Core Connections Course 1 Student 1st Edition Chapter 4 Variables and Ratios
Core Connections Course 1 Student 1st Edition Chapter 4 Exercise 4.1 Solutions Page 168 Problem 1 Answer
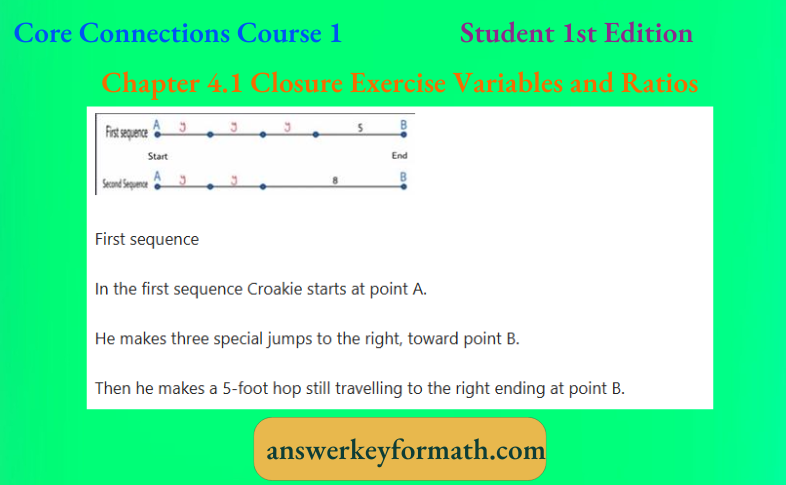
It is given that Croakie has a new special jump length. The distance between two fixed point is given by two sequences.
His trainer drew a diagram to represent his two sequences.
He used y to represent the length of Croakie’s new special jump.
Explain each of the sequence.
This can be done by counting the number of special jumps and the the length of hop for each sequence.
Let us assume Croakie moved between two points A and B. It is given that the length of Croakie’s new special jump is y.
Read and learn More Core Connections Course 1 Student 1st Edition Solutions
Second sequence
In the second sequence Croakie starts at point A.
He makes two special jumps to the right, towards point B.
Then he makes a 8-foot hop still travelling to the right ending at point B.
First sequence: In this Croakie makes his three special jumps and a 5-foot hop in between the starting and ending point.
Second sequence: In this Croakie makes his two special jumps and a 8-foot hop in between the starting and ending point.
Core Connections Course Chapter 4 Page 168 Problem 2 Answer
It is given that Croakie has a new special jump length.
The distance between two fixed point is given by two sequences.
His trainer drew a diagram to represent his two sequences.
He used y to represent the length of Croakie’s new special jump.
Determine the length of each special jump.
Equate both the sequence to determine the length of special jump.
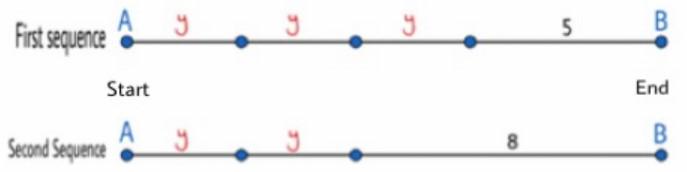
Since the two points are fixed the distance between the start and the end of his first and second sequence of jump is same.
Distance travelled in the first sequence=Distance travelled in second sequence
Three special jump +One 5-foot jump=Two special jump+one 8-foot jump
y+y+y+5=y+y+8
Solve the above relationship and find the value of the unknown y.
3y+5=2y+8
3y−2y=8−5
y=3
Therefore we have determined that Croakie travels 3 feet in each special jump.
Thus, Croakie travels 3-feet in each special jump.
Core Connections Course 1 Student 1st Edition Chapter 4 Exercise 4.1 Solutions Page 168 Problem 3 Answer
It is given that Croakie has a new special jump length.
The distance between two fixed point is given by two sequences.
His trainer drew a diagram to represent his two sequences.
He used y to represent the length of Croakie’s new special jump.
Determine length between starting and end point of sequence.
Substitute the value of each special jump in the expression of sequence.
To find the distance between starting and ending point of Croakie’s both sequence.
Substitute the value of the distance travelled by Croakie in each special jump in any of the equation to the total distance between the start and end of his sequence of jumps.
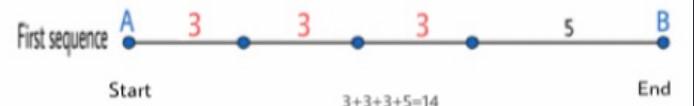
Distance travelled in the first sequence=Three special jump+One 5-foot jump
=y+y+y+5
Substitute y=3 feet in the above equation.
=3+3+3+5
=14
Therefore the distance between the start and end of his sequence of jumps is 14 feet.
The distance travelled between the start and end can be verified by using a diagram as shown below.

Thus, the distance between start and end of given sequence is 14 feet and the distance travelled between the start and end can be verified by using a diagram as shown below.
Core Connections Course Chapter 4 Page 168 Problem 4 Answer
Given the Croakie’s sequence having three special high hops is represented by an expression x+x+x+5 where x represents the distance he moves with each high hops.
Explain about the Croakie’s new sequence.
This can be done by counting the number of special high hops from the given expression of his sequence.
It is given that x represents the length of Croakie’s each high hop.
His new sequence can be described by understanding the expression of the whole sequence.
Let us assume that he moves to the right from the starting point to reach the end point.
Croakie starts at the starting point. He makes three special high hops to the right. Then he makes a 5-foot jump still travelling to reach the end point.
Thus, the Croakie’s new sequence is he makes three special high hops to the right. Then he makes a 5-foot jump still travelling to reach the end point.
Chapter 4 Exercise 4.1 Variables And Ratios Solutions Core Connections Course 1 Page 168 Problem 5 Answer
Given the Croakie’s sequence having three special high hops is represented by an expression x+x+x+5 where x represents the distance he moves with each high hops.
Draw a diagram to represent Croakie’s new sequence.
To do so assume a straight path as per the given data of Croakie’s high hop and one foot jump.
As Croakie’s new sequence is a total of 11 feet. The sum of all the jumps in the sequence or the total distance travelled is equal to 11 feet.
We can see in the following figure.
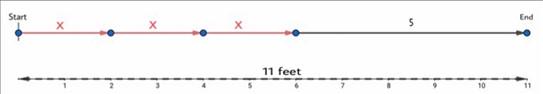
Thus, Croakie’s new sequence of total distance 11 feet is given by the figure shown below.
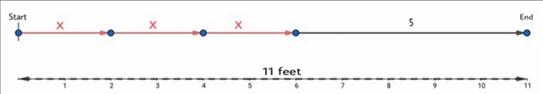
Core Connections Course Chapter 4 Page 168 Problem 6 Answer
Given the Croakie’s sequence having three special high hops is represented by an expression x+x+x+5 where x represents the distance he moves with each high hops.
Determine the length of each high hop.T
o do so solve the given expression of sequence as the given total length of sequence is 11 feet.
We can find the distance travelled by Croakie in each high hop by using the expression that represents the whole sequence.
Total distance travelled in the new sequence=Three high hops+One 5-foot jump.
=x+x+x+5
From part b that Croakie’s new sequence is a total of 11 feet.
Therefore,
x+x+x+5=11feet
3x+5=11
3x=11−5
x=6/3
x=2
It means he jumps of 2 feet with each high hop.
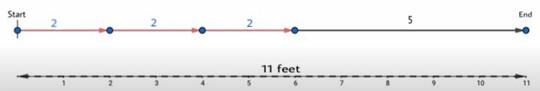
Thus, Croakie jumps a distance of 2 feet with each high hop.
Chapter 4 Exercise 4.1 Variables And Ratios Solutions Core Connections Course 1 Page 168 Problem 7 Answer
Given that Lanaya is a gymnast and is working on a new routine.
In her new routine she starts by walking 4 feet to the right.
Then she does one handspring, then a cartwheel, followed by a somersault, and then two more handsprings.
She travels the same distance for each handspring.
Draw the diagram of Lanaya’s routine and deterni the expression to represent how far Lanaya travels during her routine.
Add all the moves she made in her routine .
The diagram of Lanaya’s new routine is drawn by using the details given in the description.
For writing an expression to represent the total distance travelled by layana during her routine let us assume that she moved x feet during a handspring, y feet during a cartwheel, and z feet during the somersault.
Since, Lanaya is moving toward right we can add the length of all her movements together to know how far she travelled during her routine. Total distance traveled in the routine =
= Distance walked+ Distance moved during handspring + Distance moved during cartwheel + Distance moved during somersault +(2× Distance moved during handspring )
4ft+x+y+2+2x
We can combine like terms because it is given that Lanaya is very consistent and travels the same for each handspring.
=4+3x+y+z
Therefore an expression to represent how far Lanaya travels during her routine is given by4+3x+y+z.
Thus, the diagram of Lanaya’s routine is given by

And the expression representing how far she travels during her routine is given by 4+3x+y+z.

Core Connections Course Chapter 4 Page 168 Problem 8 Answer
Given that Lanaya is a gymnast and is working on a new routine.
In her new routine she starts by walking 4 feet to the right.
Then she does one handspring, then a cartwheel, followed by a somersault, and then two more handsprings.
She travels the same distance for each handspring.
Determine the distance she covers if she moves 6 feet during a handspring, 3 feet during a cartwheel, and 2 feet during a somersault.
Substitute the value of each move in the expression of distance traveled during her routine.
It is given that she moved 6 feet during a handspring, 3feet during a cartwheel, and 2feet during a somersault.
To find the total distance covered by Lanaya during her routine we need to substitute the value of the distance covered in each of her moves in the expression obtained in part a.
Total distance travelled in the routine
= Distance walked + Distance moved during handspring + Distance moved during cartwheel + Distance moved during somersault +(2× Distance moved during handspring )
=4ft+(3×6ft)+3ft+2ft
=4+18+5=27
Thus, Lanaya covers 27 feet during her routine.
Core Connections Course Chapter 4 Page 169 Problem 9 Answer
Given that Croakie reaches from point A to B by sliding 2ft towards right and then taking 2 flips.
And again go from point B to A by turning around, taking 1 flip and sliding 8ft.
It is asked to find distance travelled by Croakie in one somersault or flip.
We can find the length of each somersault by equating the total distance travelled to the right from point A to point B and the total distance travelled to the left from point B to point A.
Let the distance travelled in one flip be x ft.
The distance travelled from A to B=2+2x.
The distance travelled from B to A=x+8.
The distance between A and B is constant.
Therefore,2+2x=x+8
⇒2x−x=8−2
⇒x=6
So, the distance travelled by Croakie in one flip is 6ft.
Core Connections Course 1 Chapter 4 Exercise 4.1 Step-By-Step Solutions Page 169 Problem 10 Answer
Given: Croakie reaches from point A to B with 2ft slide and 2 flips.
And from B to A with 1 flip and 8ft slide.
To Find: The distance between points A and B.
Since distance from A to B is same as the distance from B to A,both the relations can be equated.
As found in part (a) that the distance AB was represented as 2+2x and x is the length of on flip and is equal to 6ft.
Hence, the distance is given as:AB=2+(2×6)
=2+12
=14ft
The distance between points A and B is 14ft.
Core Connections Course Chapter 4 Page 169 Problem 11 Answer
Given: Croakie is a frog, who can perform different tricks by moving through flips, slides, etc.
It is asked to make up a new trick and design two or more different sequences for Croakie that he can do with his new trick while performing routines that are the same length and also write the clues whatever is necessary for designing the routines of the frog.
For designing the different sequences, we must understand that Croakie has recently added a new trick to his routines, he wears a helmet and slides on his head which he calls ”brainy strainy”.
Croakie has designed following two new routines to mesmerize the audience:
Sequence 1:
- Croakie starts at point A. He hops 10 feet to the right, toward point B.
- Then he does two “brainy strainy” slides in a row, still traveling to the right.
- He turns and makes two hip hop jumps hop to the left.
- He stops to wave to the audience, still traveling to the left, repeats his 3 -foot hop three times.
- He turns and makes 11 spinning hops that are 1 foot each to the right, ending exactly at point B.
Sequence 2 :
- This time, he starts at point A, makes 2 somersaults to the right.
- Then he completes two flips in a row, landing at point B.
- From point B, he turns around and goes back by doing one flip and sliding 8 feet to the left.
- Then he performs three “brainy strainy” and finishes with a somersault in the same direction.
Therefore, the clues in designing the sequences lie in the fact that the length of the routine is the same in all sequences that is the total distance from point A to Point B is 14 feet which finally help in designing two different sequences of Croakie.
Sequence 1 is Croakie starts at point A and hops 10 feet towards the point Bto the right then does two “brainy strainy” slides in a row.
He turns and makes two hip hops jumps to the left.
He repeats 3-foot hop three times while waving towards the audience.
He turns to the right and makes 11 spinning hops that of 1 foot each and exactly ends at the point B.
Sequence 2 is Croakie starts at point A and to the right, makes two somersaults.
Then he lands at point B after completing the two flips in a row.
Then he turns around and goes back by flipping once and sliding 8 feet to the left.
In the same direction performs three “brainy strainy” and finishes with the somersault.
Core Connections Course 1 Chapter 4 Exercise 4.1 Step-By-Step Solutions Page 170 Problem 12 Answer
Given that Croakie’s one flip covers a distance of 6ft.
His new routine is 59ft long in which he makes 7 super jumps and then he hops 3ft to finish the routine.
It is asked to find the length of each super jump.
The distance covered in various steps is equated to the total distance covered.
Since, the distance of 59ft is covered in 7 super jumps and hopping of 3ft,
7 super jumps+3ft hops=59 ft
Therefore,7 super jumps=59−3 =56ft
Since 7 super jumps=56ft
A super jump=56/7 = 8ft
So, each super jump taken by Crockie is 8ft in distance.
Core Connections Course Chapter 4 Page 170 Problem 13 Answer
Given: Croakie’s one flip covers a distance of 6ft.
His new routine is 59ft long in which he makes 7 super jumps and then he hops 3ft to finish the routine.
To Find: The expression to represent Croakie’s routine.
The distance covered in various steps is equated to the total distance covered.
Let the length of each super jump be x.
Since, in 7 super jumps and hop of3ft, he covers a distance of59ft;
Hence,7x+3=59
The expression representing Croakie’s routine is given as:7x+3=59.
Solutions For Core Connections Course 1 Chapter 4 Exercise 4.1 Variables And Ratios Page 171 Problem 14 Answer
Given: Croakie’s one flip covers a distance of 6ft, and his one super jump covers a distance of 8ft.
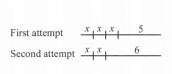
He took two attempts for his new routine as shown in the figure with x as the super-high jump, while covering the same distance in each attempt.
To Find: Length of each super-high jump.
The distance covered in various steps is in both the attempts equated, as the distance covered in both the cases is same.
Let, the super-high jump length be xft.
The two distances are represented as:
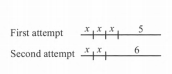
First attempt⇒x+x+x+5
⇒3x+5
Second attempt⇒x+x+6
⇒2x+6
Both these distances are equal.
Hence,3x+5=2x+6
⇒3x−2x=6−5
⇒x=1
The length of Crockie’s each super-high jump is1ft.
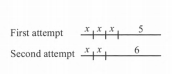
Core Connections Course Chapter 4 Page 171 Problem 15 Answer
Given: Croakie’s flip covers a distance of 6ft, his one super jump covers a distance of8ft, and his super-high jump coveres a distance of 1ft.
He took two attempts for his new routine as shown in the figure with x as the super-high jump, while covering the same distance in each attempt.
The distance covered in various steps is in both the attempts equated, as the distance covered in both the cases is same.
From part (a), the length of a super-high jump is 1ft and the whole super-high-jump routine was found to have a length described as3x+5.
Therefore, the length of the routine is calculated as 3(1)+5
=3+5
=8ft
The length of his whole super-high-jump routine is 8ft.
Core Connections Course 1 Student 1st Edition Chapter 4 Exercise 4.1 Guide Page 171 Problem 16 Answer
Given: The expression5+(−4)+12.65
To Find: The simplifies value for the given expression.
BODMAS rule is an acronym that is used to remember the order of operations to be followed while solving expressions in mathematics.
It stands for B – Brackets, O – Order of powers or roots, D – Division, M – Multiplication A – Addition, and S – Subtraction.
The simplification steps of the given expression using BODMAS are:5+(−4)+12.65
=5−4+12.65
=5+12.65−4
=17.65−4
=13.65
The expression5+(−4)+12.65=13.65
Core Connections Course Chapter 4 Page 171 Problem 17 Answer
Given: The expression6.5+(−2)+10.5
To Find: The simplifies value for the given expression.
BODMAS rule is an acronym that is used to remember the order of operations to be followed while solving expressions in mathematics.
It stands for B – Brackets, O – Order of powers or roots, D – Division, M – Multiplication A – Addition, and S – Subtraction.
The simplification steps of the given expression using BODMAS are:6.5+(−2)+10.5
=6.5−2+10.5
=6.5+10.5−2
=17−2
=15
The expression6.5+(−2)+10.5=15.
Chapter 4 Exercise 4.1 Variables And Ratios Explained Core Connections Course 1 Page 171 Problem 18 Answer
Given: The expression4(−5+100)
To Find: The simplifies value for the given expression.
BODMAS rule is an acronym that is used to remember the order of operations to be followed while solving expressions in mathematics.
It stands for B – Brackets, O – Order of powers or roots, D – Division, M – Multiplication A – Addition, and S – Subtraction.
The simplification steps of the given expression using BODMAS are:4(−5+100)
=4(−5)+4(100)
=−20+400
=380
The expression4(−5+100)=380.
Core Connections Course Chapter 4 Page 171 Problem 19 Answer
Given: The expression−212+(−102)
To Find: The simplifies value for the given expression.
BODMAS rule is an acronym that is used to remember the order of operations to be followed while solving expressions in mathematics.
It stands for B – Brackets, O – Order of powers or roots, D – Division, M – Multiplication A – Addition, and S – Subtraction.
The simplification steps of the given expression using BODMAS are:
−212+(−102)
=−212−102
=−314
Thus using BODMAS we get the answer of the expression−212+(−102)=−314.
Chapter 4 Exercise 4.1 Variables And Ratios Explained Core Connections Course 1 Page 171 Problem 20 Answer
Given: The expression4+6(3)+2(51/2−1)
To Find: The simplifies value for the given expression.
BODMAS rule is an acronym that is used to remember the order of operations to be followed while solving expressions in mathematics.
It stands for B – Brackets, O – Order of powers or roots, D – Division, M – Multiplication A – Addition, and S – Subtraction.
The simplification steps of the given expression using BODMAS are:4+6(3)+2(51/2−1)
=4+6×3+2(11/2−1)
=4+18+2×11/2−2×1
=22+11−2
=31
The expression4+6(3)+2(51/2−1)=31.
Core Connections Course Chapter 4 Page 171 Problem 21 Answer
Given: The expression5+3(5)−(4)(5)
To Find: The simplifies value for the given expression.
BODMAS rule is an acronym that is used to remember the order of operations to be followed while solving expressions in mathematics.
It stands for B – Brackets, O – Order of powers or roots, D – Division, M – Multiplication A – Addition, and S – Subtraction.
The simplification steps of the given expression using BODMAS are:5+3(5)−(4)(5)
=5+3×5−4×5
=5+15−20
=20−20
=0
The expression5+3(5)−(4)(5)=0.
Worked Examples For Core Connections Course 1 Chapter 4 Exercise 4.1 Variables And Ratios Page 171 Problem 22 Answer
Given: The expression 683÷4
To Find: The simplifies value for the given expression.
BODMAS rule is an acronym that is used to remember the order of operations to be followed while solving expressions in mathematics.
It stands for B – Brackets, O – Order of powers or roots, D – Division, M – Multiplication A – Addition, and S – Subtraction.
The simplification steps of the given expression are:
683÷4
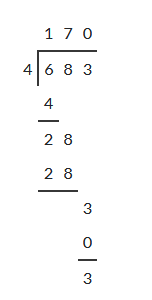
On further division, the expression equals170.75
The expression 683÷4=170.75
Core Connections Course Chapter 4 Page 171 Problem 23 Answer
Given: The expression 212÷9
To Find: The simplifies value for the given expression.
BODMAS rule is an acronym that is used to remember the order of operations to be followed while solving expressions in mathematics.
It stands for B – Brackets, O – Order of powers or roots, D – Division, M – Multiplication A – Addition, and S – Subtraction.
The simplification steps of the given expression are:
212÷9

On further division, the expression equals23.556
The expression 212÷9=23.556
Worked Examples For Core Connections Course 1 Chapter 4 Exercise 4.1 Variables And Ratios Page 171 Problem 24 Answer
Given: A decimal number0.007
To Find: The given decimal number as a fraction.
On removal of decimal, the fraction would have denominator as 1 with as many zeros as the number of figures after the decimal in the number.
The given number can be expressed as: 0.007=7/1000
The fraction form of the number 0.007 is 7/1000.
Core Connections Course Chapter 4 Page 171 Problem 25 Answer
Given: A decimal number 0.103
To Find: The given decimal number as a fraction.
On removal of decimal, the fraction would have denominator as 1 with as many zeros as the number of figures after the decimal in the number.
The given number can be expressed as:0.103=103/1000
The fraction form of the number 0.103 is 103/1000.
Core Connections Course 1 Chapter 4 Exercise 4.1 Detailed Answers Page 171 Problem 26 Answer
Given: A decimal number1.21
To Find: The given decimal number as a fraction.
On removal of decimal, the fraction would have denominator as 1 with as many zeros as the number of figures after the decimal in the number.
The given number can be expressed as: 1.21=121/100
The fraction form of the number1.21 is 121/100.
Core Connections Course Chapter 4 Page 171 Problem 27 Answer
Given: A fraction 505/1000
To Find: The value of the given fraction in decimal form.
With denominator as power of 10 the fraction will have as many number after the decimal as what the power of 10
- In case of numbers lesser than the power, extra place is filled with zero after the decimal.
The fraction can be expressed as:505/1000=505/103
=0.505
The decimal form of the number505
1000 is 0.505.
Core Connections Course 1 Chapter 4 Exercise 4.1 Detailed Answers Page 171 Problem 28 Answer
Given: A fraction 505/100
To Find: The value of the given fraction in decimal form.With denominator as power of10
the fraction will have as many number after the decimal as what the power of10
- In case of numbers lesser than the power, extra place is filled with zero after the decimal.
- Given: A fraction505/100
To Find: The value of the given fraction in decimal form.With denominator as power of10
the fraction will have as many number after the decimal as what the power of10
- In case of numbers lesser than the power, extra place is filled with zero after the decimal.
The fraction can be expressed as:505
100=505/102
=5.05
The decimal form of the number 505/100 is 5.05.
Core Connections Course Chapter 4 Page 171 Problem 29 Answer
Given: A fraction of 2/100000
To Find: The value of the given fraction in decimal form.With denominator as power of10
the fraction will have as many number after the decimal as what the power of10
- In case of numbers lesser than the power, extra place is filled with zero after the decimal.
The fraction can be expressed as:2/100000=2/105
=0.00002
The decimal form of the number 2/100000 is 0.00002.
