Differential Equations of First Order and First Degree Solved Example Problems Exercise 2.1
Example. 1: Solve \(x d y-y d x=x y^2 d x\)
Solution.
Given equation is \(x d y-y d x=x y^2 d x\)
Dividing (1) by \(\frac{x d y-y d x}{y^2}=x d x \Rightarrow x d x+\frac{y d x-x d y}{y^2}=0 \Rightarrow x d x+d(x / y)=0\)
Integrating : \(\frac{x^2}{2}+\frac{x}{y}=c\)
∴ The general solution (1) is \(\left(x^2 / 2\right)+(x / y)=c\)
Differential Equations Of First Order And First Degree Explained
Example. 2: Solve (1 + xy)x dy + (1 – yx)y dx = 0
Solution.
Given equation is (1 + xy)x dy + (1 -yx)y dx = 0 ……………………..(1)
⇒ x dy + y dx + (x dy – y dx) xy = 0 ……………………..(2)
Multiplying(2)with \(\frac{1}{x^2 y^2} \Rightarrow \frac{x d y+y d x}{x^2 y^2}+\frac{x d y-y d x}{x y}=0\)
⇒ \(\frac{d(x y)}{x^2 y^2}+\frac{1}{y} d y-\frac{1}{x} d x=0\)
Integrating : \(\int \frac{d(x y)}{x^2 y^2}+\int \frac{1}{y} d y-\int \frac{1}{x} d x=c \Rightarrow-\frac{1}{x y}+\log |y|-\log |x|=c\)
∴ The general solution of (1) is xy log(y/x) -1 = c xy.
Example. 3: Solve \(x d x+y d y+\frac{x d y-y d x}{x^2+y^2}=0\)
Solution:
Given equation is \(x d x+y d y+\frac{x d y-y d x}{x^2+y^2}=0\)
⇒ \(x d x+y d y+\frac{(x d y-y d x) / x^2}{1+\left(y^2 / x^2\right)}=0\)
⇒ x d x+y d y+\(\frac{d(y / x)}{1+(y / x)^2}=0 \Rightarrow d\left(\frac{x^2+y^2}{2}\right)+\frac{d(y / x)}{1+(y / x)^2}=0\)
Integrating, we get: \(\frac{x^2+y^2}{2}+\text{Tan}^{-1}\left(\frac{y}{x}\right)=c\)
∴ The general solution of (1) is \(\left(x^2+\dot{y}^2\right)+2 \text{Tan}^{-1}(y / x)=2 c\)
Methods To Find Integrating Factors In First-Order Equations
Example. 4. Solve ydx – xdy + logx dx = 00
Solution.
Given ydx – xdy + log x dx – 0 => log x dx – (xdy – ydx) = 0
Multiplying with \(\frac{1}{x^2} \Rightarrow \frac{1}{x^2} \log x d x-\frac{(x d y-y d x)}{x^2}=0 \Rightarrow \frac{1}{x^2} \log x d x-d\left(\frac{y}{x}\right)=0\)
Integrating: \(\int \frac{1}{x^2} \log x d x-\int d\left(\frac{y}{x}\right)=c \Rightarrow-\frac{1}{x} \log x-\int\left(-\frac{1}{x}\right) \cdot \frac{1}{x} d x-\frac{y}{x}=c\)
∴ The G.S. of (1) is \(c x+y+(1+\log x)=0\)
Example. 5. Solve \(x d y=\left[y+x \cos ^2(y / x)\right] d x\)
Solution.
Given equation is \(x d y=y d x+x \cos ^2(y / x) d x\) ……………………..(1)
⇒ \(x d y-y d x=x \cos ^2(y / x) d x\)
Dividing with \(x^2: \Rightarrow \frac{x d y-y d x}{x^2}=\frac{1}{x} \cos ^2\left(\frac{y}{x}\right) d x \Rightarrow \sec ^2 \frac{y}{x} \cdot \frac{x d y-y d x}{x^2}=\frac{1}{x} d x\)
⇒ \(\sec ^2\left(\frac{y}{x}\right) \cdot d\left(\frac{y}{x}\right)=\frac{1}{x} d x\)
Integrating : \(\int \sec ^2(y / x) \cdot d(y / x)=\int(1 / x) d x+c \Rightarrow \tan (y / x)=\log |x|+c\)
∴ The general solution of (1) is tan( y / x) = log|x| + c
Solved Example Problems For Exercise 2.1 In Differential Equations
Example. 6. Solve \(\left(x^2+y^2+x\right) d x-\left(2 x^2+2 y^2-y\right) d y=0\)
Solution.
Given \(\left(x^2+y^2\right) d x+x d x-2\left(x^2+y^2\right) d y+y d y=0\) ……………………(1)
Rearranging (1) : \(\left(x^2+y^2\right)(d x-2 d y)+x d x+y d y=0\)
⇒ \(d x-2 d y+\frac{x d x+y d y}{x^2+y^2}=0 \Rightarrow 2 d x-4 d y+\frac{2 x d x+2 y d y}{x^2+y^2}=0\)
⇒ \(2 d x-4 d y+d \log \left(x^2+y^2\right)=0\)
⇒ \(2 \int d x-4 \int d y+\int d \log \left(x^2+y^2\right)=c \Rightarrow 2 x-4 y+\log \left(x^2+y^2\right)=c\)
∴ The general solution of (1) is \(2 x-4 y+\log \left(x^2+y^2\right)=c\)
Example. 7. Solve \(\left(x^2+y^2-2 y\right) d y=2 x d x\)
Solution.
Given equation is
⇒ \(\left(x^2+y^2\right) d y=d\left(x^2+y^2\right) \Rightarrow d y=\frac{d\left(x^2+y^2\right)}{x^2+y^2} \Rightarrow \int d y=\int \frac{d\left(x^2+y^2\right)}{x^2+y^2}+c\)
∴ The general solution of (1) is \(y=\log \left(x^2+y^2\right)+c\)
Solutions For Exercise 2.1 First-Order Homogeneous Equations
Example. 8. Solve \(y d x-x d y+\left(1+x^2\right) d x+x^2 \sin y d y=0\)
Solution.
Given \((y d x-x d y)+\left(1+x^2\right) d x+x^2 \sin y d y=0\)
Dividing (1) by \(x^2 \Rightarrow \frac{y d x-x d y}{x^2}+\left(\frac{1}{x^2}+1\right) d x+\sin y d y=0\)
⇒ \(-\frac{x d y-y d x}{x^2}+\left(\frac{1}{x^2}+1\right) d x+\sin y d y=0 \Rightarrow-d(y / x)+\left(\frac{1}{x^2}+1\right) d x+\sin y d y=0\)
⇒ \(-\int d\left(\frac{y}{x}\right)+\int\left(\frac{1}{x^2}+1\right) d x+\int \sin y d y=c \Rightarrow-\left(\frac{y}{x}\right)-\left(\frac{1}{x}\right)+x-\cos y=c\)
∴ The general solution of (1) is \(x^2-y-1-x \cos y=c x\)
Homogeneous Differential Equations Exercise 2.1 Step-By-Step Solutions
Example. 9. Solve \(y\left(2 x^2 y+e^x\right) d x-\left(e^x+y^3\right) d y=0\)
Solution.
Given \(y\left(2 x^2 y+e^x\right) d x-\left(e^x+y^3\right) d y=0 \Rightarrow 2 x^2 y^2 d x+y e^x d x-e^x d y-y^3 d y=0\) ………………(1)
Dividing by \(y^2 \Rightarrow 2 x^2 d x+\left(\frac{y e^x d x-e^x d y}{y^2}\right)-y d y=0 \Rightarrow 2 x^2 \cdot d x+d\left(\frac{e^x}{y}\right)-y d y=0\)
Integrating : \(2 \int x^2 d x+\int d\left(\frac{e^x}{y}\right)-\int y d y=c \Rightarrow \frac{2 x^3}{3}+\frac{e^x}{y}-\frac{y^2}{2}=c\)
∴ The general solution of (1) is \(\frac{2 x^3}{3}+\frac{e^x}{y}-\frac{y^2}{2}=c\)
Example. 10. Solve \(\left(y-x y^2\right) d x-\left(x+x^2 y\right) d y=0\)
Solution.
Given \(\left(y-x y^2\right) d x-\left(x+x^2 y\right) d y=0 \ldots .(1) \Rightarrow(y d x-x d y)-x y(y d x+x d y)=0\)………………….. (2)
Dividing(2) by \(x y \Rightarrow\left(\frac{d x}{x}-\frac{d y}{y}\right)-(y d x+x d y)=0 \Rightarrow \frac{d x}{x}-\frac{d y}{y}-d(x y)=0\)
⇒ \(\int \frac{d x}{x}-\int \frac{d y}{y}-\int d(x y)=c \Rightarrow \log x-\log y-x y=c\)
∴ The general solution of (1) is \(\log (x / y)-x y=c\)
Methods For Solving Exercise 2.1 Differential Equations
Example. 11. Solve \(x d y-y d x=a\left(x^2+y^2\right) d y\)
Solution:
Given x dy-y dx = \(a\left(x^2+y^2\right) d y\)…….(1)
(1) can be written as \(\frac{x d y-y d x}{x^2+y^2}=a d y\)
⇒ \(d\left(\text{Tan}^{-1} \frac{y}{x}\right)=a d y\)
⇒ \(\int d\left(\text{Tan}^{-1} \frac{y}{x}\right)=a \int d y+c\)
⇒ \(\text{Tan}^{-1}(y / x)=a y+c\) is the general solution of (1).
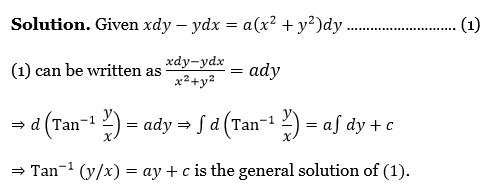
Examples Of Integrating Factors In Homogeneous Equations Exercise 2.1
Example. 12. Solve \(y d x-x d y=3 x^2 e^{x^3} y^2 d x\)
Solution.
Given equation is\(y d x-x d y=3 x^2 e^{x^3} y^2 d x\) …………………….(1)
⇒ \(\frac{y d x-x d y}{y^2}=3 x^2 e^{x^3} d x \Rightarrow d\left(\frac{x}{y}\right)=3 x^2 e^{x^3} d x \Rightarrow \int d(x / y)=\int 3 x^2 e^{x^3} d x+c\)
∴ The general solution of (1) is \(x=y e^{x^3}+c y\)
