Carnegie Learning Math Series Volume 14th Edition Chapter 2 Linear Functions
Carnegie Learning Math Series Volume 14th Edition Chapter 2 Exercise 2.1 Solution Page 41 Problem 1 Answer
Given: We have given that Animal trackers are experts at identifying animals by their footprints.
To find; here we have to guess that what animal made the tracks shown in the picture.
Animal Track Identification Guide. 1 Wolf Tracks.
They have four symmetrical toes on their front and back feet, and the front track will be a little bit longer and wider than the back. 2 Coyote Tracks. 3 Fox Tracks. 4 Dog Tracks. 5 Mountain Lion Tracks.
spotting animal tracks may pose a fun mystery to solve.
For others it may be a startling experience that rapidly turns frightening.
How you react can be a direct result of your ability to identify these paw prints.
A positive identification can put you at ease, or the unknown can bring on a sudden moment of terror.
Depending on the environment around your home, any number of animals may make a path through your back, front or side yard.
But how do you know if it’s a wild animal or just the neighbor’s cat? There are several factors you can look for to help identify the prints that are left behind.
Canine Tracks
Most of the time when you hear the word canine you immediately think of the family dog.
A coyote’s print measures between two and a half to three and a half inches long and it’s more narrow than that of a wolf.
We conclude that the coyote’s print measures between two and a half to three and a half inches long and it’s more narrow than that of a wolf.
Page 44 Problem 2 Answer
In Sequence B has figure which is closed and bounded by the lines.
We require to find the third term in sequence B.
The first term in the sequence B is closed and bounded figure formed by three lines is triangle.
The Second term in the sequence B is closed and bounded figure formed by four lines is square.
The third term in the sequence B is closed and bounded figure formed by five lines is pentagon.
The third term in the sequence B is pentagon.
Page 44 Problem 3 Answer
Sequence C: A, B, C, D, E, F, G,…
This is the sequence of alphabetic order and the first term is A and the last term is Z ( i.e 26th term. ).
Require to find the twenty-fifth term in Sequence C.
The given sequence C is
Sequence C:A,B,C,D,E,F,G,…
From the above sequence, the first term is A.
The second term is B.
The third term is C.
Similarly, counting the alphabetic terms in the sequence, we will get the twenty-fifth term as Y.
The twenty-fifth term in sequence C is Y.
Page 44 Problem 4 Answer
Given:
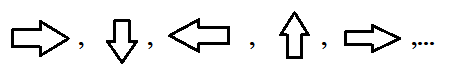
sequence D consists of the following shapes
To find: The twelfth term in the given sequence D.
The given sequence D are
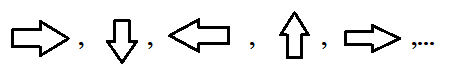
Since the above sequence is cyclic and members of the sequence are arrow symbols.
Also, it completed one cycle with every fourth term.
And, the fifth shape is the same as the shape of the first term. Here period of a cycle is 4.
Similarly, the twelfth shape is the second shape shown in the below figure.
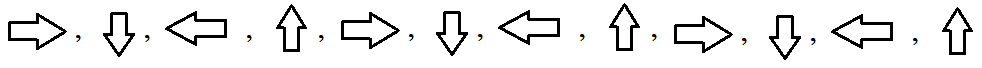
Hence, the twelfth term in the sequence is the arrow facing up.
Twelfth shape in the sequence D is arrow facing up.
Solutions For Linear Functions Exercise 2.1 In Carnegie Learning Math Series Page 45 Problem 5 Answer
Make sure each term indicates the total number of beads on the necklace after Emily completes that step
Write the first six terms in the sequence that represents this situation.
She starts with one black bead and next, she places one green bead on each side of the black bead, then total beads in second step are 3
Then, she places two black beads on each side of the green beads,its means that four beads are add with three beads and total beads are 7
Then, she places three green beads on each side of the black beads, its means that, six beads add with seven and total beads are 13
She continues this pattern two more times, alternating between black and green sets of beads.
1
1 + 2 × 1 = 3
3 + 2 × 2 = 7
7 + 2 × 3 = 13
13 + 2 × 4 = 21
21 + 2 × 5 = 31
x0 = 1,
xn = 2n + xn−1. for n ≥ 1
Sequence {1, 3, 7, 13, 21, 31,…}
Page 46 Problem 6 Answer
He creates one house and then adds additional houses by adjoining them.
The first term should indicate the number of toothpicks used for one house.
The second term should indicate the total number of toothpicks needed for two houses, and so on.
construct a sequence of the first eight terms in the sequence that represents this situation.
Six toothpicks used for one house.
11 toothpicks used for two house, since one toothpick is common for both house. So only five more toothpicks is required to attached second house with first.
He creates one house and then adds additional houses by adjoining them the he required five more toothpicks for each additional houses.
The first term (indicate the number of toothpicks used for one house) =6
The second term ( indicate the total number of toothpicks needed for two houses) =6+5=11.
Similarly, we have
3rd term =11+5=16
4th term =16+5=21
5th term=21+5=26
6th term =25+5=31
7th term =31+5=36
8th term =36+5=41
The required sequence ={6,11,16,21,26,31,36,41,…}, this is an increasing sequence and common difference is 5.
Page 46 Problem 7 Answer
They ask us how is the number of toothpicks needed to build each house represented in the sequence.
Start with 6 add 5 more toothpicks for each additional houses.
Toothpicks= 5 × number of houses + 1 or, f(x) = 5x + 1 for all x ∈ N
Where f(x) is the Toothpicks and x is number of houses.
{f(1), f(2), f(3),…} or,{6, 11, 16,…}
Toothpicks= 5 × number of houses + 1
Carnegie Learning Math Series 4th Edition Exercise 2.1 Solutions Page 47 Problem 8 Answer
Given Picture, there are eight column and six row.
Total number of card on the table is 48.
Each turn, he collects all of the cards in the right-most column, and all the cards in the bottom row.
Construct the sequence to show the number of cards removed during each of the first five turns.
In the first turn, he collects all the cards from the first column from the right-most column and the first row from the bottom
We get,
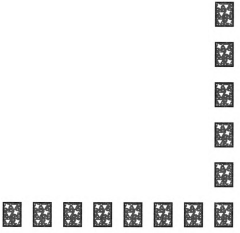
The total number of cards removed in the first turn are 13.
In the second turn, he collects all the cards from the second column from the right-most column and the second row from the bottom.
We get,
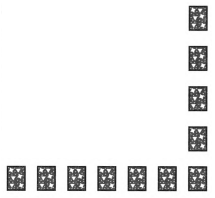
The total number of cards removed in the second turn are 11.
Since, in the second turn, the remaining rightmost column and the bottom row has 11 cards which are less than in the first turn by 2.
13−2=11
In the third turn, he collects all the cards from the third column from the right-most column and the third row from the bottom.
We get,
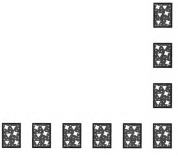
The total number of cards removed in the second turn are 9.
Since, in the third turn, the remaining rightmost column and the bottom row has 9 cards which are less than in the previous turn by 2.
So, we can write
11−2=9
In the fourth turn, he collects all the cards from the fourth column from the right-most column and the fourth row from the bottom.
We get,

The total number of cards removed in the second turn are 7.
Since, in the fourth turn, the remaining rightmost column and the bottom row has 7 cards which are less than in the previous turn by 2.
So, we can write
9−2=7
In the fifth turn, he collects all the cards from the fifth column from the right-most column and the fifth row from the bottom.
We get,

The total number of cards removed in the second turn are 5.
Since, in the fourth turn, the remaining rightmost column and the bottom row has 5 cards which are less than in the previous turn by 2.
So, we can write
7−2=5
Hence, the sequence is {13,11,9,7,5}, decreasing each term in the sequence by 2.
Sequence to show the number of cards removed during each of the first five turns is {13,11,9,7,5}.
Linear Functions Solutions Chapter 2 Exercise 2.1 Carnegie Learning Math Series Page 47 Problem 9 Answer
Given Picture, there are eight column and six row . Total number of card on the table is 48.
Each turn, he collects all of the cards in the right-most column, and all the cards in the bottom row.
Now we have to write the sequence to show the number of cards remaining after each of the first five turns.
In first turn he collects the cards in the first column and also in the bottom row, so there will be 13 cards collected.
So after first turn the remaining number of cards is
48−13=35
Now one column and one row are removed from the table.
In second turn, he collects the cards in the remaining right most column and also in the remaining bottom row, so there will be 11 cards collected.
So after second turn the remaining number of cards is 35−11=24
Now one column and one row are removed from the table.
In the similar way, in the third turn there will be 9 cards collected.
So after third turn the remaining number of cards is, 24−9=15
In the forth turn there will be 7 cards collected.
So after forth turn the remaining number of cards is, 15−7=8
In the fifth turn there will be 5 cards collected.
So after fifth turn the remaining number of cards is, 8−5=3
The sequence is : {35,24,15,8,3}.
The sequence to show the number of cards remaining after each of the first five turns is {35,24,15,8,3}.
Page 47 Problem 10 Answer
Here we have to describe the pattern shown in the each sequence.
First sequence:{13,11,9,7,5}.
Second sequence: {35,24,15,8,3}.
Now consider the first sequence,
{13,11,9,7,5}
In this sequence, the pattern is decreased by 2.
For example, 13−11=2
11−9=2
9−7=2 and so on.
Now consider the second sequence, {35,24,15,8,3}
In this sequence, each term is decreased by the values which starts in the first sequence.
For example, 48−35=13
35−24=11
24−15=9 and so on.
In he first sequence, {13,11,9,7,5} the pattern is decreased by 2.
In the second sequence, {35,24,15,8,3}
each term is decreased by the values which starts in the first sequence.
Step-By-Step Solutions For Carnegie Learning Math Series Chapter 2 Exercise 2.1 Page 48 Problem 11 Answer
Given that Lenny is making arrangements with pennies.
He has made three penny arrangements and now he wants to make five more arrangements.
Each time he adds another arrangement, he needs to add one more row to the base than the previous row in the previous arrangement.
Here we have to write the first eight terms in the sequence that represents the given situation.
Each term should indicate the total number of pennies in each arrangement.
The first arrangement will have only 1 penny.
So the first term is 1.
In the second arrangement, Lenny has to add a new row, and this new row requires an additional penny.
So the second term is,
1+2=3
In the third arrangement, Lenny has to add a new row, and this new row requires an additional penny.
So the third term is,
3+3=6
In the forth arrangement, Lenny has to add a new row, and this new row requires an additional penny.
So the forth term is,
6+4=10
In the fifth arrangement, Lenny has to add a new row, and this new row requires an additional penny.
So the fifth term is,
10+5=15
In the sixth arrangement, Lenny has to add a new row, and this new row requires an additional penny.
So the sixth term is,
15+6=21
In the seventh arrangement, Lenny has to add a new row, and this new row requires an additional penny.
So the seventh term is,
21+7=28
In the eight arrangement, Lenny has to add a new row, and this new row requires an additional penny.
So the eight term is,
28+8=36
Hence the sequence is : {1,3,6,10,15,21,28,36}.
The first eight terms in the sequence that indicates the total number of pennies in each arrangement is {1,3,6,10,15,21,28,36}.
Carnegie Learning Math Series Chapter 2 Exercise 2.1 Free Solutions Page 48 Problem 12 Answer
Since, it is given that each time Lenny adds another arrangement, he needs to add one more row to the base than the previous row in the previous arrangement.
Also, in the first arrangement, we have only one penny, and in the second arrangement we have three pennies, and in the third arrangement, we have six pennies.
This means every time when we add one row in the bottom, it will increase by 1
penny from the previous row.
The three given arrangements which indicate the total number of pennies in each arrangement is
0+1=1
1+2=3
3+3=6
Similarly, the next five sequences that indicate the total number of pennies in each arrangement can be written as
6+4=10
10+5=15
15+6=21
21+7=28
28+8=36
The pattern does not increase by the same amount each time because in order to add one more row to the base than the previous row, in the previous arrangement we need one additional penny.
Hence, the patterns do not increase by the same amount each time because each row requires an additional penny as compared to the previous one.
Carnegie Learning Math Series Exercise 2.1 Student Solutions Page 49 Problem 13 Answer
Given that, Dawson is stacking cubes in configurations that look like stairs.
Each new configuration has one additional step.
Here we have to write the first five terms in the sequence that represents this situation.
Each term should indicate the number of faces shown from the cubes shown.
The bottom faces are not shown. Given that the first cube has 5 shown faces.
Given that the first cube has 5 faces, therefore the first term is 5.
In the second configurations there will be 2 additional cube in the bottom, which include 7
additional faces.
So the total number of faces after second arrangement is,
5+7=12
In the third configurations there will be 3 additional cube in the bottom, which include 9 additional faces.
So the total number of faces after third arrangement is,
12+9=21
In the forth configurations there will be 4 additional cube in the bottom, which include 11 additional faces.
So the total number of faces after forth arrangement is,
21+11=32
In the fifth configurations there will be 5 additional cube in the bottom, which include 13 additional faces.
So the total number of faces after fifth arrangement is,
32+13=45
Hence the first five terms in the sequence is : {5,12,21,32,45}.
The first five terms in the sequence which shows the number of faces of cubes in each arrangement is : {5,12,21,32,45}.
Page 49 Problem 14 Answer
Here we have to predict the number of shown faces in a stair configuration that is 7 cubes high.
From problem (1) we concluded that the first five terms in the sequence which shows the number of faces of cubes in each arrangement is : {5,12,21,32,45}.
In the sixth configurations there will be 6 additional cube in the bottom, which include 15 additional faces.
So the total number of faces after sixth arrangement is,
45+15=60
In the sixth configurations there will be 7 additional cube in the bottom, which include 17 additional faces
So the total number of faces after seventh arrangement is,
60+17=77
Therefore, the number of shown faces in a stair configuration that is 7 cubes high is 77.
The number of shown faces in a stair configuration that is 7 cubes high is 77.
Page 50 Problem 15 Answer
arrangements of the tables that have trapezoidal shape top.
The below diagram shows the total number of students who can fit around a table
And, the second diagram shows the arrangement of tables to make a long table
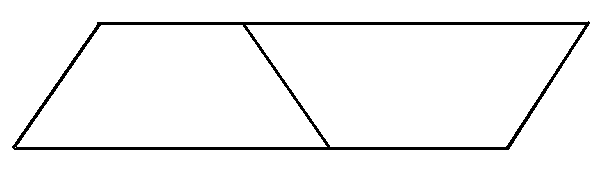
Here we have to write the first five terms in the sequence representing the total number of students that can sit around one, two, three, four, and five tables.
In the first table, it is given that 5 students can sit together.
So the first term is 5.
In the second arrangement, 2 tables will be joined together.
Since the tables are connected 3 more students can sit.
So the second term is,5+3=8
In the third arrangement, 3 tables will be joined together.
Since the tables are connected 3 more students can sit.
So the third term is,
8+3=11
In the forth arrangement, 4 tables will be joined together.
Since the tables are connected 3 more students can sit.
So the forth term is,
11+3=14
In the fifth arrangement, 5 tables will be joined together.
Since the tables are connected 3 more students can sit.
So the fifth term is,
14+3=17
Hence, the sequence is : {5,8,11,14,17}.
The first 5 terms in the sequence that represents the total number of students that can sit around one, two, three, four, and five tables is {5,8,11,14,17}.
Linear Functions Exercise 2.1 Carnegie Learning 4th Edition Answers Page 51 Problem 16 Answer
We are given an initial picture of a flower at stage 0 with a pair of petals.
We are required to write first five terms of the sequence.
Given is that at stage 0, a flower has a pair of petals i.e., 2 petals.
So, at stage 1, there will be two pairs of petals i.e., 4 petals.
Similarly, at stage two, there will be three pairs i.e., 6 petals.
At stage three, there will be four pairs i.e., 8 petals.
At stage four, there will be five pairs i.e., 10 petals.
So, the first five terms of the sequence will be
2,4,6,8,10
The first five terms of the sequence which represents the number of petals of a flower and at stage 0 with a pair of petals are:
2,4,6,8,10
Page 52 Problem 17 Answer
Given that every Friday, Sarah earns $14 for babysitting.
And given every Saturday, Sarah spends $10 going out.
Now we have to write a sequence to show the amounts of money Sarah has every Friday after babysitting and every Saturday after going out with her friends for five consecutive weeks.
And the sequence should have 10 terms.
Given that every Friday, Sarah earns $14 for babysitting.
Therefore, the first term is 14.
And every Saturday, Sarah spends $ 10 going out.
Therefore the second term is,14−10=4
Again Friday, Sarah earns $14 for babysitting.
Therefore the third term is, 4+14=18
Again Saturday, Sarah spends $10 going out.
Therefore the forth term is, 18−10=8
Again Friday, Sarah earns $14 for babysitting.
Therefore the fifth term is, 8+14=22
Again Saturday, Sarah spends $10 going out.
Therefore the sixth term is, 22−10=12
Again Friday, Sarah earns $14 for babysitting.
Therefore the seventh term is, 12+14=26
Again Saturday, Sarah spends $10 going out.
Therefore the eight term is, 26−10=16
Again Friday, Sarah earns $14 for babysitting.
Therefore the ninth term is, 16+14=30
Again Saturday, Sarah spends $10 going out.
Therefore the forth term is, 30−10=20
Hence the sequence is: {14,4,18,8,22,12,26,16,30,20}.
The sequence to show the amounts of money Sarah has every Friday after babysitting and every Saturday after going out with her friends for five consecutive weeks is {14,4,18,8,22,12,26,16,30,20}.
Page 52 Problem 18 Answer
We are given that students start collecting cans in the second week of their school and they collected 120 cans per week.
We are required to determine the sequence to calculate the running total of cans collected through first nine weeks of school.
We can say, by definition of sequence, that there is an increase of 120 per week as they increase.
So, in the first week, they collected nothing i.e., the first term will be 0.
Now, for the next week, they collect 120 cans per week, so the next term will be 120.
In third week, they collect 120 more cans, i.e., the third term will be 240.
So, we can write the sequence for nine weeks as
0,120,240,360,480,600,720,840,960
The sequence for the running total of cans collected in first nine weeks if they collected 120cans per week will be:
0,120,360,480,600,720,840,960
Page 54 Problem 19 Answer
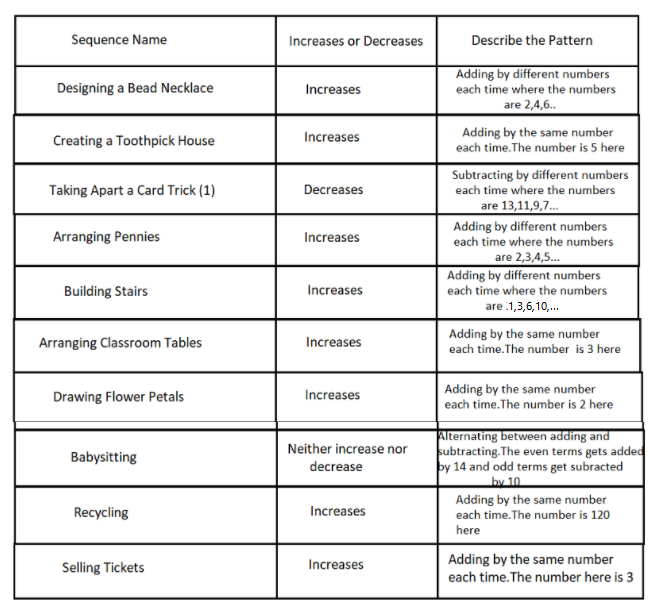
We have to describe the pattern of each sequence given in the table and determine which among the sequences are increasing and which are decreasing.
We have to tabulate our findings in the table given.
For designing a bead necklace, Emily started with one black color bead, and then she added one green color bead on both sides of the black beads and she continues the same alternating pattern of black and green beads by increasing the number of beads every time.
So, the beads of the necklace increase by following the pattern
0+1=1
[First black bead]
For, adding both sides one green bead, we can write
1+1=2
So, the total number of beads in the necklace are 1+2=3
Now, again we add two black beads on both sides of the green beads
2+2=4
So, the total number of beads in the necklace are 2+3+2=7.
So, it follows the pattern of adding different numbers of beads as 2,4,6,8,…
For crafting toothpick houses,
To make the first house we need 5 toothpicks.
For the second house, we need 4 toothpicks.
So, the sequence will be 5,5+4,5+4+4,5+4+4+4,…
=5,9,13,17,…
The followed term is 4 more than the previous one.
It is a increasing sequence.
or taking apart a card Trick(1)
First turn: we will remove 6 cards from the right side and 7 cards from the bottom side.
Total 13 cards removed.
Second turn: We will remove 5 cards from the right side and 6 cards from the bottom side.
Total 11 cards removed.
Third turn: We will remove 4 cards from the right side and 5 cards from the bottom side.
Total 9 cards revoved.
The sequence is 13,11,9,7,…
The followed term is 2 less from the previous term, so it is decreasing sequence.
Arranging pennies
The number of pennies for the first arrangement is 1.
The number of pennies for the second arrangement is 3.
The number of pennies for the third arrangement is 6.
The number of pennies for the third arrangement is 6+4=10
The sequence is 1,3,6,10,…
The followed term is greater than the previous term,
It is an increasing sequence.
Building strains
The number of blocks of the first strain is 1
The number of blocks of the second strain is 3
The number of blocks of the third strain is (3+3)=6
The number of blocks of the fourth strain is (6+4)=10
The sequence is 1,3,6,10…
The followed term is greater than the previous term. It is an increasing sequence.
Arranging classroom
The number of students on the first bench is 5.
The number of students on the second bench is 5+4=9.
The number of students on the third bench is 5+4+4=13
The sequence is 5,9,13,17,…
The followed term is greater than the previous term. It is an increasing sequence.
Drawing flower petals
The number of petals in zero stage is 2.
The number of petals in the first stage is (2+2)=4
The number of petals in the second stage is (4+2)=6
The sequence is 2,4,6,8,…
The followed term is greater than the previous term. It is an increasing sequence.
Babysitting
First week, Sarah spends ($14+$10)=$24
Second week, Sarah spends ($14+$10)=$24
Third week, Sarah spends ($14+$10)=$24
The sequence is 24,24,24,…
The sequence is neither increasing nor decreasing.
Recycling
The number of cans collected on the first week is 120.
The number of cans collected on the second week is (120+120)=240
The number of cans collected on the third week is (120+120+120)=360
The sequence is 120,240,360,480,…
The followed term is greater than the previous term. It is an increasing sequence.
Selling Tickets
The total amount in his cash box is 2×$10+5×$5+21×$1=$66
Each ticket cost $3
The total amount in his cash box after selling the first ticket is $66+3=$69
The total amount in his cash box after selling the second ticket is $66+$3+$3=$72
The sequence is 66,69,72,75,…
The followed term is greater than the previous term. It is an increasing sequence.
Using the conclusions from problem 1 to problem 9, we complete the given table
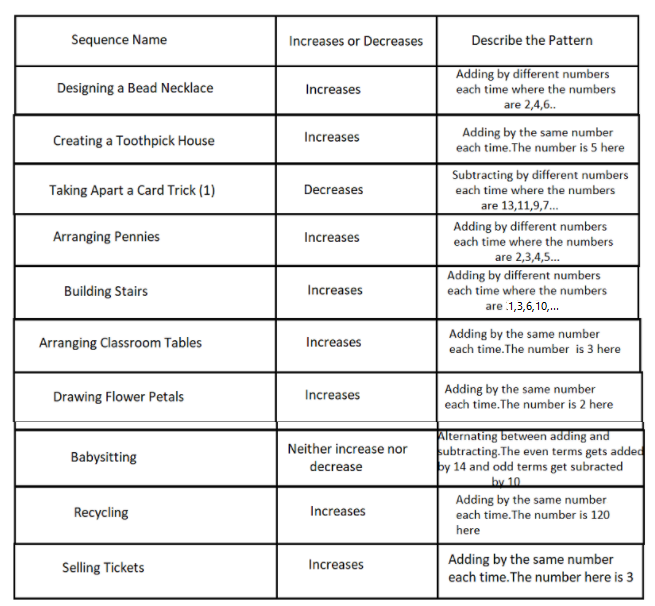
Hence we recorded our conclusions.
Page 54 Problem 20 Answer
Given:
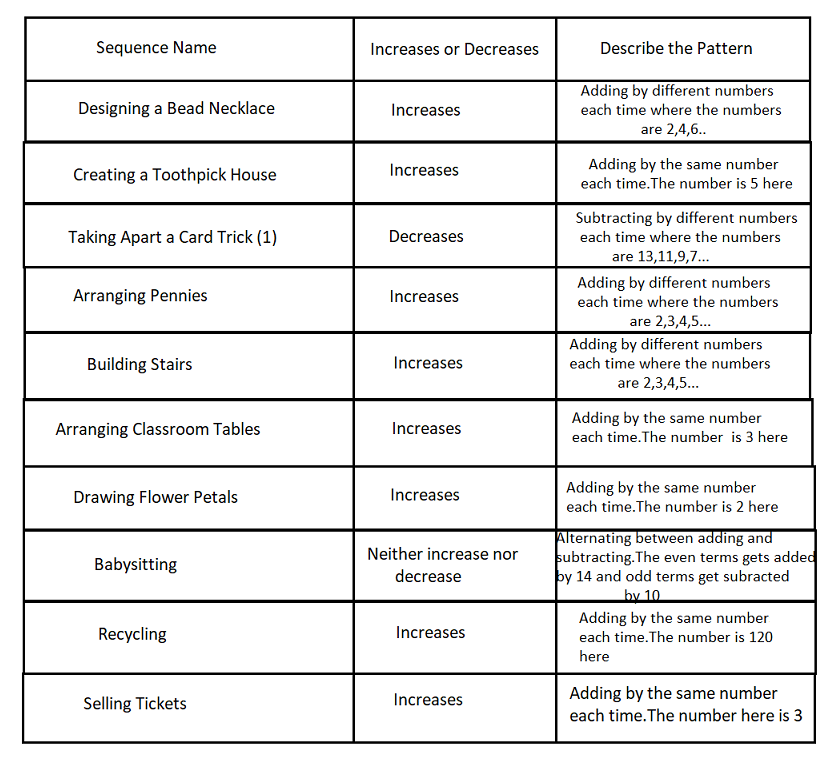
From problem 2,
The necklace designed by Emily contains alternating beads of black and green colour beads.
She starts with one black bead, then she placed one green bead on both sides of the black beads and so on.
She follows the above steps six times.
To find:
Which sequences are similar and why in the given steps.
To check if two sequences are similar we just have to check if they have similar pattern.
Consider the table which we found in the previous problem
Designing a bead necklace, taking apart a card trick, arranging pennies and Building stairs have a similar pattern which is “adding or subtracting by a different number each time, with the numbers being part of a pattern”.
Hence these sequences are similar.
Creating a Toothpick House, arranging classroom tables, drawing flower petals, recycling, and selling tickets follow a similar pattern which is “adding by the same number each time”.
Hence these sequences are similar.
Babysitting is not similar to any other sequence in the given collection as it has a completely different pattern.
Hence we found sequences that are similar from the given collection of sequences that are designing a bead necklace, taking apart a card trick, arranging pennies, and building stairs since it’s adding or subtracting by a different number each time, with the numbers being part of a pattern.
