Geometry Student Text 2nd Edition Chapter 2Parallel and Perpendicular Lines
Carnegie Learning Geometry Student Text 2nd Edition Chapter 2 Exercise 2.5 Solution Page 106 Problem 1 Answer
We are given a triangle ΔRAD
we have to explain how many line segments, angles, and vertices are needed to form a triangle.
A line does not have any endpoints.
A ray has only one fixed point.
A line segment is a part of a line that has a fixed length.
Perpendicular lines have a 90∘ angle between them.
Parallel lines do not meet.
Read and learn More Carnegie Learning Geometry Student Text 2nd Edition Solutions
We need three sides, three angles to draw the triangle, without which the triangle is not possible.
A triangle has three sides, three angles, and three vertices.
The sum of all internal angles of a triangle is always equal to180°.
This is called the angle sum property of a triangle.
The sum of the length of any two sides of a triangle is greater than the length of the third side.
Carnegie Learning Geometry Chapter 2 Page 106 Problem 2 Answer
We are given a triangle
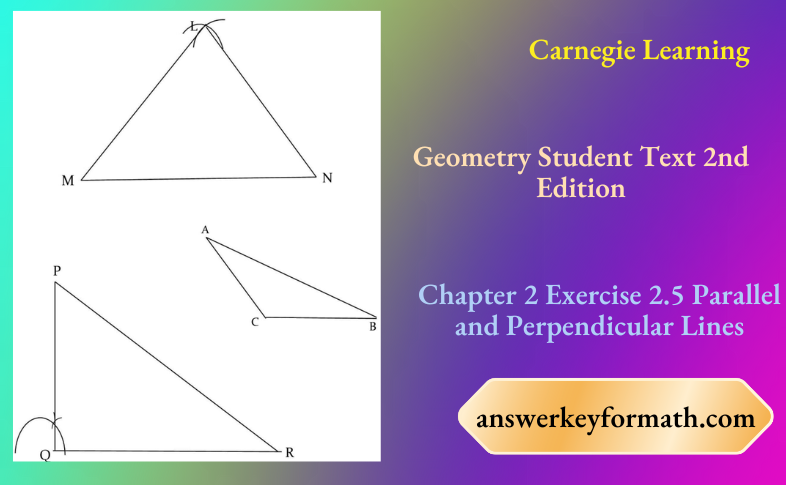
We have to label the vertices of the triangles and then use symbols to name each triangle.
We have labeled all the three triangles.
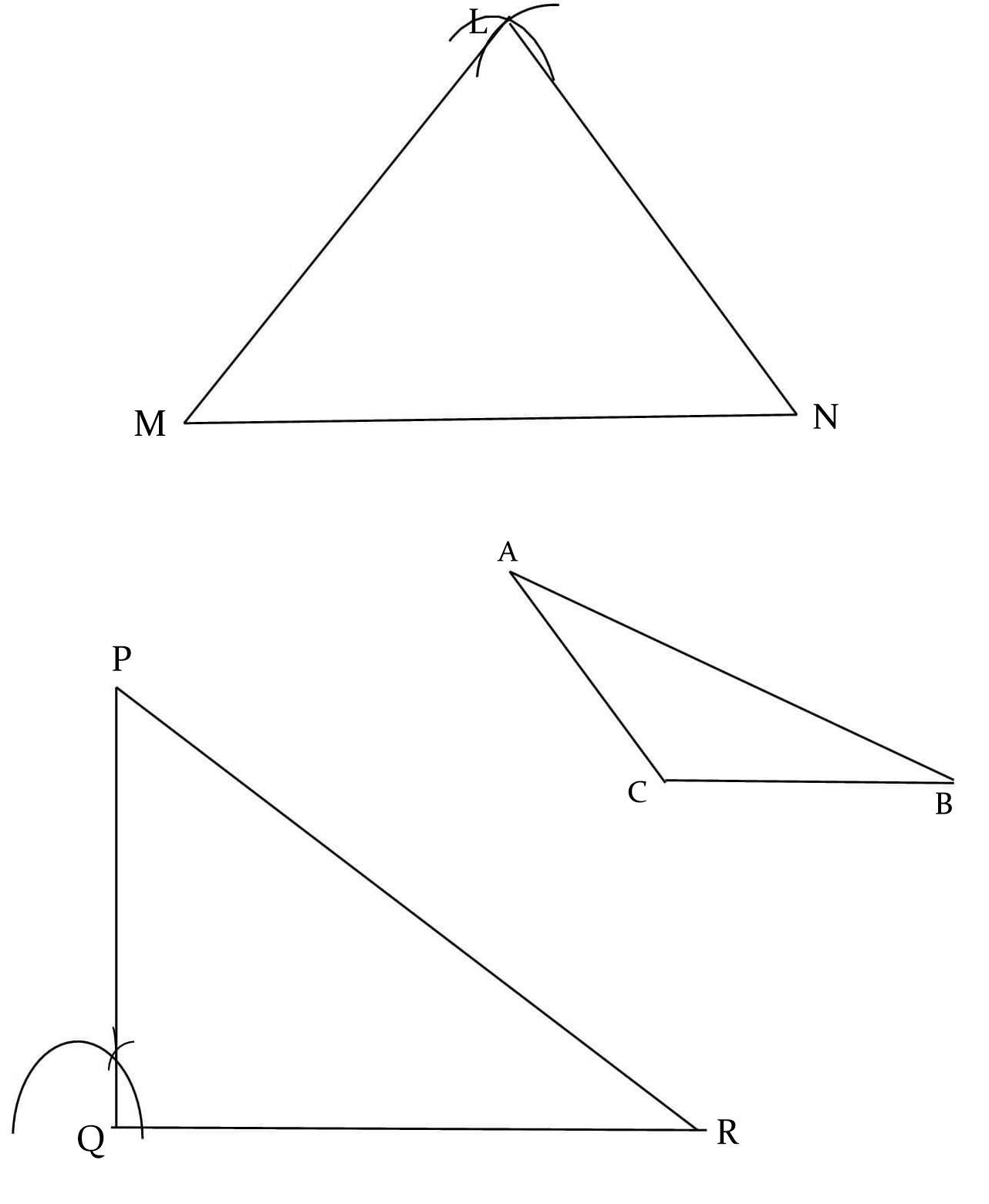
ΔLMN is an scalene triangle in which all sides are unequal.
ΔACB is a obtuse triangle in which ∠ACB is an obtuse angle.
ΔPQR is a right triangle in which ∠PQR is right angle.
Hence, ΔLMN is a scalene triangle, ΔACB is obtuse triangle, ΔPQR is right triangle.
Page 106 Problem 3 Answer
We are given a triangle ΔRAD.
We have to shade the interior of ΔRAD.
We need three sides, three angles to draw the triangle, without which the triangle is not possible.
The shaded area lies inside the triangle.
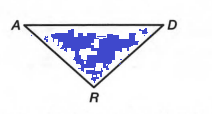
Hence, the shaded area is shown in the following tringle.
Solutions for Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Exercise 2.5 In Carnegie Learning Geometry Page 106 Problem 4 Answer
A triangle has three line segments and three angles.
We have to name the three sides and the three angles of ΔRAD.
A triangle has three sides, three angles, and three vertices.
The sum of all internal angles of a triangle is always equal to180∘.
This is called the angle sum property of a triangle.
The sum of the length of any two sides of a triangle is greater than the length of the third side.
Three sides of ΔRAD: RA,AD, RD
Three angles ofΔRAD:∠RAD,∠ADR,∠ARD
Carnegie Learning Geometry Chapter 2 Page 106 Problem 5 Answer
We are given
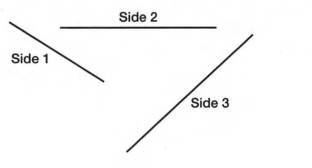
We have to construct a triangle with the three sides shown.
Steps to draw triangle
- Draw a straight line.
- Span the segment with your compass.
- Trace a quarter-circle arc.
- Switch the compass around.
- Draw a second arc
- Mark the point where the two arcs cross
- Finish the triangle.
The required figure is,
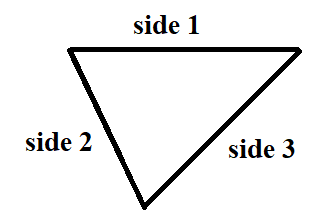
Hence, the triangle figure is,
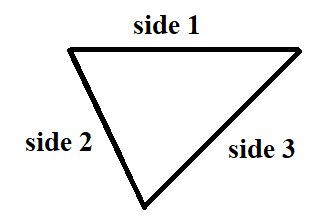
Page 106 Problem 6 Answer
We have to compare the triangle that you constructed with the triangles that your classmates constructed.
The triangle that we constructed,
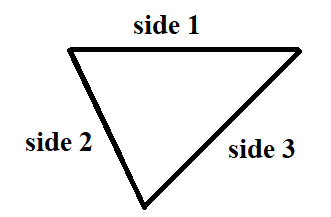
The triangle that our classmate constructed.
We can see the shape of both triangles is the same but the position of the line is at different places.
Both triangles are congruent to each other.
Both are the same because the length of the sides is the same.
Hence, both triangles are the same because the length of the sides is the same.
Carnegie Learning Geometry Chapter 2 Page 107 Problem 7 Answer
To draw : Quadrilateral ABCD.
The drawing is done using MS paint
The quadrilateral is
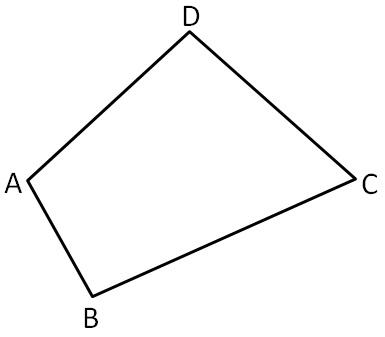
The drawing is
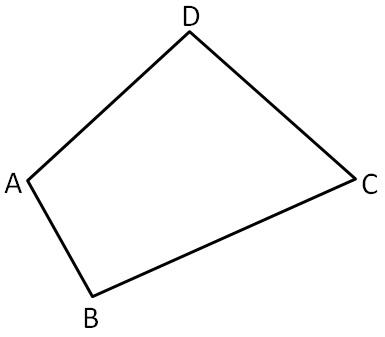
ABCD is a quadrilateral.
Carnegie Learning Geometry 2nd Edition Exercise 2.5 Solutions Page 107 Problem 8 Answer
To explain : How many angles, sides, and vertices are needed to form a quadrilateral
A quadrilateral has 4 sides, 4 angles and 4 vertices.A quadrilateral can be regular or irregular.
The sum of all the interior angles of a quadrilateral is 360°.
Number of Angles=4
Sides=4
Vertices=4
Carnegie Learning Geometry Chapter 2 Page 107 Problem 9 Answer
To name: Two pairs of consecutive sides.
Given :
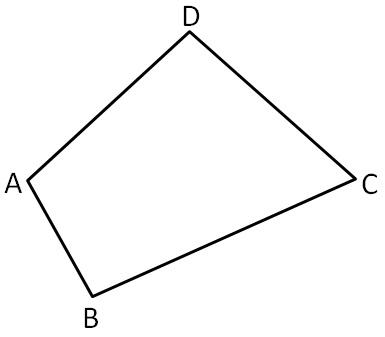
The pairs of consecutive sides are
AB,BC
CD,BC
The pairs of consecutive sides are
AB,BC
BC,CD
Parallel And Perpendicular Lines Solutions Chapter 2 Exercise 2.5 Carnegie Learning Geometry Page 107 Problem 10 Answer
To name : Two pairs of consecutive angles .
Given :
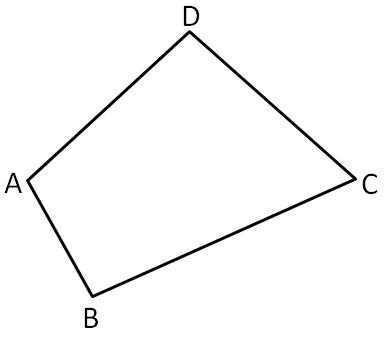
The pairs of consecutive angles are
∠ABC,∠BCD
∠ADC,∠BCD
The pairs of consecutive angles are
∠ABC,∠BCD
∠ADC,∠BCD
Carnegie Learning Geometry Chapter 2 Page 107 Problem 11 Answer
To name: Two pairs of opposite sides.
Given :
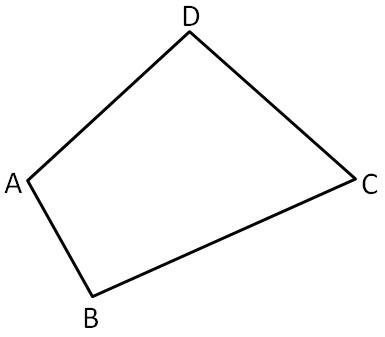
Two pairs of opposite sides are
AD,BC
AB,CD
Two pairs of opposite sides are
AD,BC
AB,CD
Page 107 Problem 12 Answer
To name: Two pairs of opposite angles .
Given :
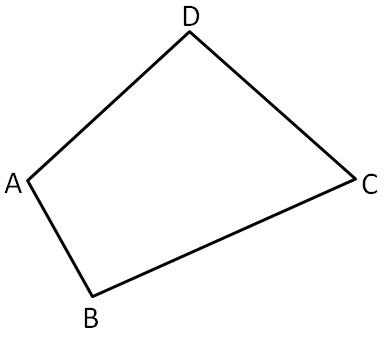
Two pairs of opposite angles are
∠B,∠D
∠A,∠C
Two pairs of opposite angles are
∠B,∠D
∠A,∠C
Carnegie Learning Geometry Chapter 2 Page 108 Problem 13 Answer
To construct: A quadrilateral with the four sides shown. Label and name the quadrilateral.
Given :
The quadrilateral is
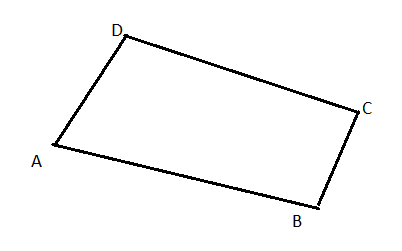
The quadrilateral is
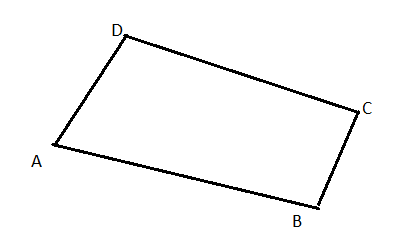
Step-By-Step Solutions For Carnegie Learning Geometry Chapter 2 Exercise 2.5 Page 108 Problem 14 Answer
To compare: The quadrilateral that you constructed with the quadrilaterals that your classmates constructed.
What do you observe, why
Given :
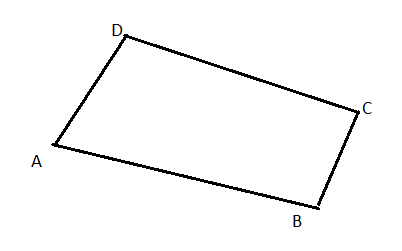
Here only sides is given, angles are not given.
A student can draw this many ways with different angles
Hence the quadrilaterals drawn by student will not be same
The quadrilaterals drawn by student will not be same
Carnegie Learning Geometry Chapter 2 Page 108 Problem 15 Answer
To draw : And name the diagonals in each figure.
Given :
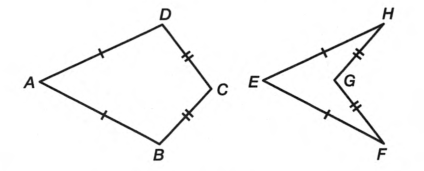
The drawing with diagonals is
In first figure diagonals are AC,BD
In second figure diagonals are EG,FH
The drawing with diagonals is
Page 109 Problem 16 Answer
To explain: What is the difference between the diagonals of the quadrilaterals
Given :
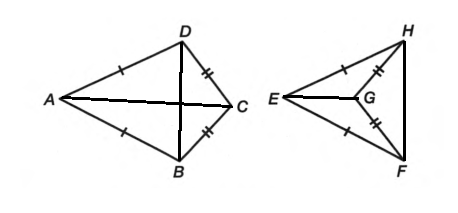
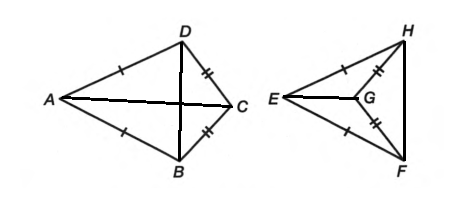
In first figure both diagonals are inside quadrilateral
In second figure one diagonal is inside and other is outside quadrilateral
In first figure both diagonals are inside quadrilateral, in second figure one diagonal is inside and other is outside quadrilateral
Carnegie Learning Geometry Chapter 2 Page 109 Problem 17 Answer
To classify : Each quadrilateral as convex or concave.
If the quadrilateral is concave, draw a line segment that connects two points in the interior such that the line segment is not completely in the interior of the figure.
Given :
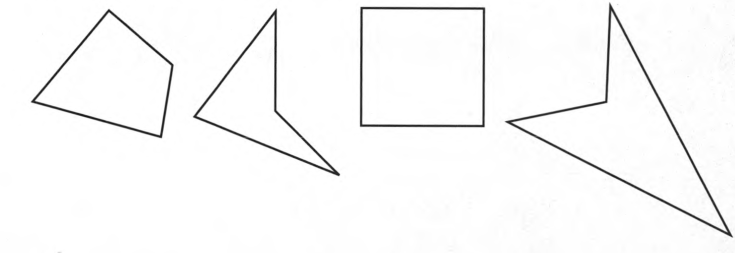
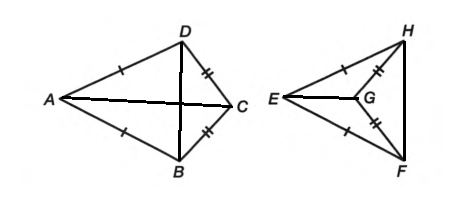
Convex
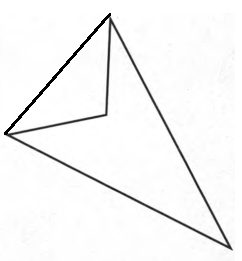
b) Concave
c) Convex
d) Concave
Quadrilaterals are classified
Carnegie Learning Geometry Chapter 2 Exercise 2.5 Free Solutions Page 109 Problem 18 Answer
To sketch A convex pentagon, a concave pentagon, and a regular pentagon.
Convex pentagon
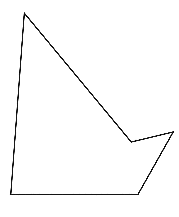
Concave pentagon
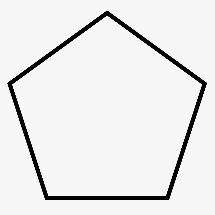
Regular pentagon
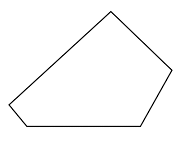
Convex pentagon
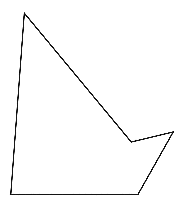
Concave pentagon
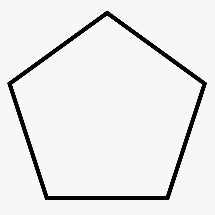
Regular pentagon

Carnegie Learning Geometry Chapter 2 Page 110 Problem 19 Answer
To construct A pentagon with the five sides shown.
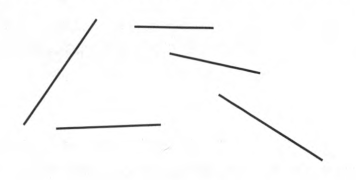
Given
The pentagon is
Page 110 Problem 20 Answer
To compare : The pentagon that you constructed with those that your classmates constructed, What do you observe, why
Some pentagons are similar some are different.
Given :
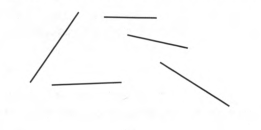
With above sided students can many polygons
Student 1
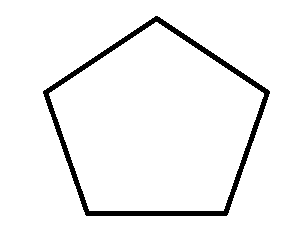
Student 2
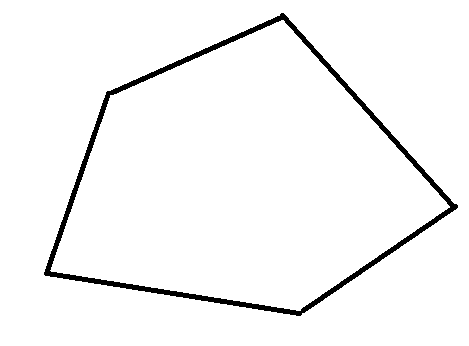
We can see both pentagons are not same.
This differs from student to student
The pentagons are not same for all the students.
The order and angle of joining the lines are different in different students. Hence the pentagons are different.
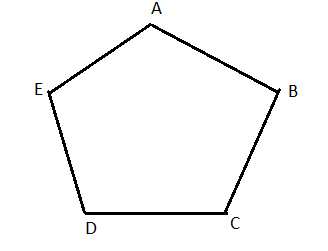
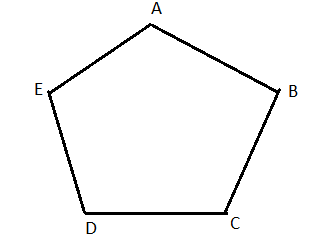
Carnegie Learning Geometry Chapter 2 Page 110 Problem 21 Answer
To name : Two pairs of consecutive sides and two pairs of consecutive angles in pentagon ABCDE.
The pentagons is
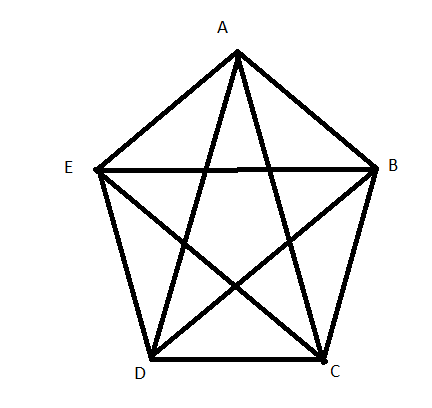
Consecutive sides
AE,AB
DE,EA
Consecutive angle
∠DEA,∠EAB
∠ABC∠EAB
Consecutive sides AE,AB and DE,EA
Consecutive angles∠DEA,∠EAB and ∠ABC,∠EAB
Page 111 Problem 22 Answer
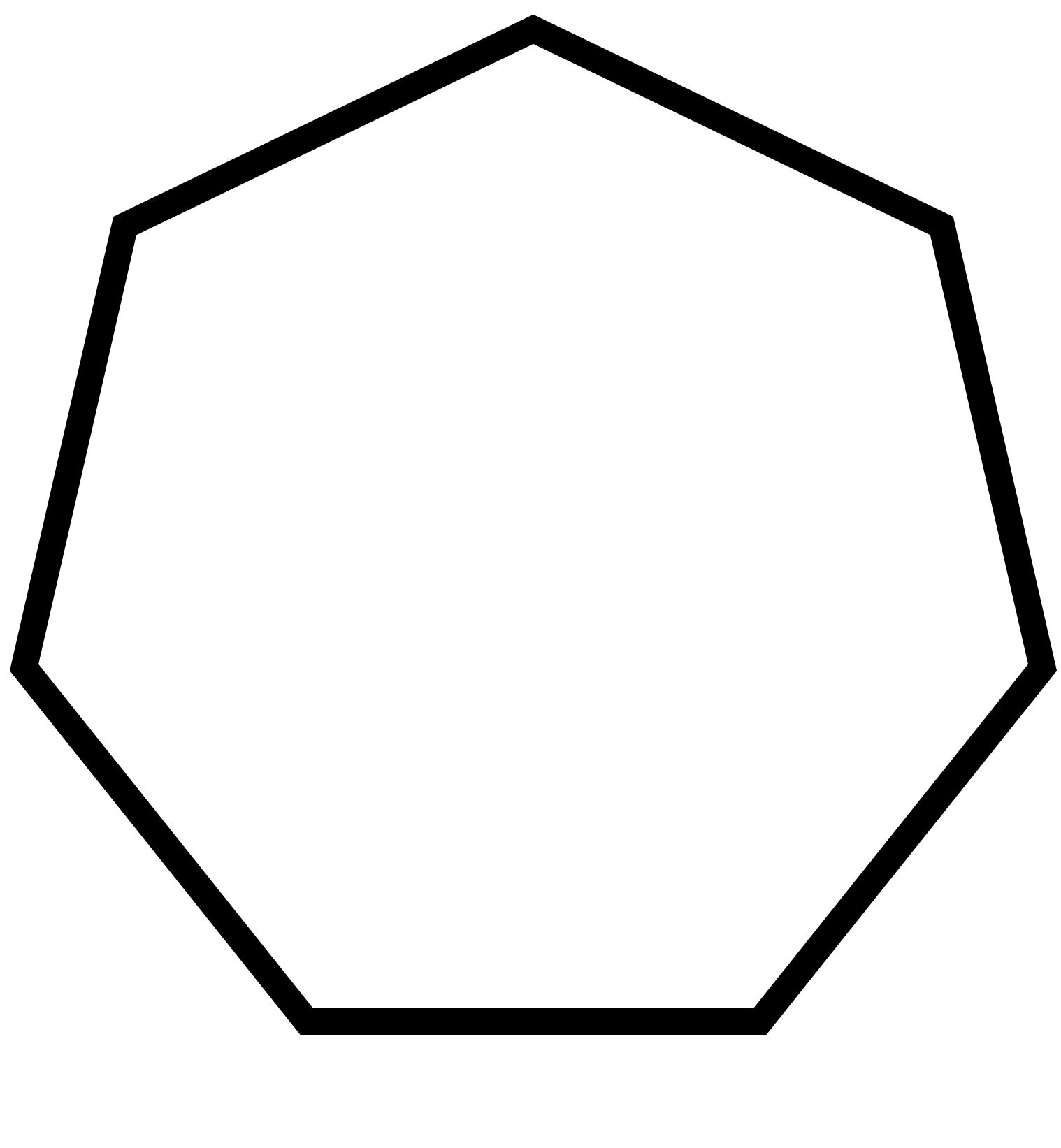
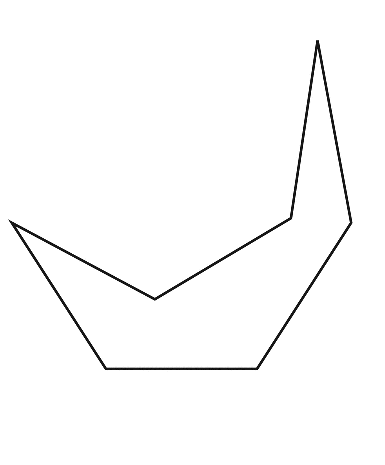
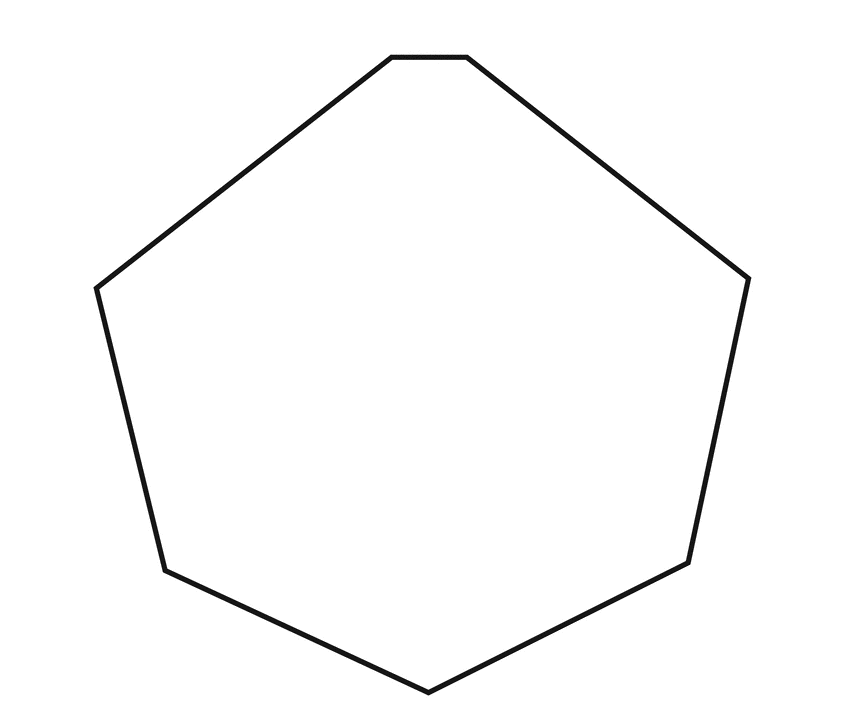
To sketch A convex heptagon, a concave heptagon, and a regular heptagon.
Concave heptagon
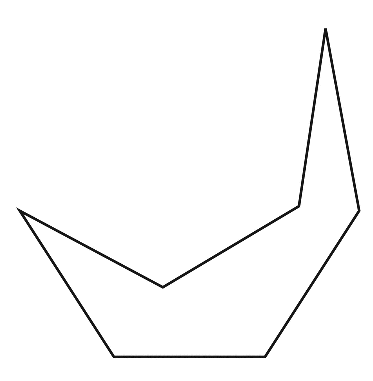
Convex heptagon
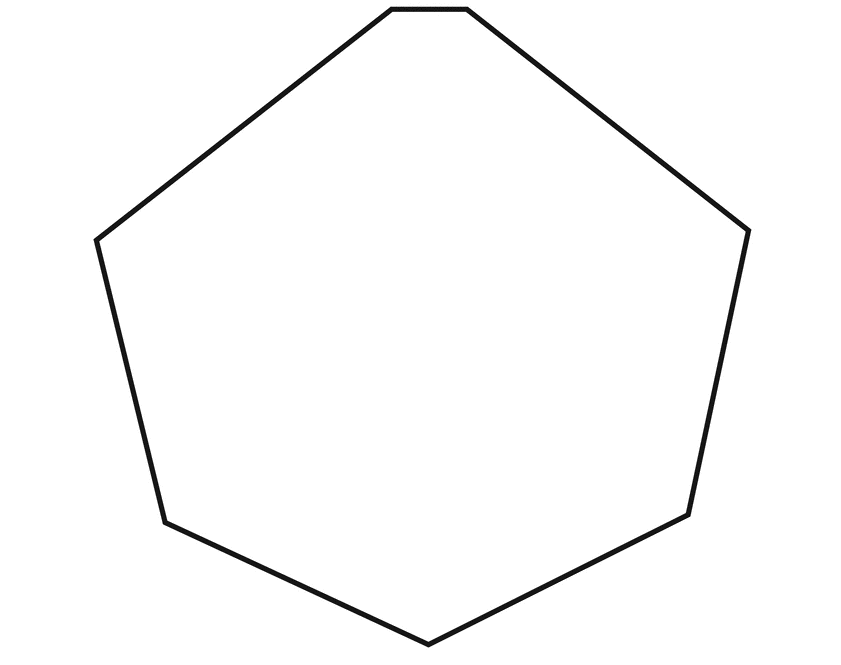
Regular heptagon
Concave heptagon
Convex heptagon
Regular heptagon
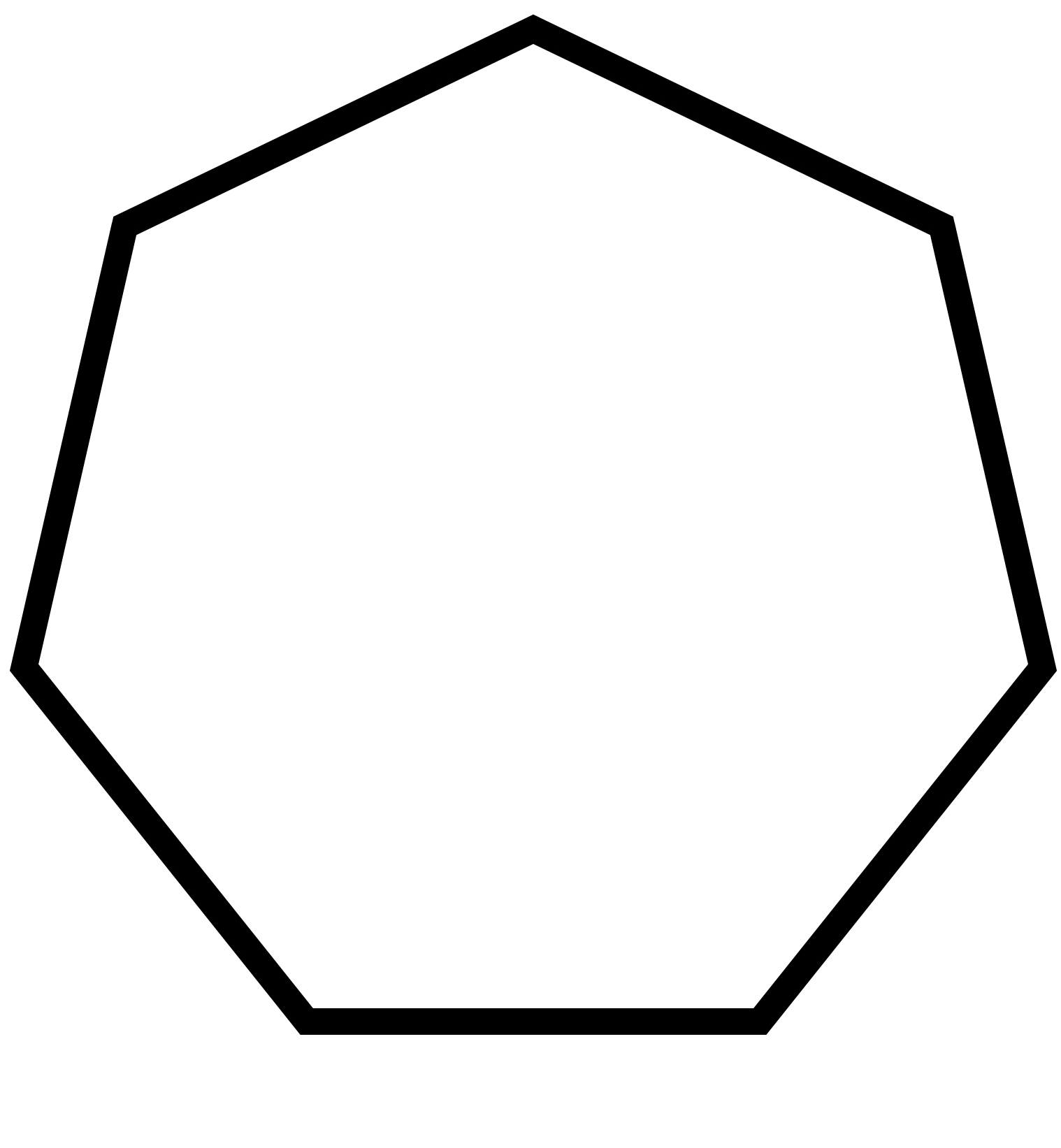
Carnegie Learning Geometry Chapter 2 Page 111 Problem 23 Answer
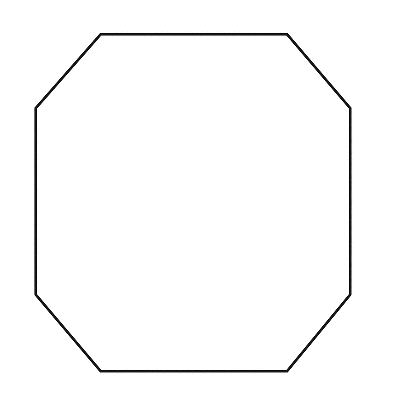
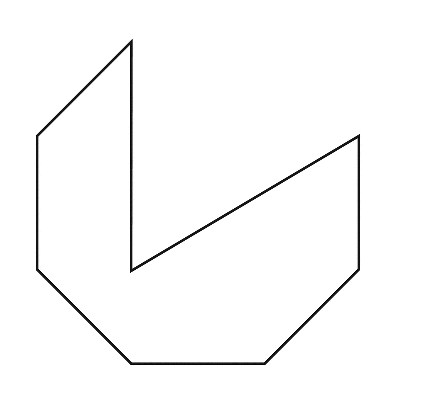
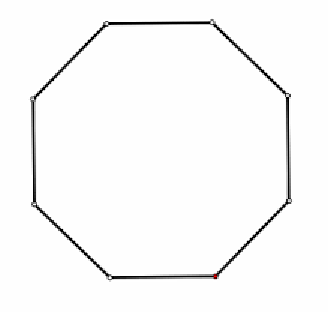
To sketch A convex octagon, a concave octagon, and a regular octagon.
Convex octagon
Concave octagon
Regular octagon
Convex octagon
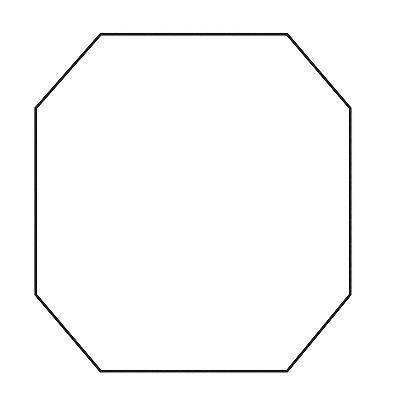
Concave octagon
Regular octagon
Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Exercise 2.5 Carnegie Learning 2nd Edition Answers Page 111 Problem 24 Answer
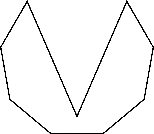
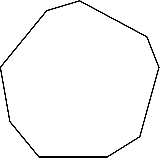
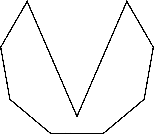
To sketch : A convex nonagon, a concave nonagon, and a regular nonagon.
Convex nonagon
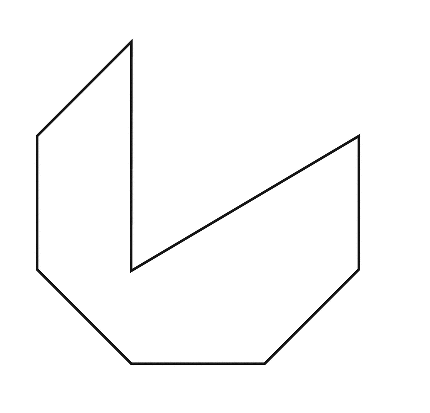
Concave nonagon
Regular nonagon
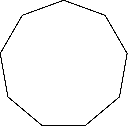
Convex nonagon
Concave nonagon
Regular nonagon
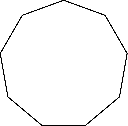
Carnegie Learning Geometry Chapter 2 Page 112 Problem 25 Answer
To classify : Each polygon as regular or irregular, and then classify each polygon as convex or concave.
Explain your reasoning.
Given :
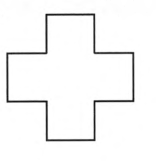
Here all sides are same but all angles are not same
Hence irregular polygon
Here all angles are not less than 1800
Hence concave polygon
Hence the given figure is concave irregular polygon
Page 112 Problem 26 Answer
To classify : Each polygon as regular or irregular, and then classify each polygon as convex or concave. Explain your reasoning.
Given :

Here all angles are same but all sides are not same
Hence irregular polygon
Here all angles are less than900
Hence convex polygon
Hence the given figure is Convex irregular polygon
Carnegie Learning Geometry Chapter 2 Page 112 Problem 27 Answer
To classify : Each polygon as regular or irregular, and then classify each polygon as convex or concave. Explain your reasoning.
Given :
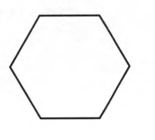
Here all sides and all angles are same
Hence regular polygon
Here all angles are less than1800
Hence convex polygon
Convex regular polygon
Page 112 Problem 28 Answer
To classify: Each polygon as regular or irregular, and then classify each polygon as convex or concave. Explain your reasoning.
Given :

The figure is not a polygon, this figure cannot be formed using lines.
The figure is not a polygon, this figure cannot be formed using lines.
