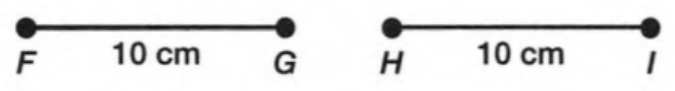Geometry Student Text 2nd Edition Chapter 2 Parallel and Perpendicular Lines
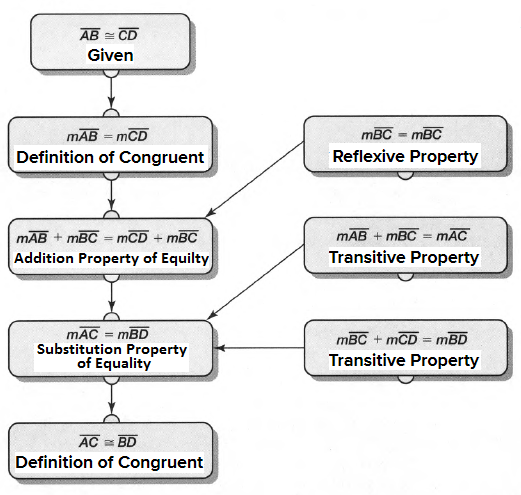
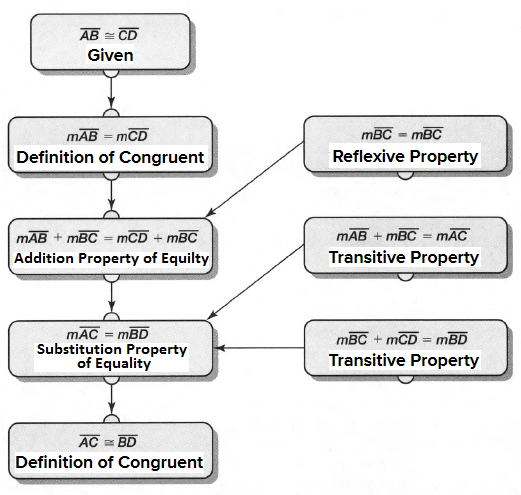
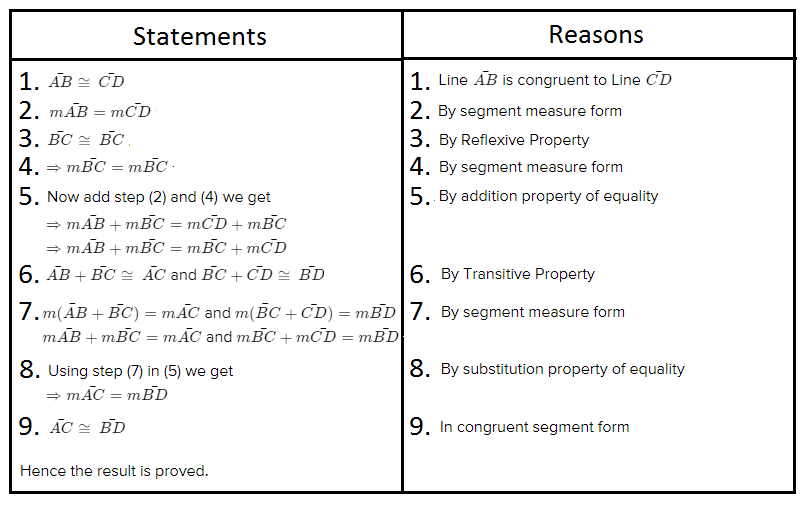
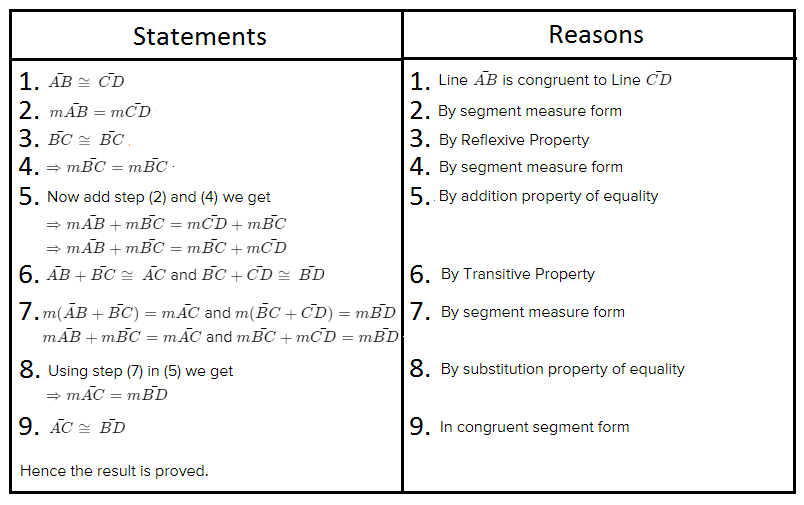
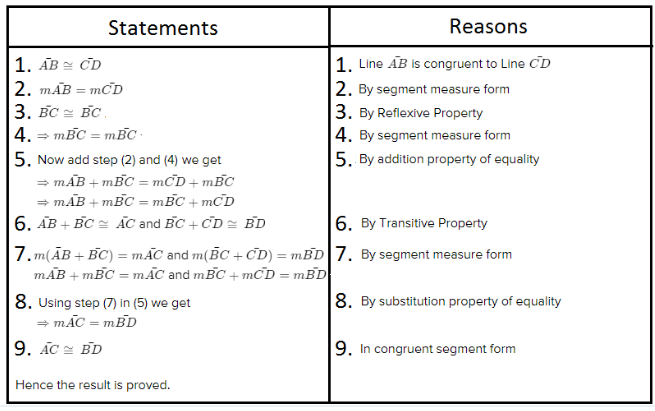
Carnegie Learning Geometry Student Text 2nd Edition Chapter 2 Exercise 2.1 Solution Page 78 Problem 1 Answer
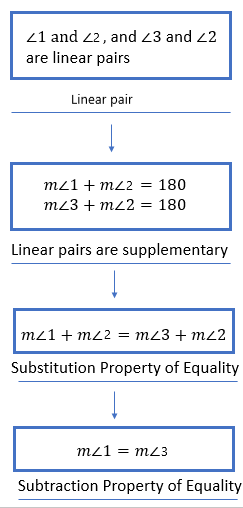
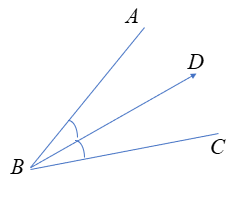
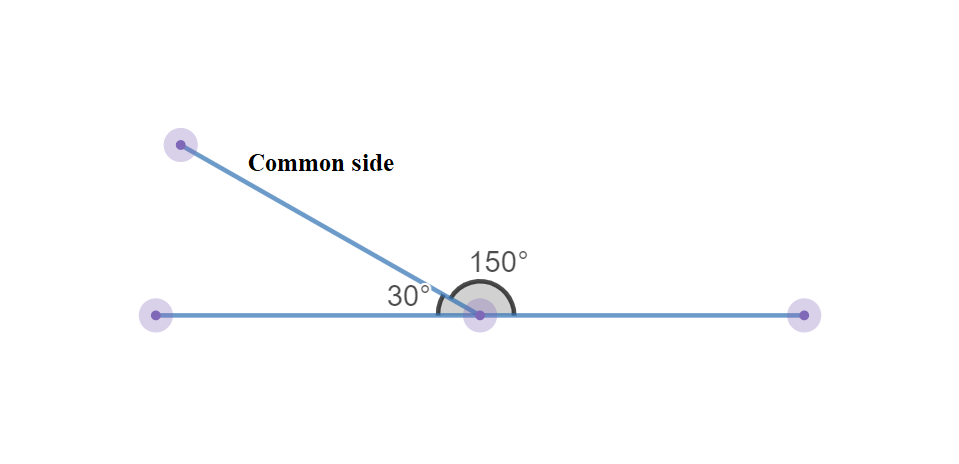
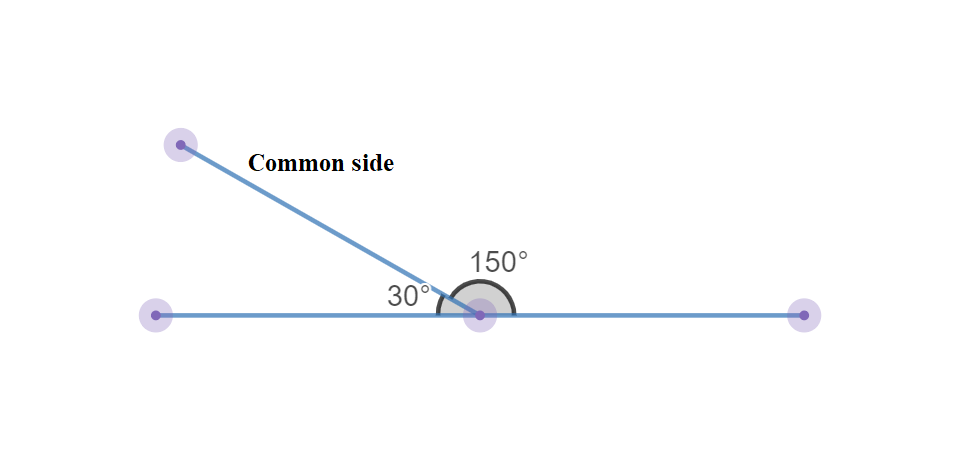
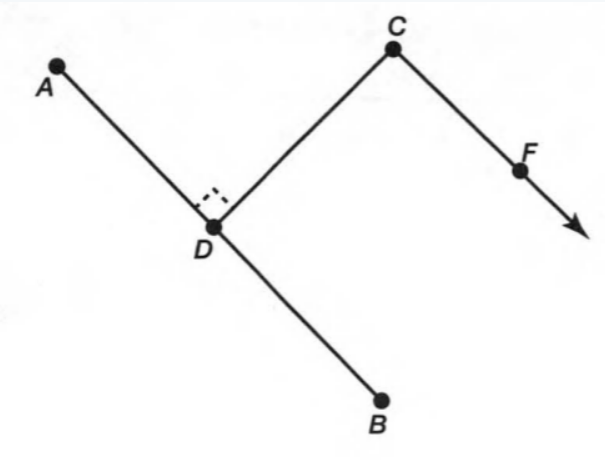
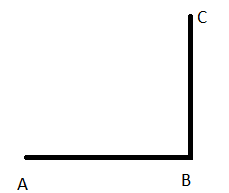
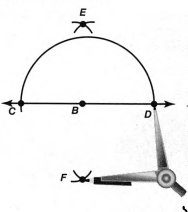
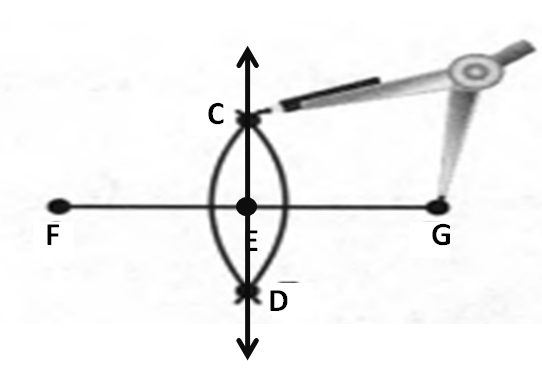
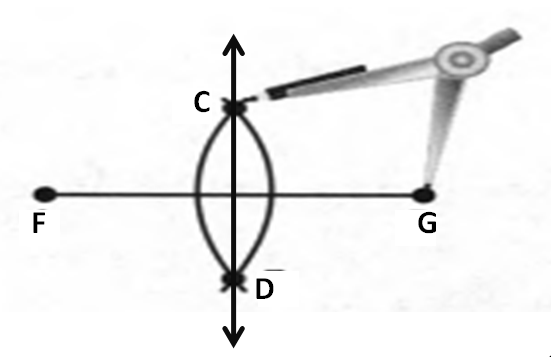
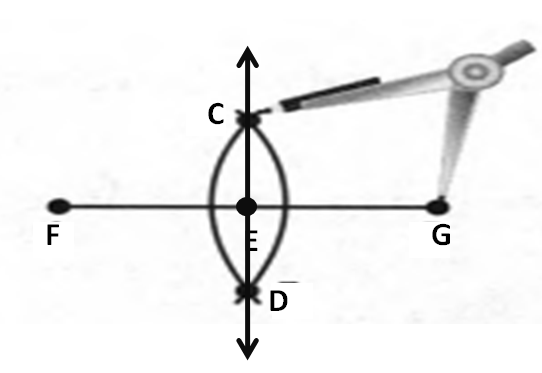
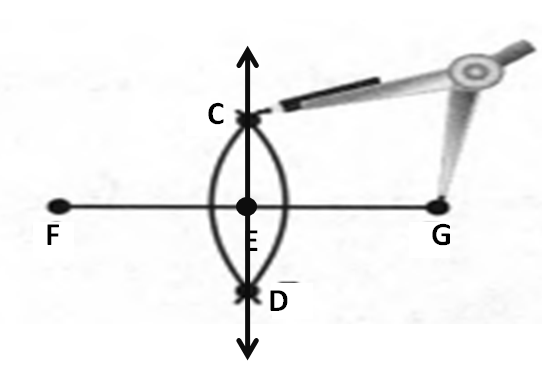
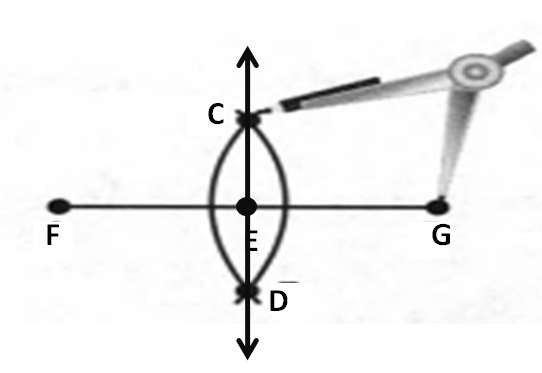
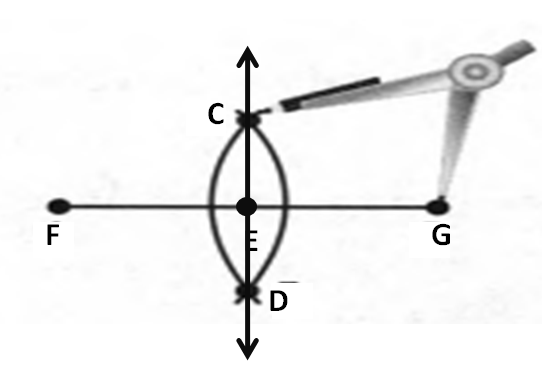
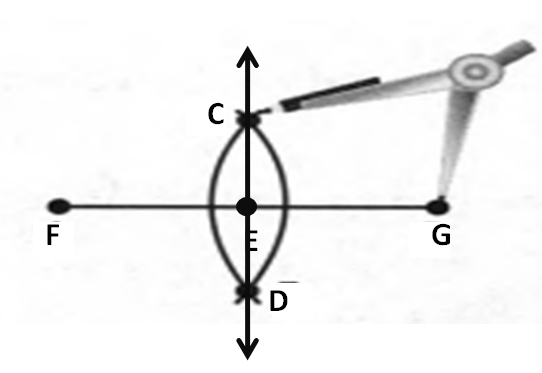
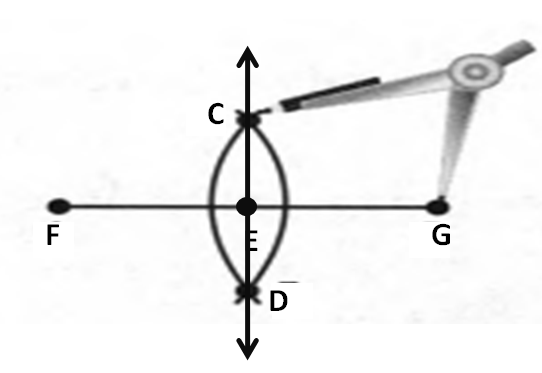
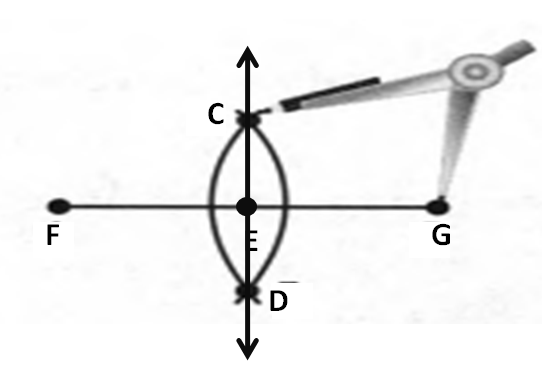
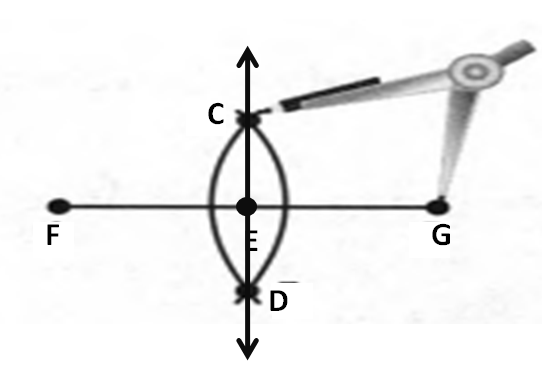
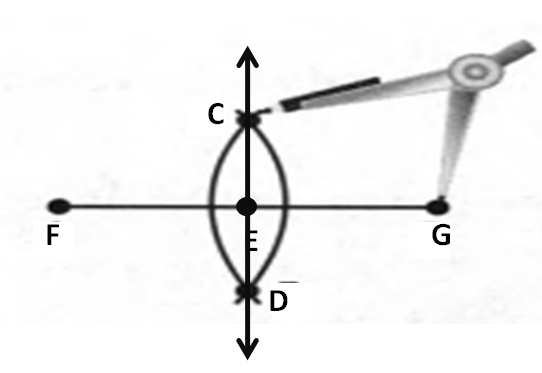
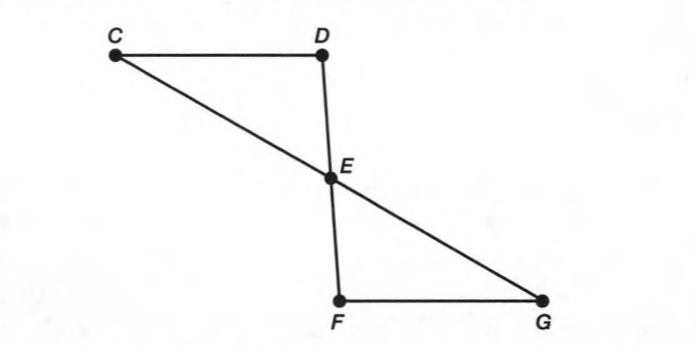
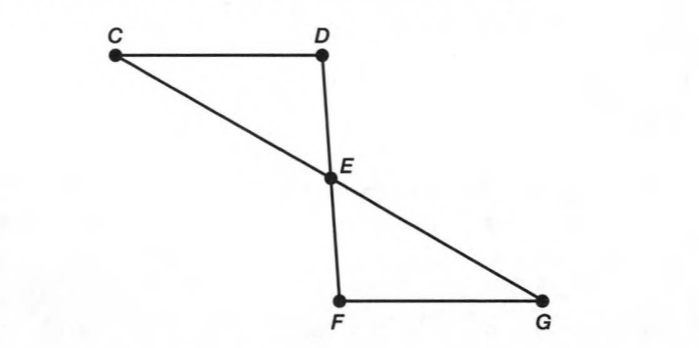
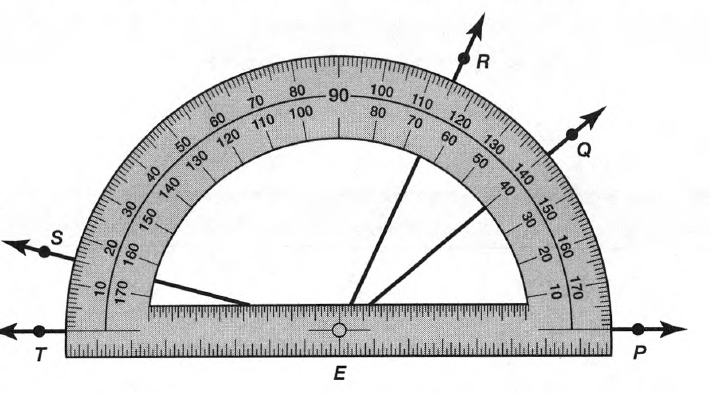
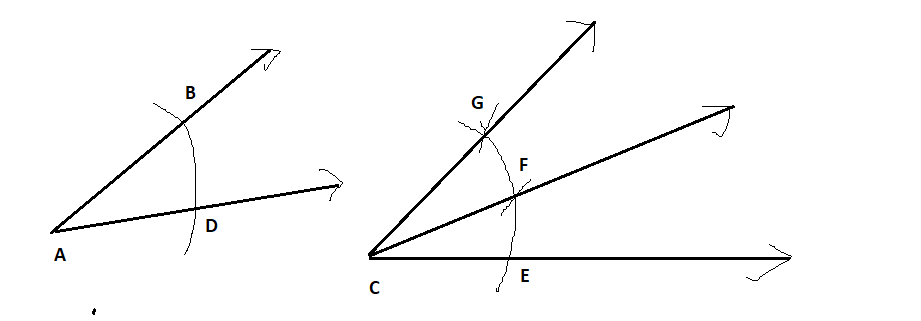
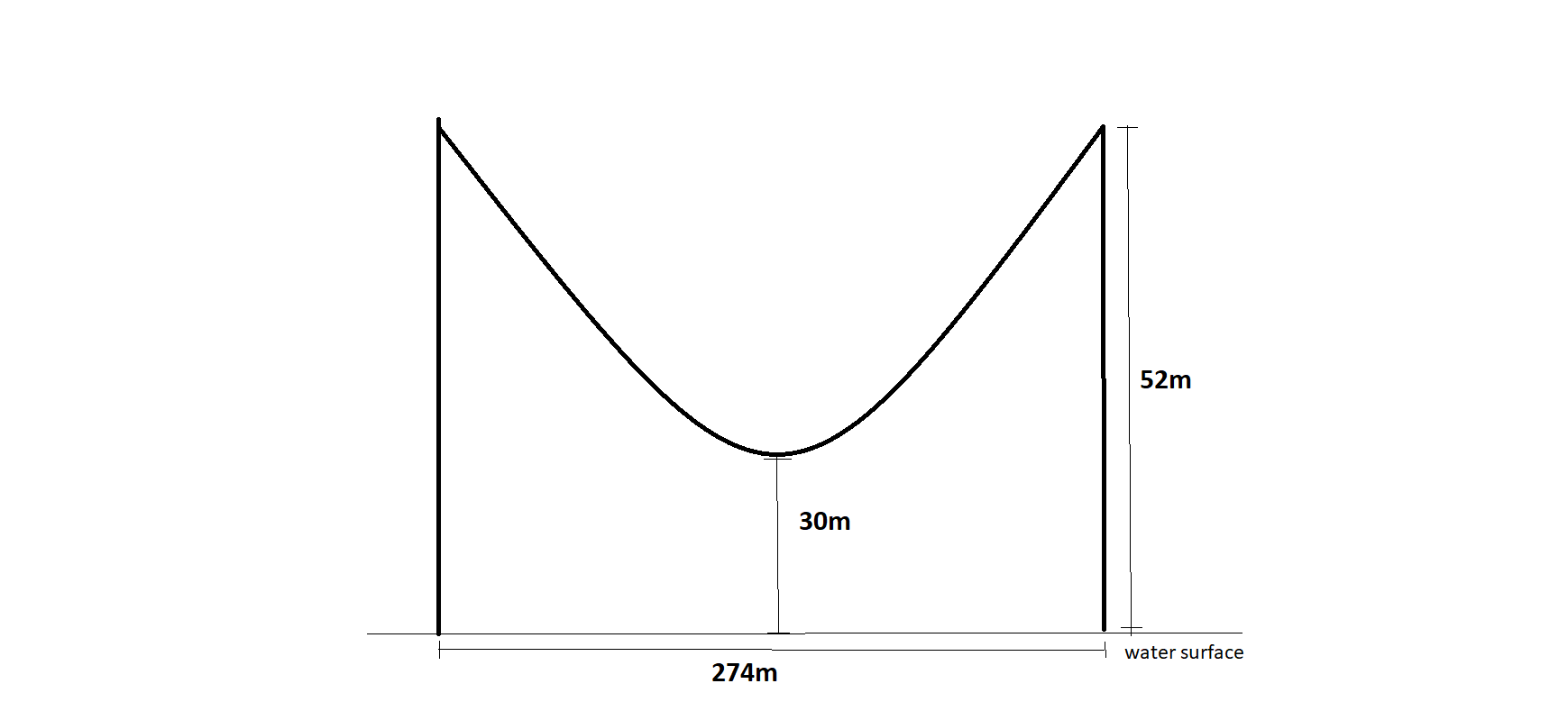
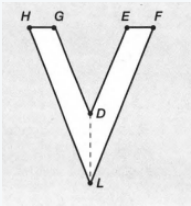
Given: You need to make a large letter “V” out of the poster board to complete a school project.
You are given two pieces of rectangular poster board, each measuring 1″ x 12″To Make your letter “V” similar to the one shown.
we will proceed step by step as per the question.
Take two pieces of poster board
Draw a rough sketch of V on the poster board
Then cut side GDLH and EFLD
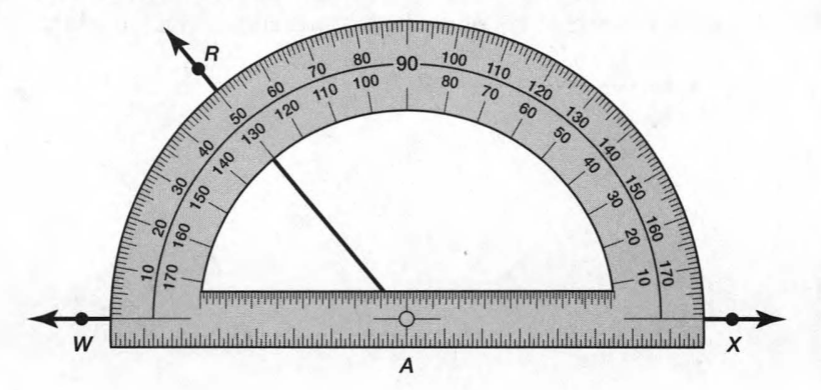
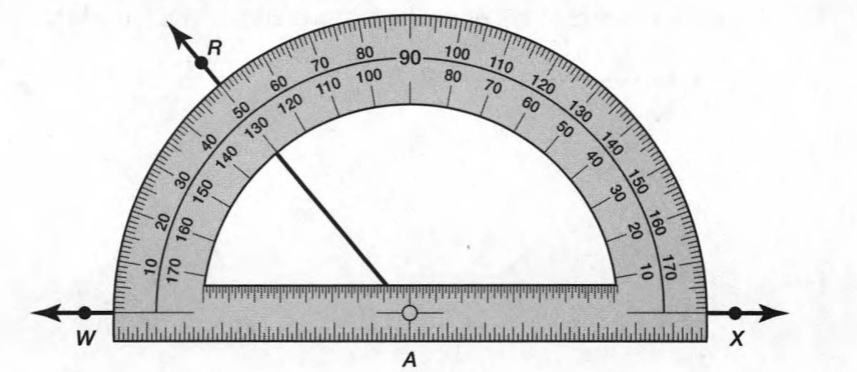
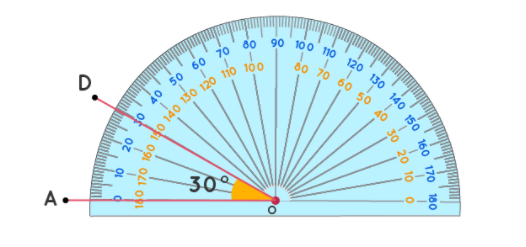
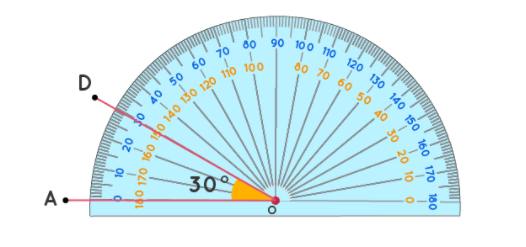
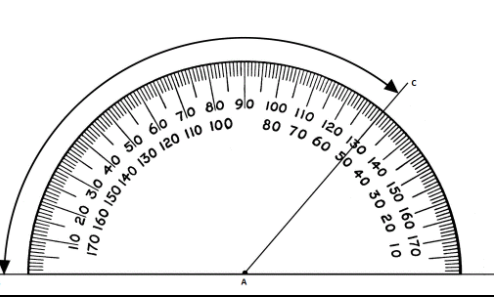
Now take the protractor and measure the ∠GDE=40o
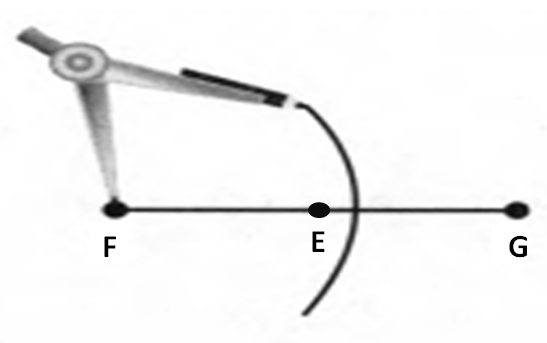
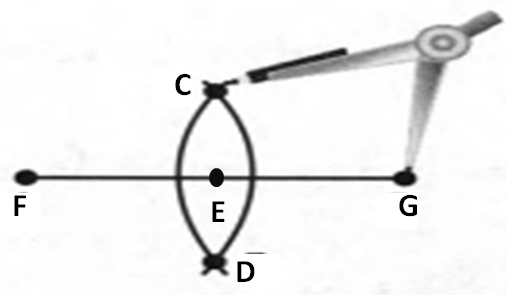
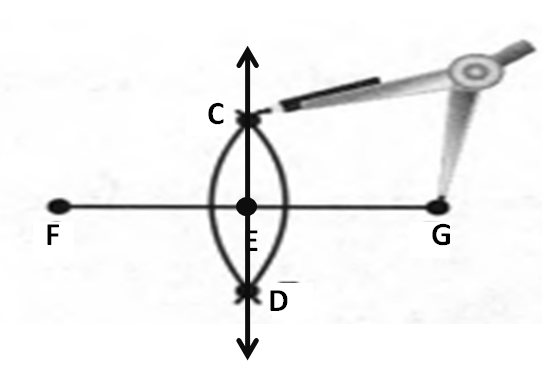
Also with the help of scale measure the segment HL=FL=12 inches
Hence, by following the above steps we can make a large letter “V” out of poster board to complete a school project.
Read and learn More Carnegie Learning Geometry Student Text 2nd Edition Solutions
Page 78 Problem 2 Answer
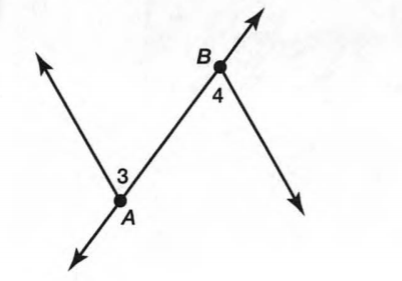
We have given the following diagram of letter V:-
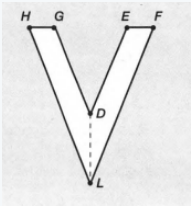
We have to find that how many interior angles are located in V.
The given diagram is:-
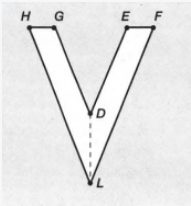
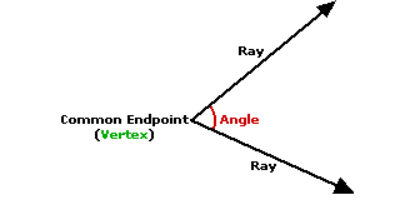
We know that when two lines are joined then there exists an angle between them.
Here we can see that the line HG is joined with lines HL and GD.
So there are two angles ∠LHG and ∠HGD.
Also, the line EF joined with lines ED and FL.
So there are two angles ∠DEF and ∠EFL
Further, the line HL joined with FL, and line GD joined with ED.
So there are two more angles ∠GDE and ∠ELH
Hence there exist total of six angles interior the letter V.
The are total six interior angles in the following letter V.
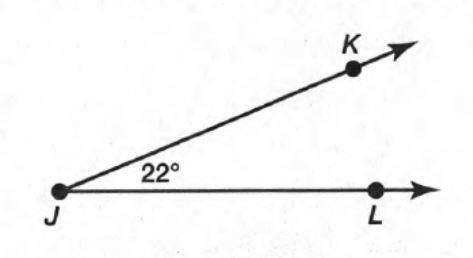
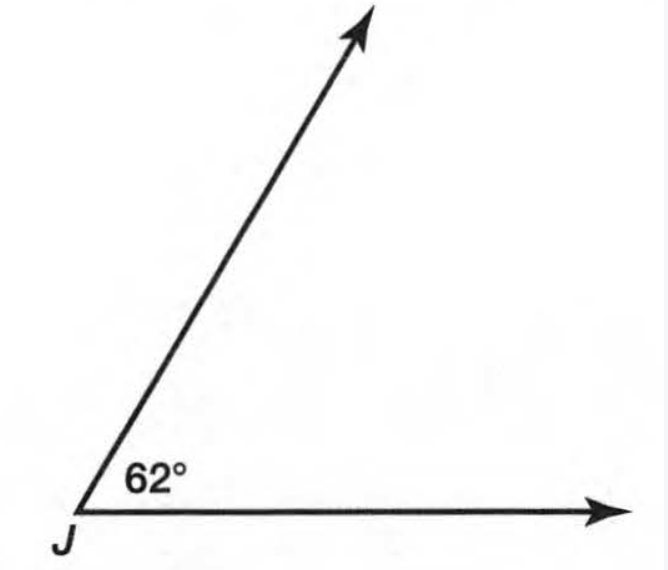
Carnegie Learning Geometry Student Text 2nd Edition Chapter 2 Exercise 2.1 Solution Page 78 Problem 3 Answer
Page 79 Problem 4 Answer
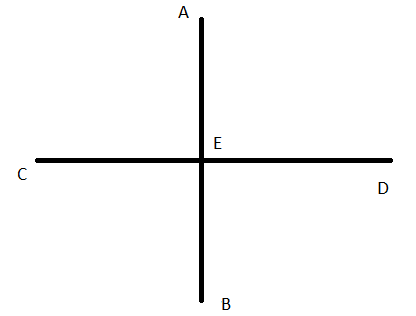
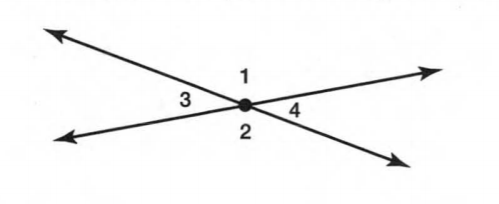
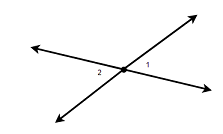
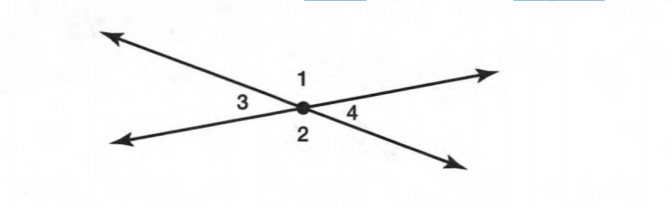
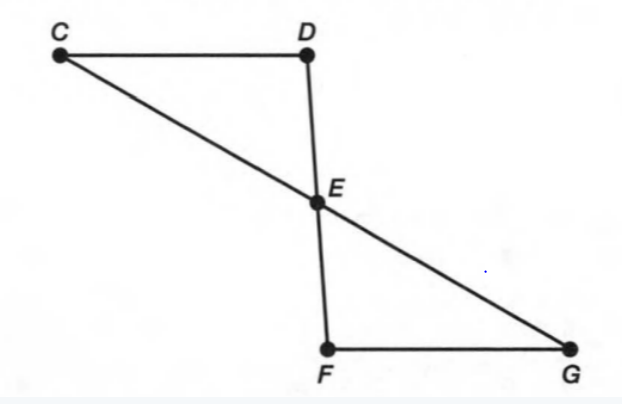
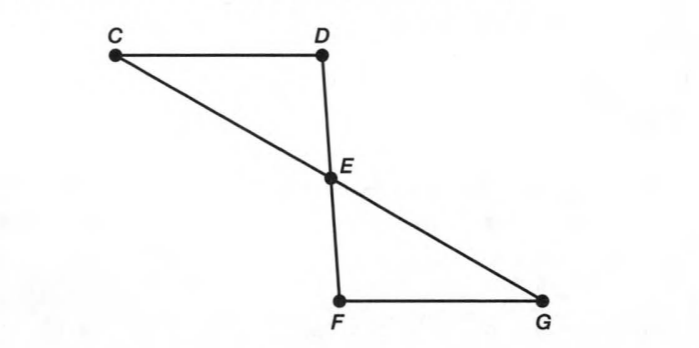
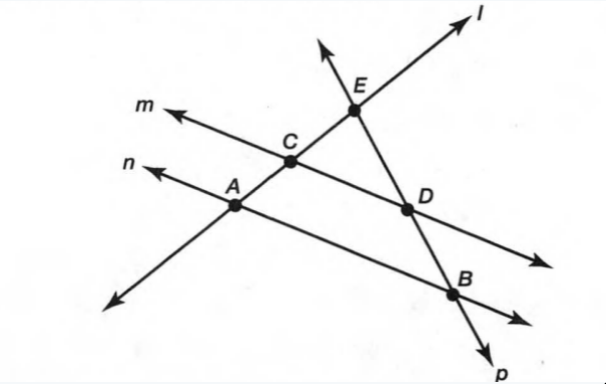
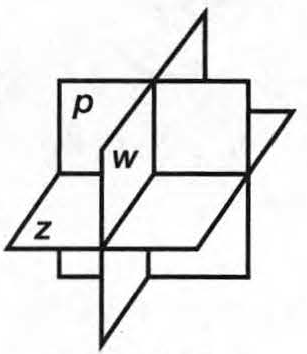
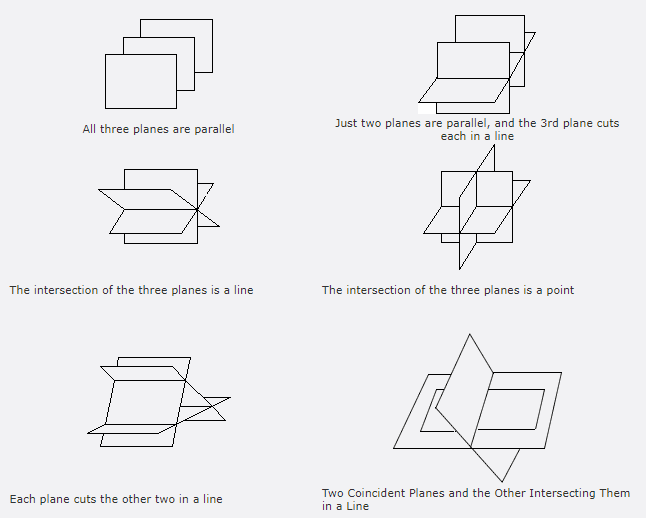
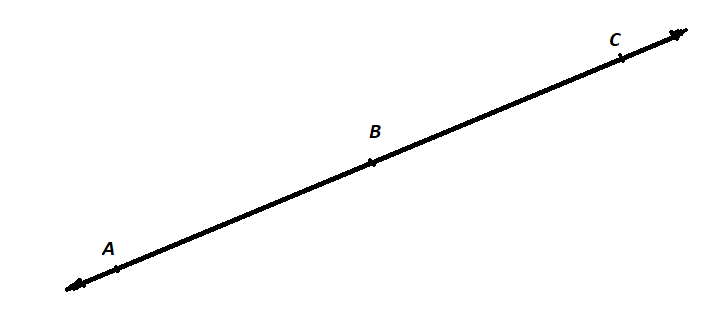
A figure is given,
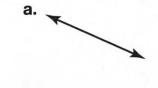
we have to identify which case is shown in figure.
Here, two lines coincide with each other.
that means two lines intersect at an infinite number of points.
so, two intersecting lines will be coplanar on the same plane.
Hence, the given figure identifies case 2: two coplanar lines intersect at an infinite number of points.
Page 79 Problem 5 Answer
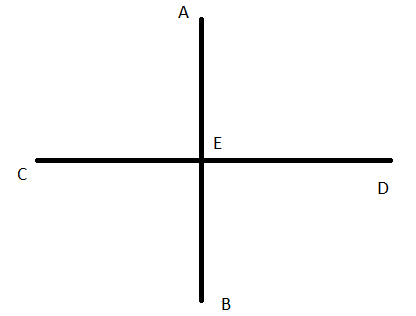
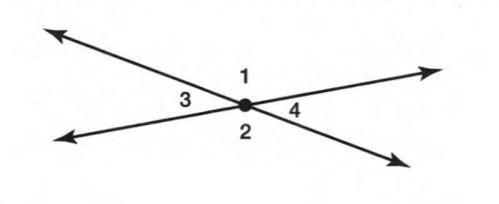
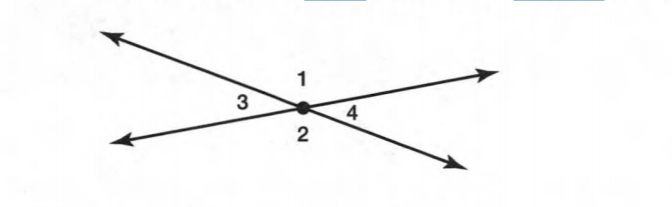
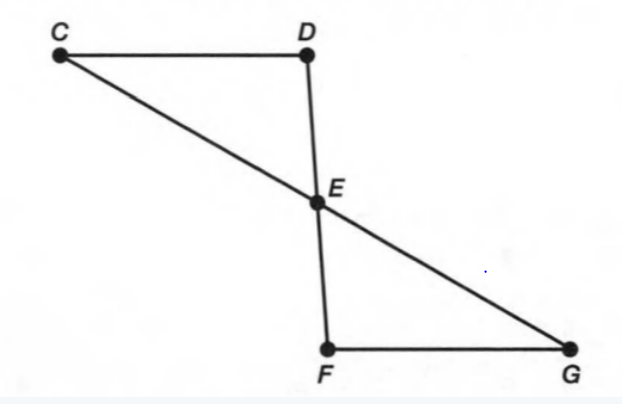
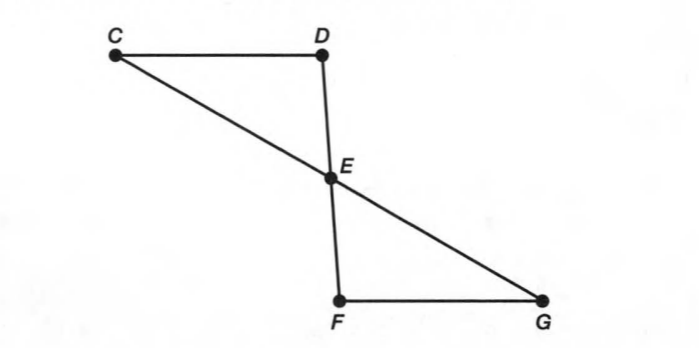
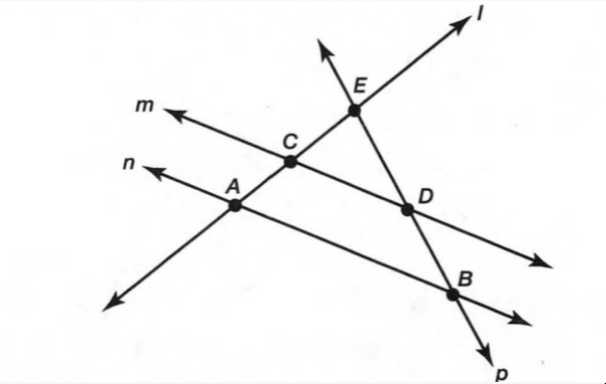
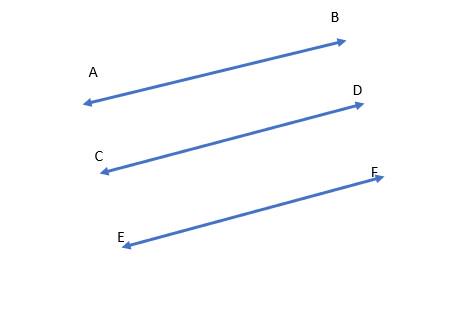
A figure is given.
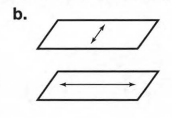
we have to identify which case is shown in figure.
when two lines lie on the same plane, two lines are coplanar.
But, each line lies on own plane.
so, two lines will not coplanar.
Hence, the given figure identifies case 4: two lines are not coplanar.
Page 79 Problem 6 Answer
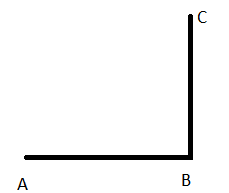
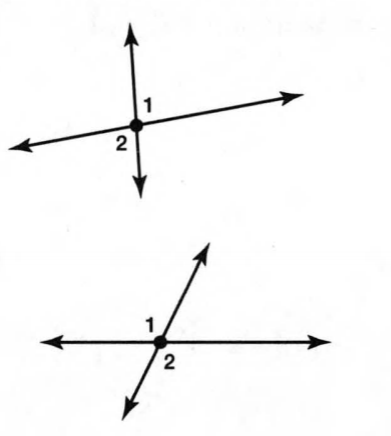
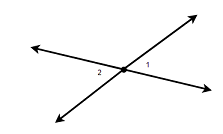
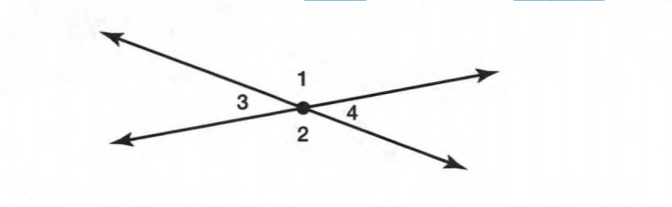
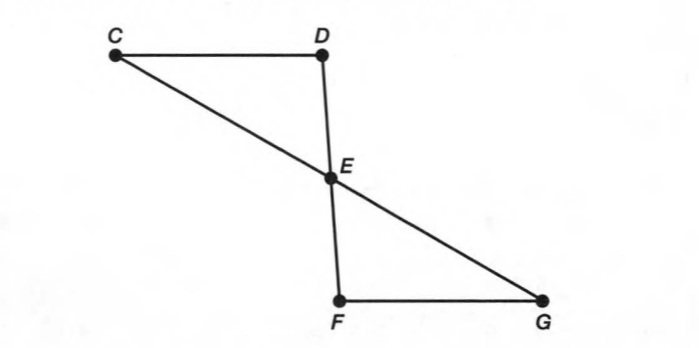
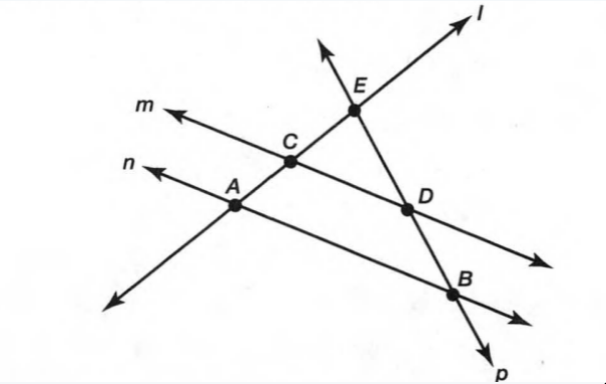
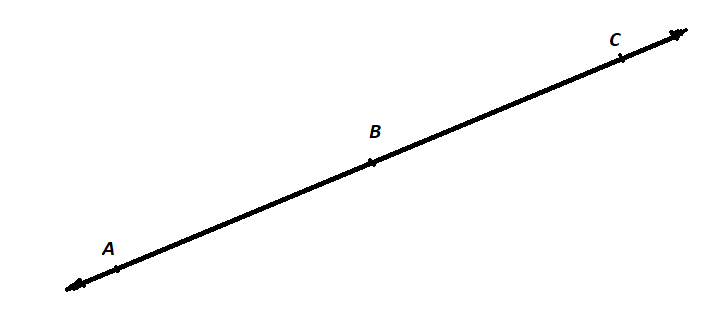
A figure is given,
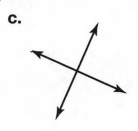
we have to identify which case is shown in the figure.
we know that two intersecting lines are always coplanar and these lines lie on the same plane.
so, here two lines are intersecting at a single point and they lie on the same plane.
that is the two intersecting lines are coplanar on the same plane.
Hence, the given figure identifies case 1: two coplanar lines intersect at a single point.
Page 79 Problem 7 Answer
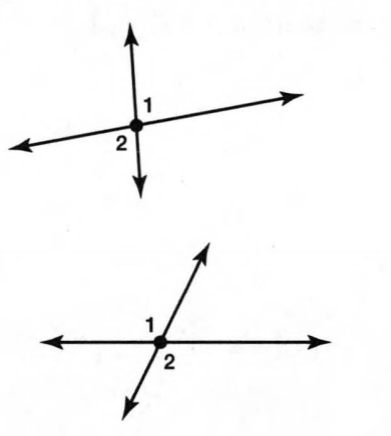
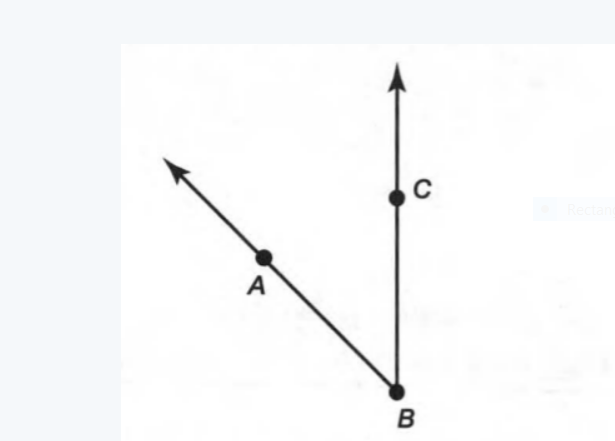
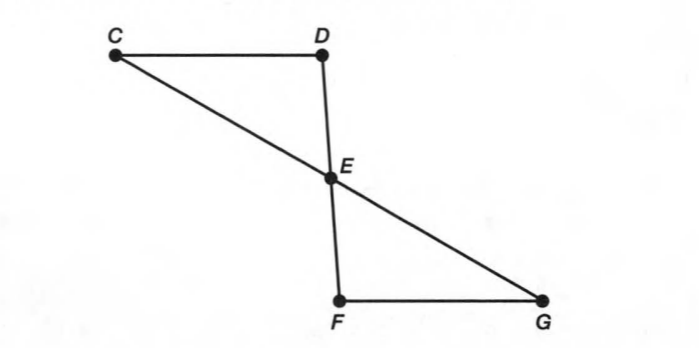
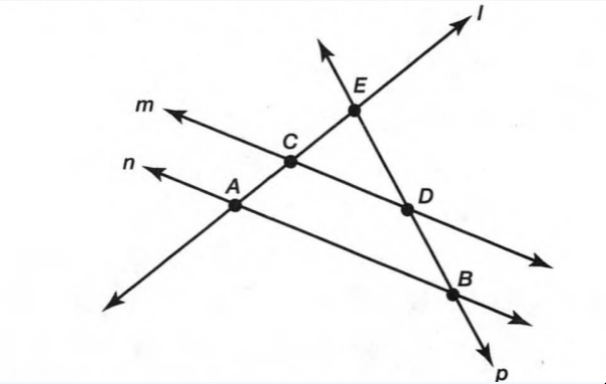
A figure is given,
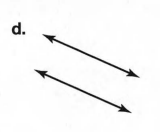
we have to identify which case is shown in figure.
we know that two lines are parallel if they are coplanar on the same plane and do not intersect.
so, two coplanar lines do not intersect.
Hence, the given figure identifies case 3: two coplanar lines do not intersect.
Page 80 Problem 8 Answer
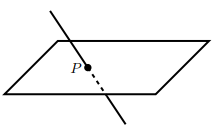
Given, two lines intersect at a single point.
Explain: Are the lines are always coplanar?
Two intersecting lines must be always coplanar,
because each line exists in many plane, but the two intersect means they share at least one plane.
so , the two lines will not always share all planes.
Though, they can be coplanar on the same plane
Hence, the two intersecting lines are always coplanar on the same plane.
Solutions for Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Exercise 2.1 in Carnegie Learning Geometry Page 80 Problem 9 Answer
Given, two lines intersect at an infinite number of points.
Explain: Are the lines always coplanar :
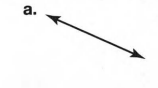
since, two lines coincide with each other and intersect at an infinite number of points.
so, each line exists in many plane but two lines intersect means that means they share at least on plane.
so, the two lines will not share all planes.
though, they can be coplanar on the same plane.
Hence, two intersecting lines are always coplanar on the same plane.
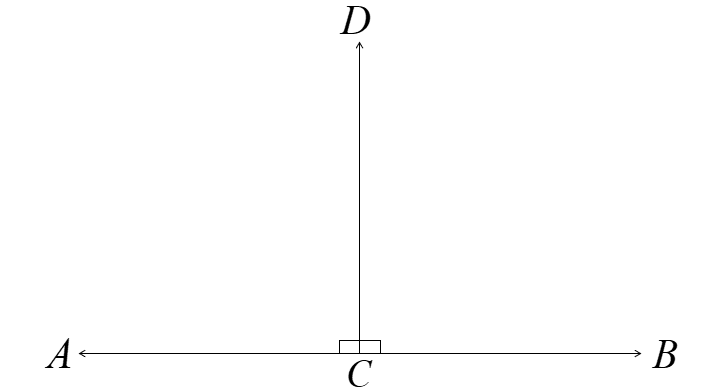
Page 80 Problem 10 Answer
Given, Two lines are parallel.
Describe the distance between a point on one line and the other line.
A figure is drawn,
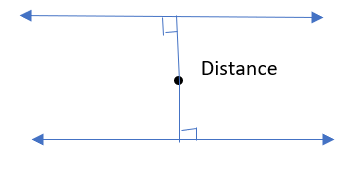
since , two lines are parallel and do not intersect.
that means two lines are coplanar in the same plane.
and the length of segment is drawn from the point perpendicular to the line.
so , the distance between two parallel lines in the plane is the minimum distance between a point on one line and other line.
thus, it equals the perpendicular distance from any point on one line to other line.
Hence, it equals the perpendicular distance from any point on one line to the other line.
Page 80 Problem 11 Answer
To explain: why the skew lines can not intersect.
Any two intersecting lines must lie in the same plane, are called as co planar lines.
we know that The skew lines are non-co planar lines.
By the definition of the skew lines, any two lines in the different planes, which are not parallel and do not intersect each other.
Therefore, The skew lines cannot intersect.
Hence, The skew lines cannot intersect.
Carnegie Learning Geometry 2nd Edition Exercise 2.1 solutions Page 81 Problem 12 Answer
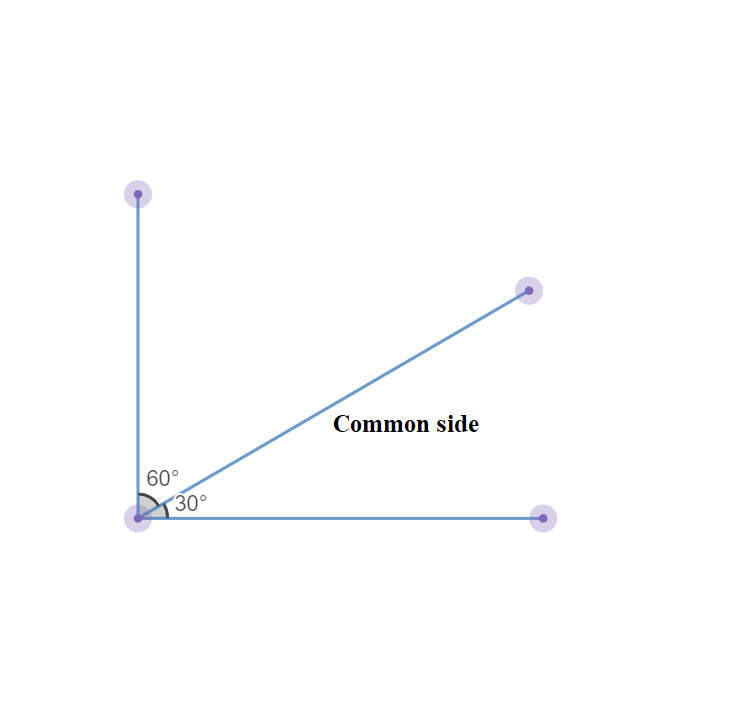
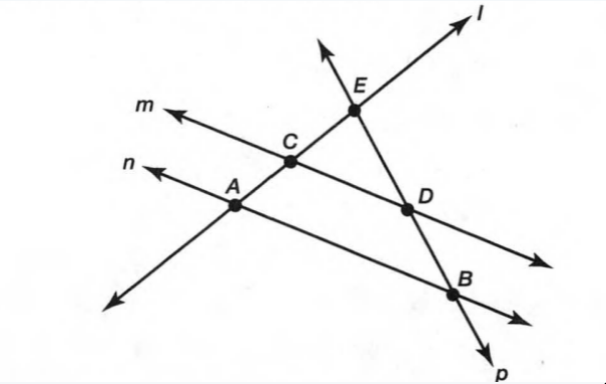
Given: Two parallel lines l1,l2 and the linely intersects the parallel lines.
To find: The lines that each transversal intersects.
A transversal is a line that intersects two or more lines at distinct points.
Given: Two parallel lines l1, and l2 intersected by the linely.
By the definition of the transversal line: A transversal is a line that intersects two or more lines at distinct points.
Since, The linely intersect the two parallel lines.
Therefore, The linely is the transversal line.
The line ly is the transversal line.
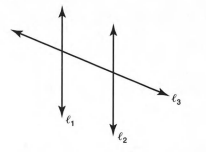
Page 81 Problem 13 Answer
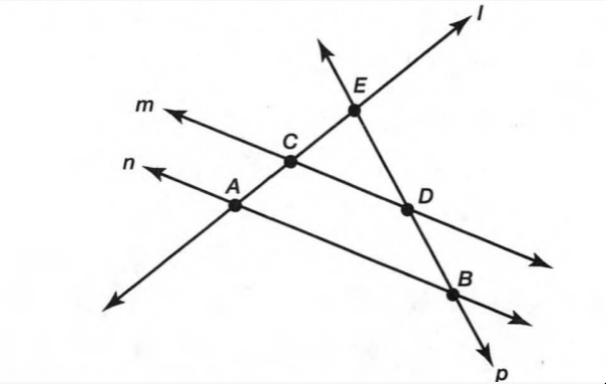
Given: Two non parallel lines l1,l2 and the line l3 intersects the non- parallel lines.
To find: The lines that each transversal intersects.
Given:Two non parallel lines l1,l2 and the line l3 intersects the non- parallel lines.
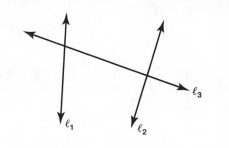
By the definition of the transversal line:A transversal is a line that intersects two or more lines at distinct points.
Since, The linel3 intersect the two non- parallel lines.
Therefore, The linel3 is the non-transversal line.
The linel3 is the transversal line.
The lines l1,l2 are two non parallel lines.
Page 82 Problem 14 Answer
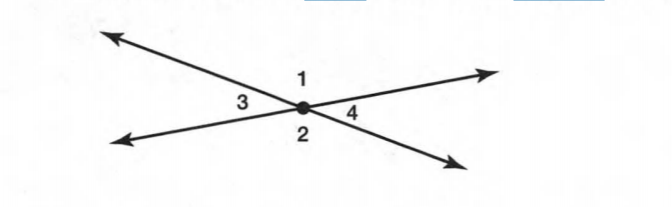
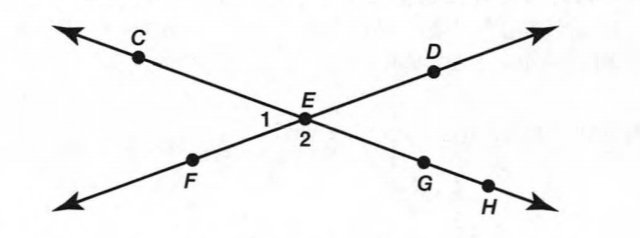
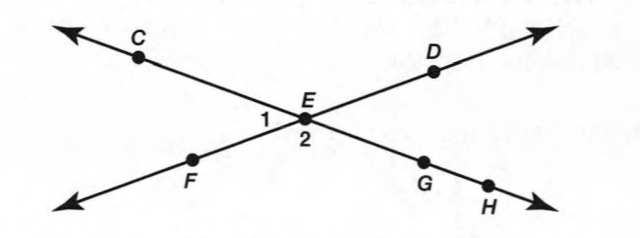
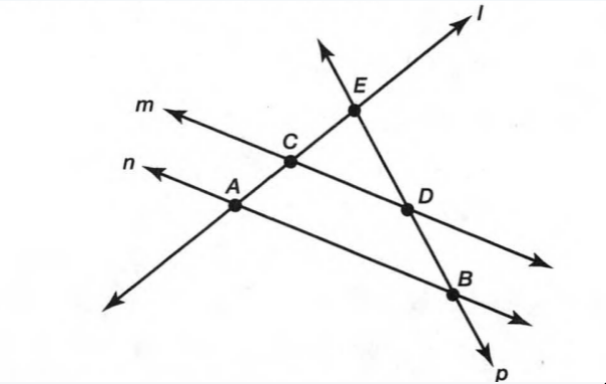
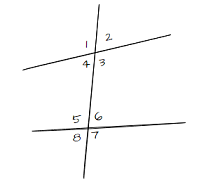
Given: Two non-parallel lines m,n cut by the transversal line p.
To find: all interior angles.
Given: Two non- parallel linesm,n cut by the transversal line p.
To find: all interior angles.
Interior angles are a pair of angles that forms a straight lines.
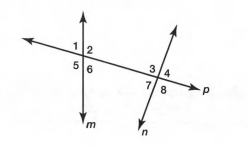
In the above diagram
∠1,∠2 and ∠5,∠6 are the pair interior angles formed by the linem and p.
∠3,∠4 and ∠7,∠8 are the pair interior angles formed by the linen and p.
Hence,The interior angles formed by two lines are∠1,∠2 and ∠5,∠6
∠3,∠4 and ∠7,∠8.
Page 82 Problem 15 Answer
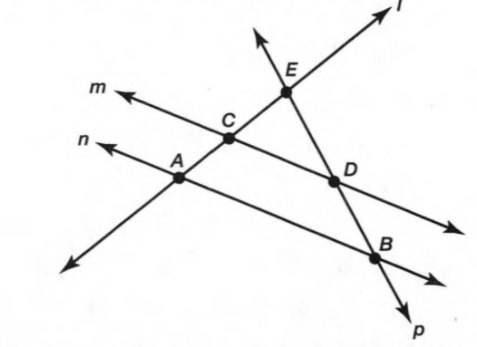
Given: Two non- parallel linesm,n
cut by the transversal line p.
To find: other interior and exterior angles.
Four of the eight angles are interior angles. The other four are exterior angles.
Angle 2 is an interior angle. Angle 1 is an exterior angle.
Interior angles are the angles that lie in the area enclosed between two parallel lines.
Exterior angles are the angles that lie in the area outside the parallel lines.
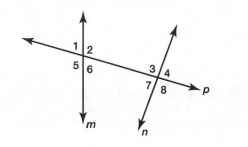
In the above diagram ∠2,∠3,∠6,∠7 are interior angles.
∠1,∠5,∠4,∠8 are exterior angles.
Hence, The interior angles are∠2,∠3,∠6,∠7
The exterior angles are∠1,∠4,∠5,∠8
Page 82 Problem 16 Answer
Given: Two non- parallel lines m,n cut by the transversal line P.
To find: all other pairs of same-side interior angles.
Given: One pair of same-side interior angles is∠2 and ∠3.
To find: all other pairs of same-side interior angles.
Same side interior angles are two angles that are on the interior of (between) the two lines and on the same side of the transversal.
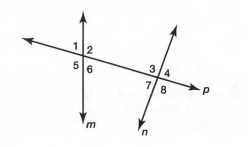
In the above diagram, ∠2,∠3,∠6 and ∠7 are same side interior angles.
Hence,The same side interior angles formed by two lines are∠2,∠3 and ∠6,∠7.
Parallel And Perpendicular Lines Solutions Chapter 2 Exercise 2.1 Carnegie Learning Geometry Page 83 Problem 17 Answer
Given:Two non- parallel lines m,n cut by the transversal line P.
To find: all other pairs of alternate exterior angles.
Given: One pair of alternate exterior angles is∠2 and ∠3.
To find: all other pairs of alternate exterior angles.
Alternate exterior angles are the angles formed on the opposite sides of the transversal.
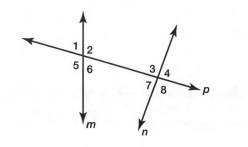
In the above diagram, ∠2,∠3 and ∠6,∠7 are alternate exterior angles.
Hence,The alternate exterior angles formed by two lines are∠2,∠3 and ∠6,∠7.
Step-By-Step Solutions For Carnegie Learning Geometry Chapter 2 Exercise 2.1 Page 83 Problem 18 Answer
Given:Two non- parallel lines m,n cut by the transversal line P.
To find: All other pairs of same-side exterior angles.
Given: One pair of same-side exterior angles is∠1 and∠4.
To find: All other pairs of same-side exterior angles.
Same side exterior angles are two angles that are on the exterior of the two lines and on the same side of the transversal.
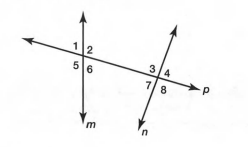
In the above diagram, ∠1,∠4 and ∠5,∠8 are same side exterior angles.
Hence,The same side exterior angles formed by two lines are∠1,∠4 and ∠5,∠8.
Page 84 Problem 19 Answer
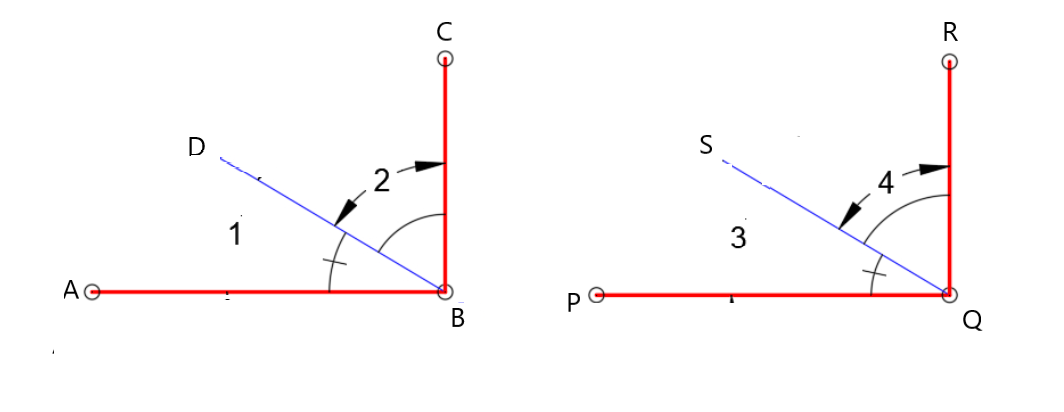
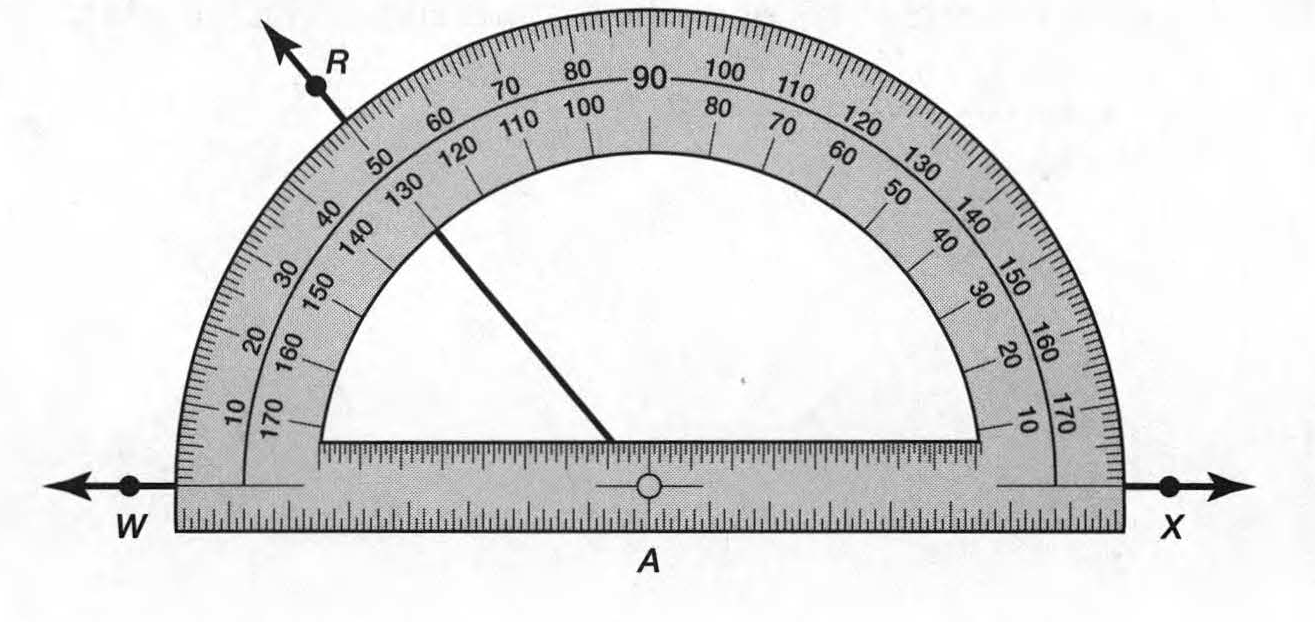
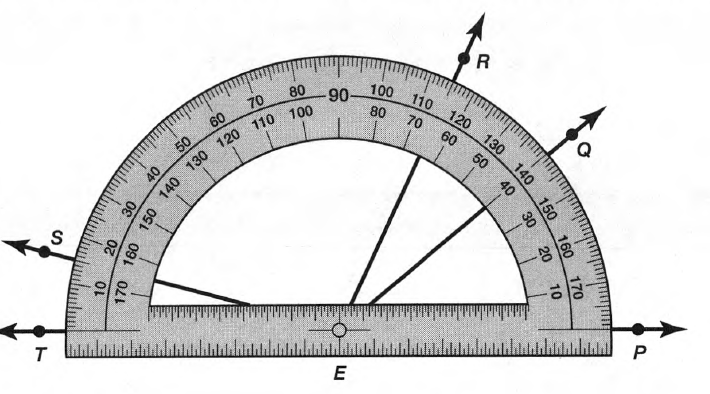
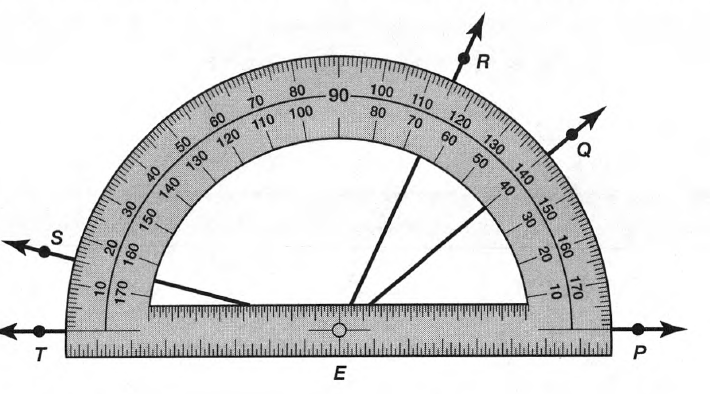
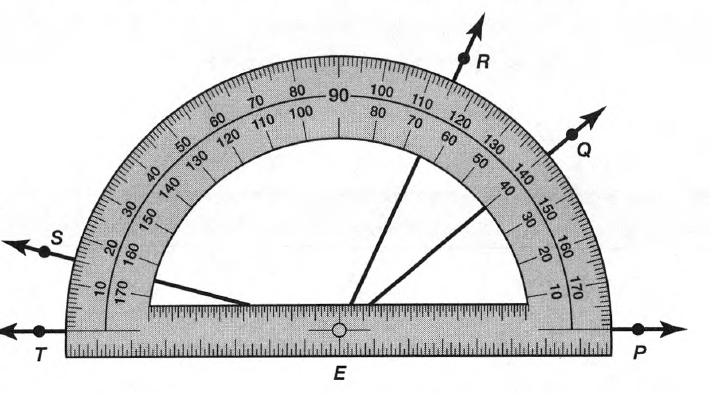
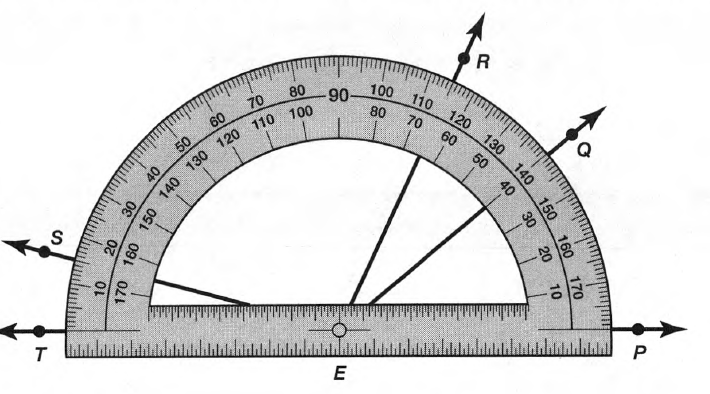
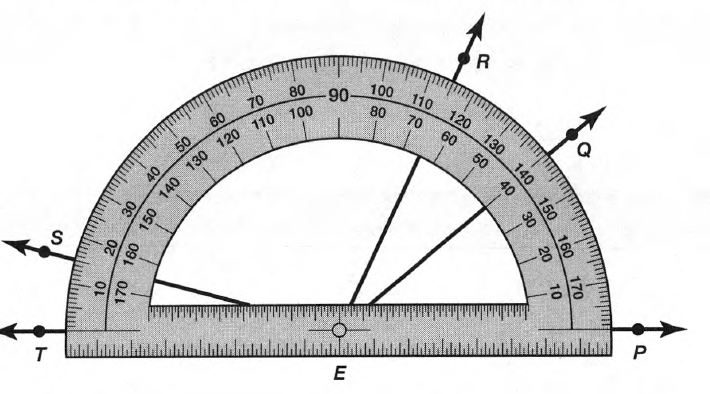
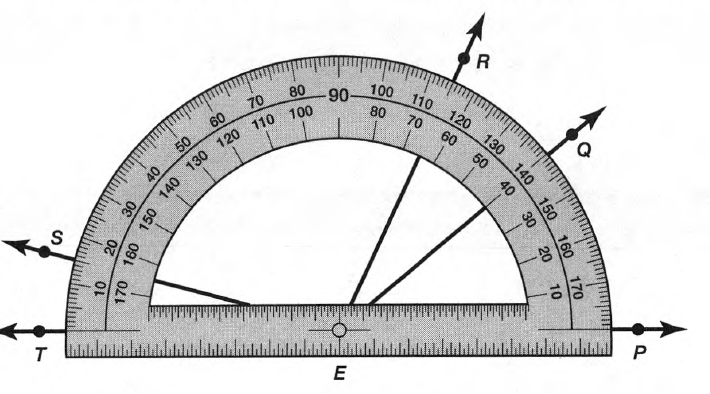
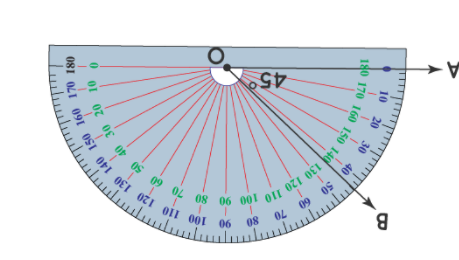
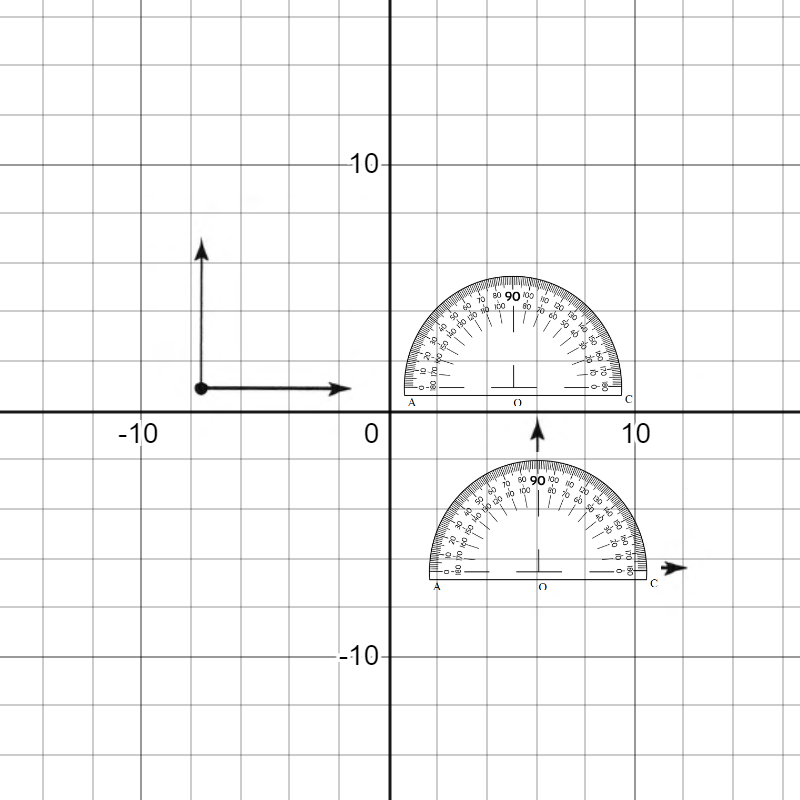
Given: Draw two non-parallel lines cut by a transversal, number each angle, and then use a protractor to measure each angle.
To Draw two non-parallel lines cut by a transversal and to measure each angle.
Two non-parallel lines can be drawn as
Place the hole of the protractor at the vertex of ∠1 with the flat part of the protractor lined with the horizontal side of the angle and then read the measure of the angle among the lower numbers of the protractor.
∠1=98°
Similarly, measure all the angles
∠2=82°
∠3=98°
∠4=82°
∠5=92°
∠6=88°
∠7=92°
∠8=88°
Hence, by following the above steps we can draw two non-parallel lines cut by a transversal and then use a protractor to measure each angle.
Carnegie Learning Geometry Chapter 2 Exercise 2.1 Free Solutions Page 84 Problem 20 Answer
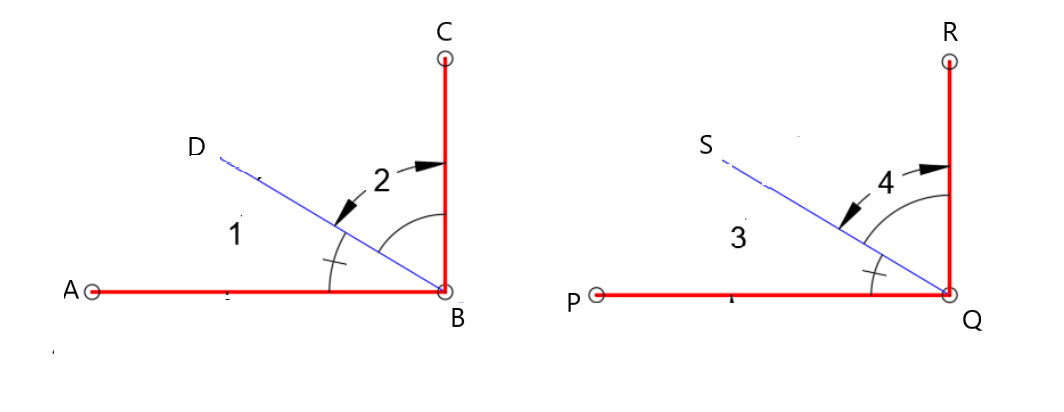
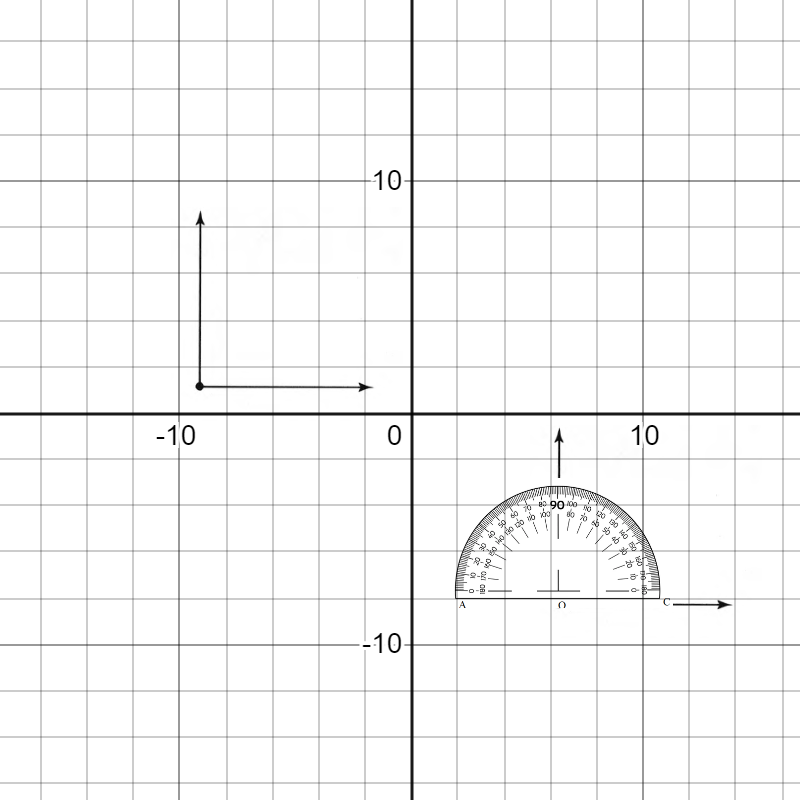
To draw: Two parallel lines and transversal and measure the angles by the protractor.
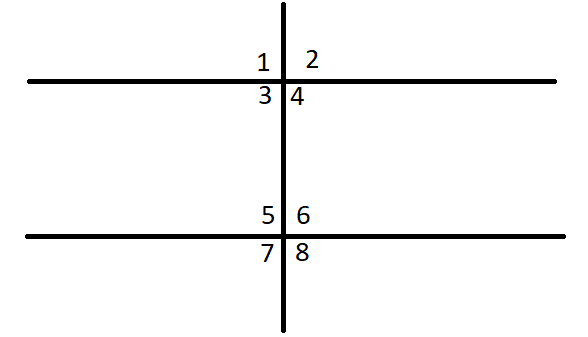
All the angles are 90∘.
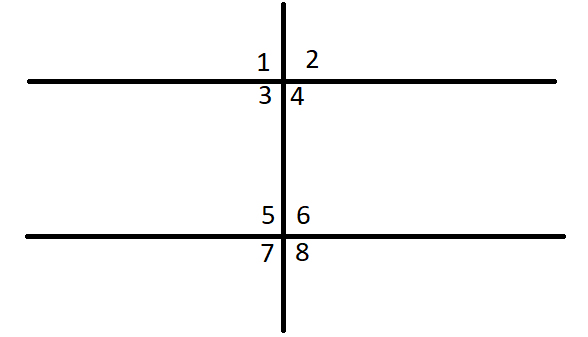
All the angles are 90∘.
Page 84 Problem 21 Answer
Given: The two parallel and non-parallel lines and their transversals.
For parallel lines, the alternate interior angles are equal but not in the case of the non-parallel lines.
For parallel lines, the alternate interior angles are equal but not in the case of the non-parallel lines.
Page 84 Problem 22 Answer
Given: The two parallel and non-parallel lines and their transversals.
For parallel lines, the alternate exterior angles are equal but not in the case of the non-parallel lines.
For parallel lines, the alternate exterior angles are equal but not in the case of the non-parallel lines.
Carnegie Learning Geometry Exercise 2.1 Student Solutions Page 84 Problem 23 Answer
Given: The two parallel and non-parallel lines and their transversals.
For parallel lines, the corresponding angles are equal but not in the case of the non-parallel lines.
For parallel lines, the corresponding angles are equal but not in the case of the non-parallel lines.
Page 84 Problem 24 Answer
Given: The two parallel and non-parallel lines and their transversals.
The same side interior angles are supplementary for parallel lines but not in the case of the non-parallel lines.
The same side interior angles are supplementary for parallel lines but not in the case of the non-parallel lines.
Page 84 Problem 25 Answer
Given: The two parallel and non-parallel lines and their transversals.
The same side exterior angles are supplementary for the parallel lines but not for the non-parallel lines.
The same side exterior angles are supplementary for the parallel lines but not for the non-parallel lines.
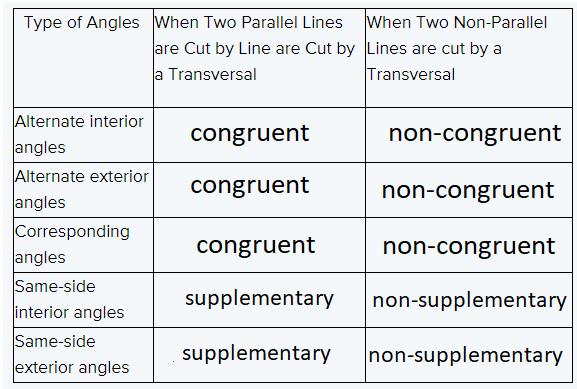
Page 85 Problem 26 Answer
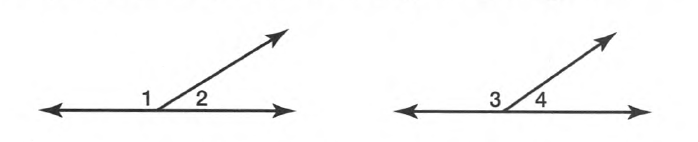
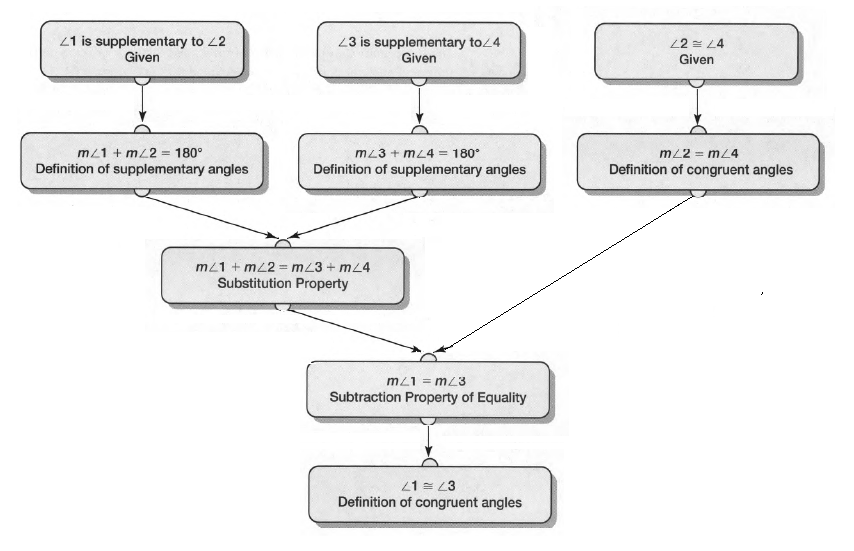
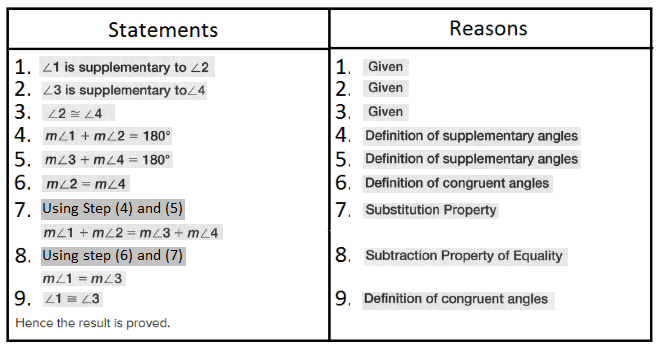
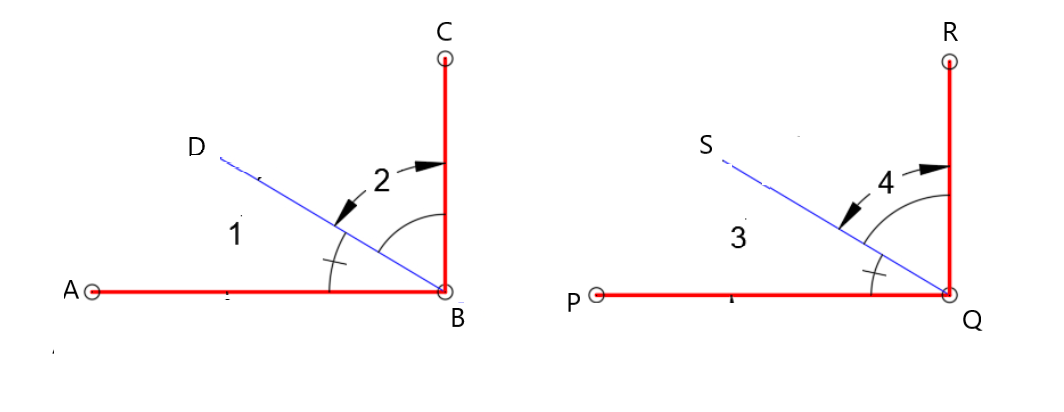
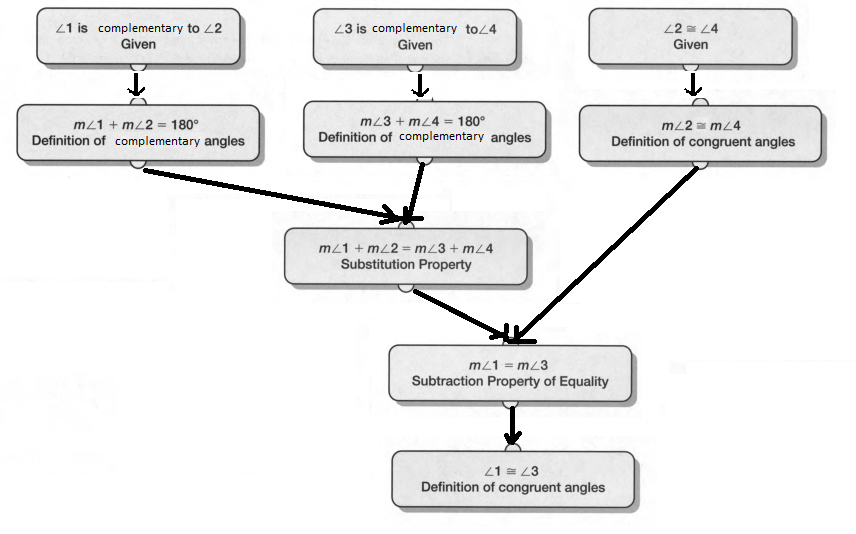
Given:
To specify inductive or deductive reasoning to summarize the conclusion
As per the question we have used deductive reasoning to summarize the conclusion.
Hence, deductive reasoning was used to summarize the conclusion.
Page 85 Problem 27 Answer
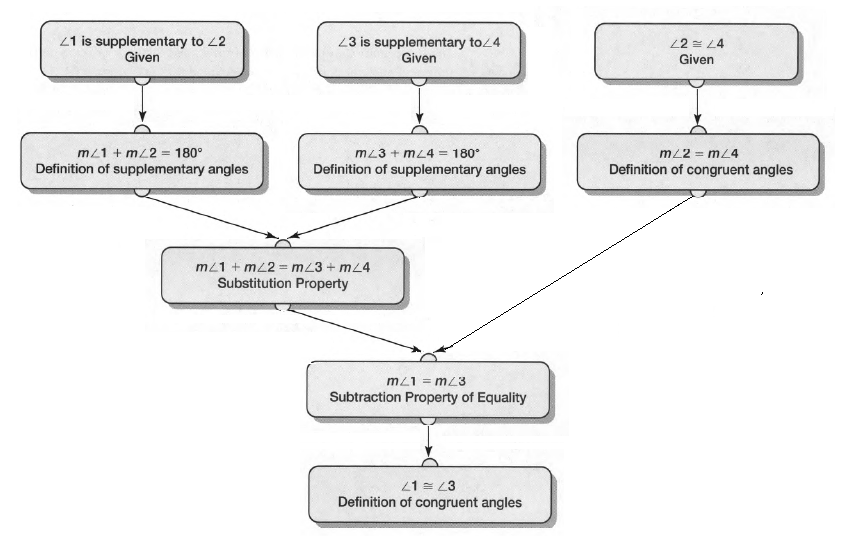
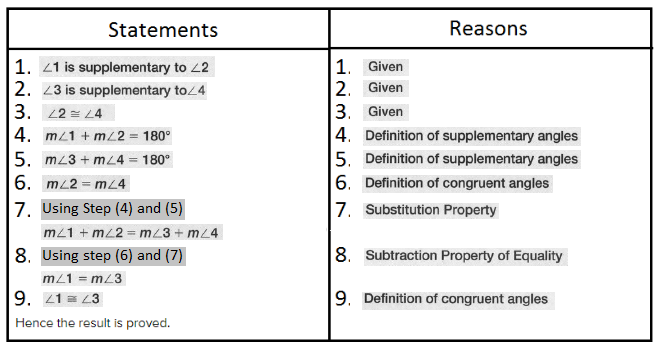
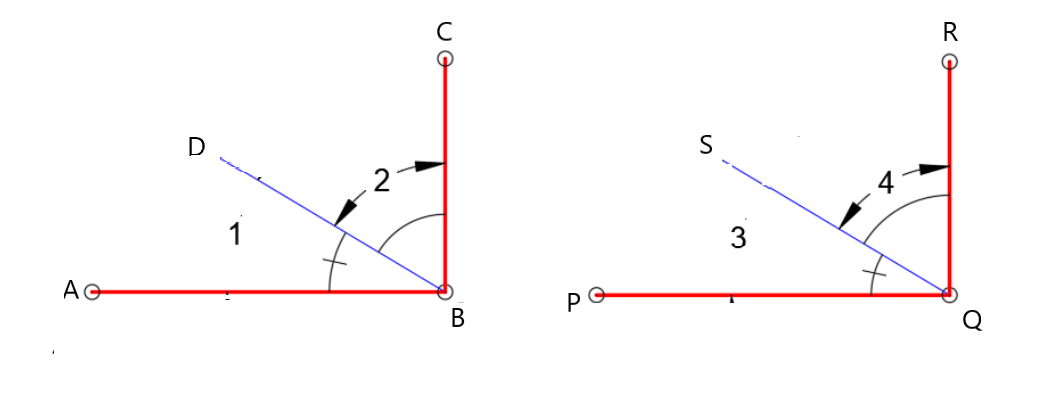
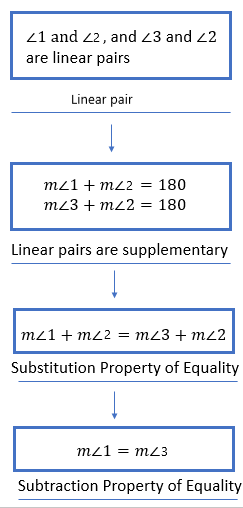
Given:
To specify inductive or deductive reasoning to summarize the conclusion
As per the question we have used deductive reasoning to summarize the conclusion.
Hence, deductive reasoning was used to summarize the conclusion.
Parallel And Perpendicular Lines Exercise 2.1 Carnegie Learning 2nd Edition Answers Page 85 Problem 28 Answer
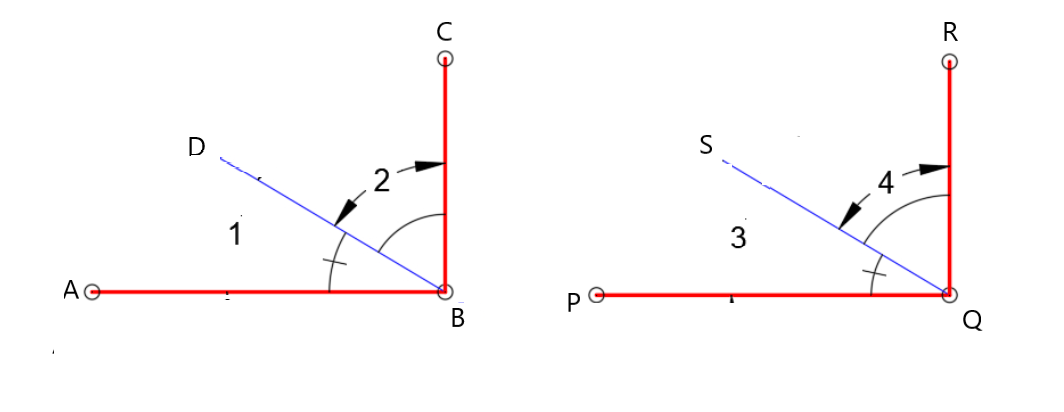
Given:
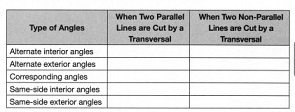
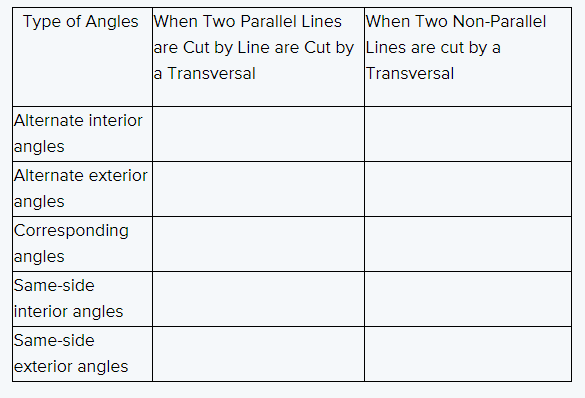
To Compare the measures of the angles everyone used and your chart to the charts of the rest of your class.
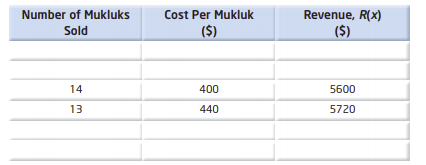
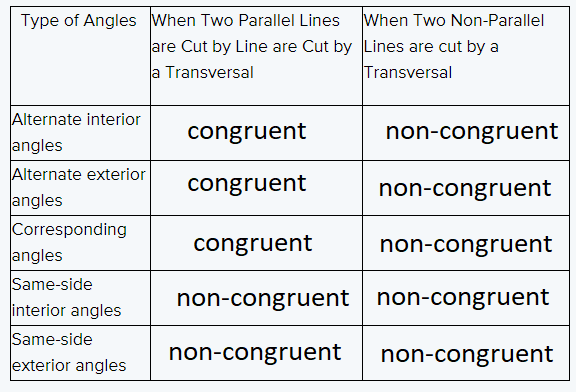
After comparing the measures of the angles everyone used and your chart to the charts of the rest of your class we conclude the following table
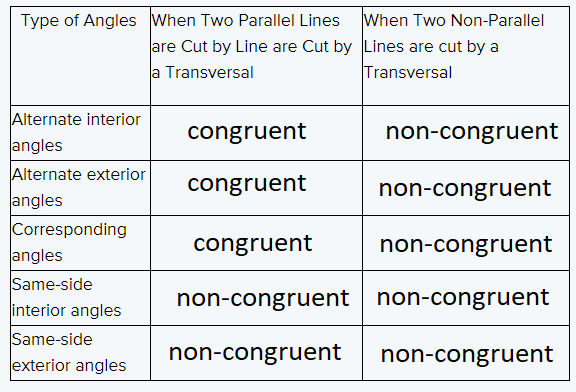
Hence, After comparing the measures of the angles everyone used and your chart to the charts of the rest of your class we conclude the following table
Page 85 Problem 29 Answer
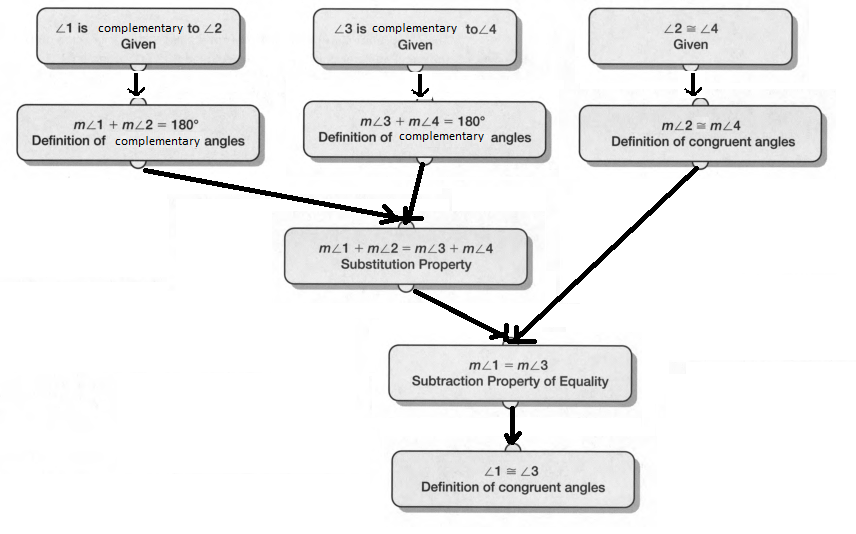
Given:
To state the relationships in the chart as conjectures or theorems
The relationship in the char can be stated as conjectures and theorems as from the table
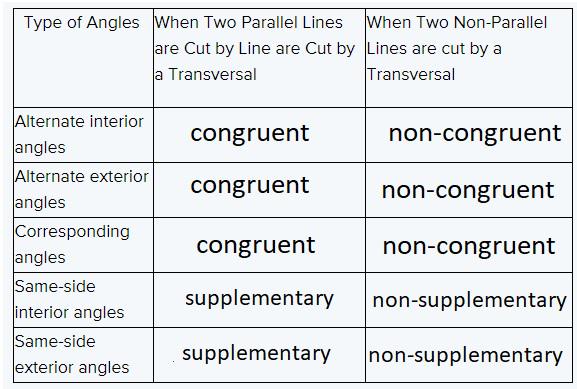
We can say that for alternate interior angles when two parallel lines are cut by a transverse
they are congruent, which can be specified by theorem.
Whereas when two non-parallel lines are cut by a transversal they are non-congruent, which can be specified by conjectures.
Similarly, all other angles can be stated as conjectures and theorems.
There are three instances that would be enough evidence to be considered proof of the relationship.
In the case of alternate interior angles when two parallel lines are cut by a transverse
they are congruent, which can be specified by theorem.
Whereas when two non-parallel lines are cut by a transversal they are non-congruent, which can be specified by conjectures.
Similar is the case for alternate interior angles and corresponding angles.
Hence, we can state the relationships in the chart as conjectures or theorems.
There are three instances that would be enough evidence to be considered proof of the relationship.