Core Connections Course 1 Student 1st Edition Chapter 3 Portions and Integers
Core Connections Course 1 Student 1st Edition Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 Solutions Page 99 Problem 1 Answer
Given that the joke: The clerk asked Ron, “Do you want your pizza cut into eight slices or twelve,” Ron replied “I’m not hungry enough to eat twelve.”
It is asked what is the fraction that makes the joke work.
The joke was funny because the quantity of pizza doesn’t change when you cut the same pizza into 8 pieces or 12 pieces.
So, he eats the whole pizza in 8 pieces.
Thus, Pizza’s quantity remains same that makes the joke work.
Core Connections Course 1 Student 1st Edition Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 Solutions Page 100 Problem 2 Answer
Given that a Giant one:
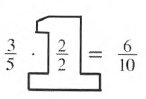
It is asked to find whether 3/5 is equivalent to 6/10 or not.
Now we will use the definition of equivalent fraction to solve given problem.
Yes, 3/5 is equivalent to 6/10.
We can check by factoring out the common factors.
6/10=3⋅2/5⋅2 =3/5.
Hence, it is correct.
Read and learn More Core Connections Course 1 Student 1st Edition Solutions
Thus, 3/5 is equivalent to 6/10 is correct.
Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 Portions And Integers Solutions Core Connections Course 1 Page 100 Problem 3 Answer
Given that a Giant one:
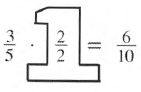
It is asked to find at least two other fractions or ratios that are equivalent to 3/5.
Now we will use the definition of equivalent fraction to solve given problem.
The two other fractions that are equivalent to 3/5 can be found by Giant one
3/5⋅3/3=9/15.
3/5⋅4/4=12/20.
Thus, 9/15,12/20 are two equivalent fraction of 3/5.
Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 Portions And Integers Solutions Core Connections Course 1 Page 100 Problem 4 Answer
Core Connections Course 1 Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 Step-By-Step Solutions Page 100 Problem 5 Answer
Given fraction is 9/8.
It is asked to find four equivalent fraction by using Giant One.
Now we will use the definition of Giant One to solve given problem.
We can choose any number for the Giant one.
The four fractions that are equivalent to 9/8 is:
9/8⋅2/2=18/16
9/8⋅3/3=27/24
9/8⋅4/4=36/32
9/8⋅5/5=45/40.
Thus, the four equivalent fractions of 9/8 are 18/16,27/24,36/32,45/40.
Core Connections Course 1 Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 Step-By-Step Solutions Page 100 Problem 6 Answer
Given giant one are:
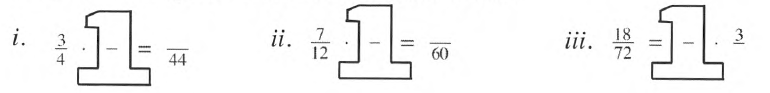
It is asked to find the missing numbers in the fractions of given giant One.
Now we will use the definition of giant one to solve given problem.
Given: 3/4⋅□/□=44.
Here we know the result’s denominator as 44.
Let the number in the giant one be n.
Now let us only solve the denominator.
4⋅n=44
n=44/4
n=11.
Now we got the giant number then the result will be
3/4⋅11/11=33/44.
Given: 7/12⋅□/□=−60.
Here we know the result’s denominator as 60.
Let the number in the giant one be n.
Now let us only solve the denominator
12⋅n=60
n=60/12
n=5.
Now we got the giant number then the result will be
7/12⋅5/5=35/60.
Given: 18/72=□/□⋅3−.
Here we know the result’s numerator as 18.
Let the number in the giant one be n.
Now let us only solve the numerator.
3⋅n=18
n=18/3
n=6.
Now we got the giant number then the result will be
18/72=6/6⋅3/12.
Thus, the complete giant one are: 3/4⋅11/11=33/44,
7/12⋅5/5=35/60,
18/72 =6/6⋅3/12.
Solutions For Core Connections Course 1 Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 Portions And Integers Page 100 Problem 7 Answer
Given Giant One are:
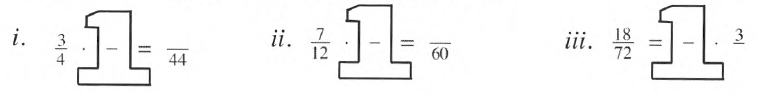
It is asked what computation could help that find the numbers to use in the Giant Ones.
From the part(a),we can say that multiplication will help to find the numbers to use in the Giant Ones.
Thus, multiplication will help to find the numbers to use in the Giant Ones.
Solutions For Core Connections Course 1 Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 Portions And Integers Page 101 Problem 8 Answer
Given giant one is:
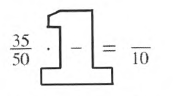
It is asked How is the giant one that you used here different from the ones that you found in problem 3−5.
Now we will find complete giant and compare it with the previous problem.
Given: 35/50⋅□/□=10.
Here we know the result’s denominator as10.
Let the number in the giant one be n.
Now let us only solve the denominator,
60⋅n=10
n=10/50
n=1/5.
Now we got the giant number then the result will be
35/50⋅1/5
1/5=7/10.
In the previous Problem, giant ones are: 3/4⋅11/11=33/44,
7/12⋅5/5=35/60,
18/72=6/6⋅3/12.
Now comparing both problem giant ones, we can say that the giant ones we got in the previous problems are whole numbers but here we got the fractions.
Thus, the giant ones we got in the previous problems are whole numbers but in this problem, we got the fractions.
Core Connections Course 1 Student 1st Edition Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 Guide Page 101 Problem 9 Answer
Given Giant One is:
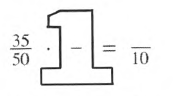
It is asked whether you can think of a different way to make sense of this problem or not.
Complete equivalent fraction with Giant One is: 35/50⋅1/5
1/5=7/10.
From above result, we can say that fractions will be confusing so let us make them to decimals which will be helpful.
Thus, we can use decimals in place of fractions to make it easy.
Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 Portions And Integers Explained Core Connections Course 1 Page 101 Problem 10 Answer
Given: 55/500
=5⋅11/5⋅100
=11/100.
It is asked to find giant one and two equivalent fraction in given problem.
Solution: Giant one is a fraction that is equal to 1.
Multiplying any fraction by a giant one will create a new fraction equivalent to the original fraction.
Here, the giant one is 5/5 and two equivalent fractions are 55/500 and 11/100.
Thus, in 55/500
=5⋅11/5⋅100
=11/100 the giant one is 5/5 and two equivalent fractions are 55/500 and 11/100.
Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 Portions And Integers Explained Core Connections Course 1 Page 101 Problem 11 Answer
Given that Tessa’s work is: 55/500=5⋅11/5⋅100=11/100.
It is asked whether Tessa’s work make sense or not and it is possible to expressed 11/100 in lowest terms, if it is, then how can you tell.
Yes, Tessa’s work make sense because it is in lowest term.
11/100 is the lowest terms.
As we can see, there are no common factors to cancel out the numerators and denominators.
Thus, Tessa’s work 55/500 =5⋅11/5⋅100=11/100 make sense and 11/100 is expressed in lowest term.
Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 Portions And Integers Explained Core Connections Course 1 Page 101 Problem 12 Answer
Given that Tessa’s another work: 28/60=2⋅14/2⋅30=14/30.
It is asked whether Tessa’s work is correct or not and also tell that her fraction expressed in lowest terms or not, if not then figure out the lowest terms for this fraction.
Simplifying a fraction is the process of rewriting it in lowest terms.
Now we will use this definition of lowest term of fraction to solve given problem.
Tessa’s work was wrong this time. As the results were not the lowest terms they still have the common factors to cancel out.
It can be further done.
14/30=2⋅7/2⋅15
=7/15.
Thus, Tessa’s work was wrong and the lowest term of fraction 28/30 is 7/15.
Worked Examples For Core Connections Course 1 Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 Portions And Integers Page 101 Problem 13 Answer
Given fractions are: 24/36,30/48,56/98.
It is asked to simplify given fractions and write them in lowest terms.
If we write a fraction in lowest terms, we use the smallest whole numbers possible to express the fraction.
Now we will use this rule to solve given problem.
Given: 24/36,30/48,56/98.
24/36=12⋅2/12⋅3 =2/3.
30/48=6⋅5/6⋅8 =5/8.
56/98=14⋅4/14⋅7 =4/7.
Thus, the given fraction’s simplified fraction in lowest term are: 24/36=2/3,30/48=5/8,56/98=4/7.
Worked Examples For Core Connections Course 1 Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 Portions And Integers Page 102 Problem 14 Answer
Given that Tessa’s work: 60/72=2⋅2⋅3⋅5/2⋅2⋅2⋅3⋅3 =12⋅5/12⋅6.
It is asked how did Tessa figure out that 12 is the greatest common factor of 60 and 72.
Solution: from the given Tessa’s work, we can say that first, she factored the number to the prime numbers then she calculated the common factors from two numbers which is the greatest common factor.
Thus, in 60/72=2⋅2⋅3⋅5/2⋅2⋅2⋅3⋅3
=12⋅5/12⋅6
Tessa figure out that 12 is the greatest common factor of 60 and 72 by factoring the numbers into the prime factor.
Worked Examples For Core Connections Course 1 Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 Portions And Integers Page 102 Problem 15 Answer
Given that Tessa’s work: 60/72 =2⋅2⋅3⋅5/2⋅2⋅2⋅3⋅3 =12⋅5/12⋅6.
It is asked how can factoring into prime factors help to find the greatest common factor of any two numbers.
While factoring a number into prime factors we can find the common factors between two numbers then we can multiply those common factors which will be the greatest common factor.
Thus, factoring a number into prime factors helps to find the greatest common factor of any two numbers by finding the common factors between two numbers.
Core Connections Course 1 Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 Detailed Answers Page 102 Problem 16 Answer
Given fraction are: 24/30,18/45,30/63.
It is asked to find to simplify given fractions in one step and state the greatest common factor.
Now we will simplifies these fraction by using factoring and find greatest common factor.
Given: 24/30,18/45,30/63.
24/30=6⋅4/6⋅5
Greatest common factor is 6.
=4/5.
18/45=9⋅2/9⋅5
Greatest common factor is 9.
=2/5.
30/63=3⋅10/3⋅21
Greatest common factor is 3.
=10/21.
Thus, simplified form of given fractions are: 24/30=4/5,
18/45=2/5,
30/63=10/21.
Core Connections Course 1 Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 Detailed Answers Page 102 Problem 17 Answer
Given that Andy and Bill found a quick way to figure out that 1/3⋅3/8=1/8.
it is asked to show how the Giant One can help to explain their shortcut, then use the Giant One to calculate 2/5⋅5/7 quickly.
Now we will use the definition of Giant One to solve given problem.
Andy and Bill found a quick way to figure out that 1/3⋅3/8=1/8.
Let us try to explain the shortcut.
LHS=1/3⋅3/8=1⋅3/3⋅8
=1⋅3/β⋅8
=1/8
=RHS
This shortcut mainly tells to cancel the greatest common factor when dividing two number.
2/5⋅5/7=2⋅5/5⋅7
=2/7.
Thus, the solution is: 2/5⋅5/7=2/7.
Core Connections Course 1 Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 Detailed Answers Page 102 Problem 18 Answer
Given product is: 1/2⋅3/5⋅2/3.
It is asked to use the Giant One to calculate given product quickly.
Now we will use the definition of Giant One to solve given problem.
Given: 1/2⋅3/5⋅2/3.
Now we will cancel out the common factor in denominator and numerator.
1/2⋅3/5⋅2/3
=1⋅3⋅2/2⋅5⋅3
=1/5.
Thus, the solution is: 1/2⋅3/5⋅2/3 = 1/5.
Core Connections Course 1 Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 Detailed Answers Page 102 Problem 19 Answer
Given that the product of two fraction is 1/7.
It is asked to find two fractions between 0 and 1 that have a product of 1/7.
Now we will take any arbitrary fraction then multiply them and check its result matched to 1/7 or not.
Let us consider two fractions between 0 and 1 as 1/5 and 5/7.
Now multiplying the two fractions will results in 1/7.
1/5⋅5/7
=1⋅5/5⋅7
=5⋅1/5⋅7
Using Giant One =1/7.
Hence, fractions are 1/5,5/7.
Thus, two fractions between 0 and 1 that have a product of 1/7 are: 1/5,5/7.
Core Connections Course 1 Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 Detailed Answers Page 102 Problem 20 Answer
Given that the product of two fraction is 3/4.
It is asked to find two fractions between 1/2 and 1 that have a product of 3/4.
Now we will take any arbitrary fraction then multiply them and check its result matched to 3/4 or not.
Let us consider two fractions between 1/2 and 1 as 9/10 and 10/12
Now multiplying the two fractions will results in 3/4.
9/10⋅10/12
=9⋅10/10⋅12
=3⋅3⋅10/10⋅3⋅4
=30⋅3/30⋅4
Using Giant One =3/4.
Hence, fractions are 9/10,10/12.
Thus, two fractions between 1/2 and 1 that have a product of 3/4 are: 9/10,10/12.
Core Connections Course 1 Student 1st Edition Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 Portions Answers Page 102 Problem 21 Answer
Given products are: 1/2⋅2/3,1/2⋅2/3⋅3/4,1/2⋅2/3⋅3/4⋅4/5.
It is asked to find the products for given fractions, then predict the next two problems in the sequence and find the products them.
Now we will multiply given fraction and using sequence of given fraction, we will find next two sequence of problem.
Given: 1/2⋅2/3,1/2⋅2/3⋅3/4,1/2⋅2/3⋅3/4⋅4/5.
1/2⋅2/3=2⋅1/2⋅3 =1/3.
1/2⋅2/3⋅3/4=6⋅1/6⋅4 =1/4.
1/2⋅2/3⋅3/4⋅4/5=24⋅1/24⋅5 =1/5.
The next two problems in the sequence are
1/2⋅2/3⋅3/4⋅4/5⋅5/6=120⋅1/120⋅6 =1/6.
1/2⋅2/3⋅3/4⋅4/5⋅5/6⋅6/7=720⋅1/720⋅7 1/7.
Thus, the solution is: 1/2⋅2/3=1/3,1/2⋅2/3⋅3/4=1/4,1/2⋅2/3⋅3/4⋅4/5=1/5,1/2⋅2/3⋅3/4⋅4/5⋅5/6
=1/6,1/2⋅2/3⋅3/4⋅4/5⋅5/6⋅6/7=1/7.
Core Connections Course 1 Student 1st Edition Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 Portions Answers Page 103 Problem 22 Answer
It is asked to explain about the giant one and its uses by taking example.
Now we will take a title “The Giant One and Equivalent Fractions” and explain about it by taking an arbitrary example.
Title: “The Giant One and Equivalent Fractions”
Giant one is used to minimize the fractions by factoring out the common factors and it also helps to make numerator or denominator equivalent to some number.
Let us consider an example:
15/20=5⋅3/5⋅4 =3/4.
Here, we got the simplest fraction
Thus, Giant one is used to minimize the fractions by factoring out the common factors and it also helps to make numerator or denominator equivalent to some number.
Core Connections Course 1 Student 1st Edition Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 Portions Answers Page 103 Problem 23 Answer
Given:
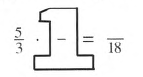
It is asked to complete the given Giant One.
Now we will use the definition of Giant One to solve given problem.
Given: 5/3⋅ GiantOne. = 18.
We should choose Giant one so that the denominator will be equal to 18.
So the Giant one is 1=6/6
Now5/3⋅6/6
=5⋅6/3⋅6
=30/18.
Thus, the solution is: 5/3⋅6/6=30/18.
Core Connections Course 1 Student 1st Edition Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 Portions Answers Page 103 Problem 24 Answer
Given giant one expression is:
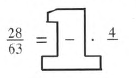
It is asked to complete the given giant one.
Now we will use the definition of giant one to solve given problem.
Given: 28/63=GiantOne⋅4−.
We should choose Giant one so that the numerator will be equal to 28.
So the Giant one is 1=7/7.
Now,28/63=7/7⋅4/9.
Thus, the solution is: 28/63=7/7⋅4/9.
Core Connections Course 1 Student 1st Edition Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 Solutions Page 103 Problem 25 Answer
Given:
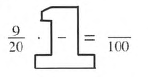
It is asked to complete the given Giant One.
Now we will use the definition of Giant One to solve given problem.
Given: 9/20⋅G.O=100.
We should choose Giant one so that the denominator will be equal to 100. So the Giant one is 1=5/5.
Now, 9/20⋅5/5
=9⋅5/20⋅5
=45/100.
Thus, the solution is: 45/100=9/20⋅5/5.
Core Connections Course 1 Student 1st Edition Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 Solutions Page 103 Problem 26 Answer
Given that Rachel says that she ran 115 yards and she went farther than Beth, who only ran 327 feet.
It is asked to explain whether Rachel is correct or not.
Now we will use unit conversion yard into feet (1yard=3feet) to solve given problem.
First let us convert the units of distance Rachel ran from yards to feet by multiplying 3 to it.
115⋅3=345 feet.
As the Beth ran 327 feet, Rachel was correct she ran farther than Beth.
Thus, Rachel was correct , she ran farther than Beth.
Core Connections Course 1 Student 1st Edition Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 Solutions Page 104 Problem 27 Answer
Given that the histogram which shows the heights of players on two basketball teams, the Tigers and the Panthers:
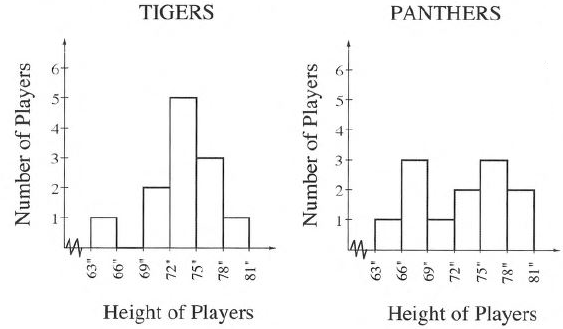
It is asked to explain which team has taller players and which has shorter players.
Now we will use the given histogram to solve given problem.
Let us consider the taller players as the heights from 72 to 81.
The number of players taller in Tigers is 5+3+1=9 player.
The number of players taller in Panthers is 2+3+2=7 player.
So, Tigers have taller players than Panthers.
Let us consider the shorter players as the heights from 63 to 72.
The number of players shorter in Tigers is 2+0+1=3 player.
The number of players shorter in Panthers is 1+3+1=5 player.
So, Panthers have Shorter players than Tigers.
Thus, Tigers have taller players than Panthers and Panthers have Shorter players than Tigers.
Core Connections Course 1 Student 1st Edition Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 Solutions Page 104 Problem 28 Answer
Given that the histogram which shows the heights of players on two basketball teams, the Tigers and the Panthers:
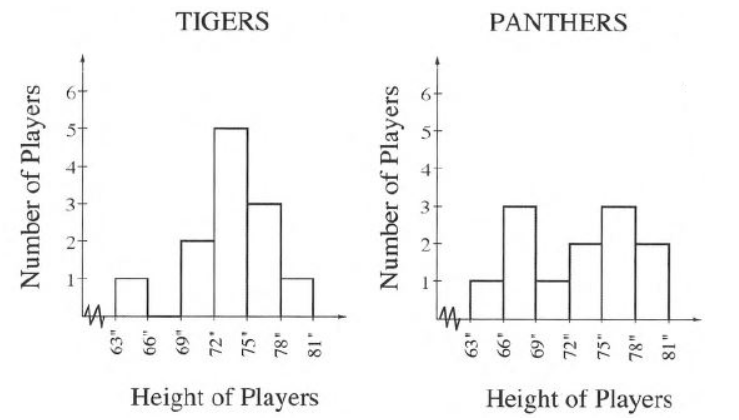
It is asked to explain which team has heights that vary more.Now we will use above histogram to solve given problem.
Given histogram is:
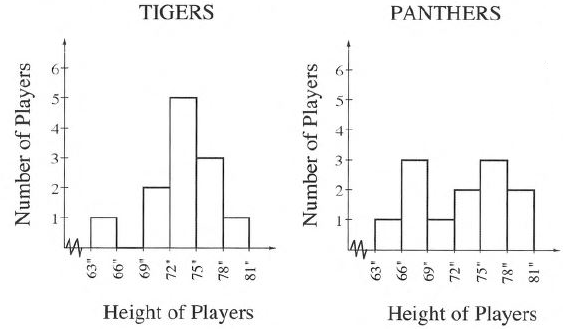
From the above histogram, the heights of Panther players are between 63−66,66−69,69−72,72−75,75−78,78,81.
It means, we can say that the height of Panther players is 6 different type.
The height of Tigers players are between 63−66,69−72,72−75,75−78,78−81.
It means the height of Tigers players is 5 different type.
So, the players of tigers height varies is less than that of Panthers.
Thus, Panther team has heights that vary more.
Core Connections Course 1 Student 1st Edition Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 Solutions Page 104 Problem 29 Answer
Given that the histogram which shows the heights of players on two basketball teams, the Tigers and the Panthers:
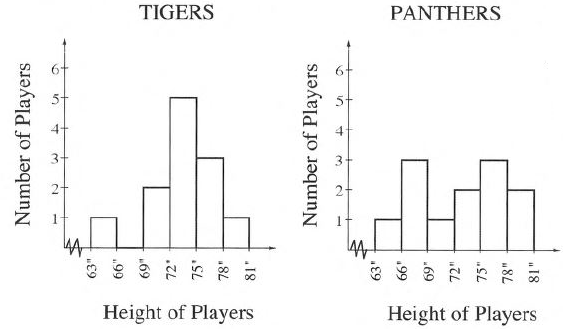
It is asked to explain which team has more players that are about the same height.
From the histogram graph, panthers have maximum players at 75 to 78 or 66 to 69 height are 3.
But Tiger have players at 72 to 75 height are 5.
So, Tigers have maximum players at same height.
Thus, Tigers have more players at same height.
Core Connections Course 1 Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 Step-By-Step Solutions Page 104 Problem 30 Answer
A triangle is given-
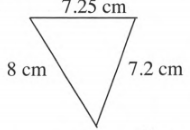
We have to find the perimeter of the given triangle.
Perimeter- The sum of the sides of the triangle is the perimeter of the triangle.
Perimeter =8+7.25+7.2
Perimeter=22.45cm
The perimeter of the given triangle is 22.45cm.
Core Connections Course 1 Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 Step-By-Step Solutions Page 104 Problem 31 Answer
Following diagram is given-
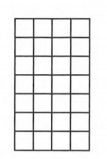
The length of the side of small square is of 1 unit.
We have to find the area of the given rectangle.
Area of the rectangle=l×b
Where l=length, b=breadth
The length of the large rectangle is l=4units
The breadth of the large rectangle is b=7units.
Area of the given rectangle=l×b=4×7 =28unit2
The area of the large rectangle is 28unit2.
Core Connections Course 1 Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 Step-By-Step Solutions Page 104 Problem 32 Answer
A rectangle is given-

Length of the rectangle l=8inches
Width of the rectangle b=2inches
We have to find the area and perimeter of the given rectangle.
Area of the rectangle=l×b
Perimeter of the rectangle=2×(l+b)
Area of the given rectangle=8×2=16inch2
Perimeter of the given rectangle=2×(8+2)=2×10=20inch
Area of the given rectangle is 16inch2
Perimeter of the given rectangle is 20 inch.
