:
⇒ z + y + 100° + 87° = 360°
⇒ 70° + y + 100°+ 87° = 360°
⇒ y + 257° = 360°
⇒ y = 360° − 257°
⇒ y = 103°
The value of variable are y = 103°, z = 70°.
Exercise 6.1 The Polygon-Sum Theorems Savvas Geometry Answers Page 357 Exercise 19 Problem 20
Given: The figure as
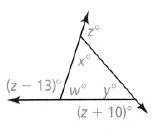
To find –The value of each variable.
We will be using the angle sum property of the polygon and the linear pair property to find the missing values.
We know by polygon exterior angle sum property that the sum of all exterior angles is 360°, so here we have:
⇒ z + (z − 13°) + (z + 10°) = 360°
⇒ z + z + z − 13°+ 10° = 360°
⇒ 3z = 360° + 3
⇒ z = \(\frac{363}{3}\)
⇒ z = 121°
Now, we that each each interior angle makes linear pair with the exterior angle, so we have:
⇒ z + x = 180°
⇒ x = 180° − z
⇒ x = 180° − 121°
⇒ x = 59°
As, (z − 13° ) makes linear pair with w so we have:
⇒ z − 13° + w = 180°
⇒ w = 180° − 13° − 121°
⇒ w = 46°
Again (z + 10o) makes a linear pair with y, so we have:
⇒ z + 10° + y = 180°
⇒ y = 180° − 10°− 121°
⇒ y = 49°
The values of the variables are :- x = 59° ,y = 49° ,z = 121° ,w = 46°
