Geometry Homework Practice Workbook 1st Edition Chapter 1 Points Lines and Planes
Geometry Homework Practice Workbook 1st Edition Chapter 1 Exercise 1.5 Solution Page 9 Problem 1 Answer
The given diagram is,
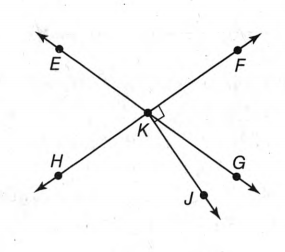
In this figure, You can use the corner of a piece of paper to see that ∠EKF and ∠GKH are each larger than a right angle.
Therefore, ∠EKF and ∠GKH are two obtuse vertical angles.
Page 9 Problem 2 Answer
The given diagram is,
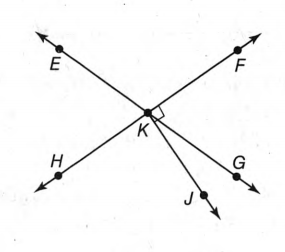
In the figure, the angles “∠EKF & ∠FKG”, “∠FKG & ∠GKH”, “∠GKH & ∠HKE”, and “∠HKE & ∠EKF” are adjacent to each other after the intersection of the two lines and The sum of angles of a linear pair is always equal to 180°.
Read and Learn More Geometry, Homework Practice Workbook 1st Edition Solutions
Therefore, the linear pair are “∠EKF & ∠FKG”, “∠FKG & ∠GKH”, “∠GKH & ∠HKE”, and “∠HKE & ∠EKF”.
Solutions For Points, Lines, and Planes Exercise 1.5 Page 9 Problem 3 Answer
The given diagram is,
Page 9 Problem 4 Answer
The given diagram is,
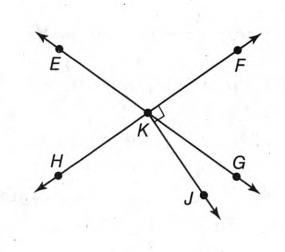
In the figure, the sum of the angles ∠FKG & ∠GKH form a straight angle.Again, the sum of the angles ∠FKG & ∠FKE forms a straight angle.
Therefore, the supplementary angles of ∠FKG are ∠GKH and ∠FKE.
Geometry Homework Practice Workbook Chapter 1 Page 9 Problem 5 Answer
Let the measures of an angle is x°. Then the other measure of angle which is complement to x°, is(x−24)°. [∵ one angle measures 24 degrees more than the other]So, (x)°+(x+24)°=90°
Or, 2x° +24=90°
Or, 2x°=90°−24°=66°
Or, x°=66°/2=33°
Therefore, the measure of an angle is 33° and its complement if one angle measures 24 degrees more than the other is (90−33)°=57°.
Geometry Workbook 1st Edition Exercise 1.5 Solutions Page 9 Problem 6 Answer
Let the measures of an angle is x°.
Then the other measure of angle which is a supplement to x°, is(x−36)°.[∵the supplement of an angle is 36 less than the measure of the angle.]
So, (x°)+(x−36)°=180°
Or, 2x°−36°=180°
Or, 2x°=180°+36°=216°
Or, x°=216/2°=108°
Therefore, the measure of an angle is108° and its supplement of an angle is 36 less than the measure of the angle is (108°−36°)=72°.
Geometry Homework Practice Workbook Chapter 1 Page 9 Problem 7 Answer
The given diagram is,
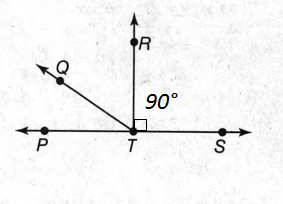
In the figure, TR⃗⊥TS⃗,
Then the angle between TR⃗&TS⃗=m∠RTS=90°.
So, by the problem, 8x+18=90°
Or, 8x=90°−18°=72°
Or, x=72/8=9.
Therefore, the value of x is 9.
Page 9 Problem 8 Answer
The given diagram is,
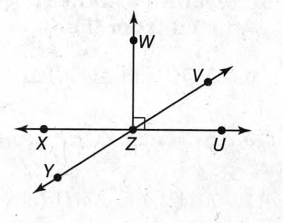
In the figure, it is clear that the angle ∠WZU forms an angle 90°, that means right angle.
Yes, ∠WZU is a right angle.
Points, Lines, And Planes Solutions Chapter 1 Exercise 1.5 Geometry Workbook Page 9 Problem 9 Answer
The given diagram is,
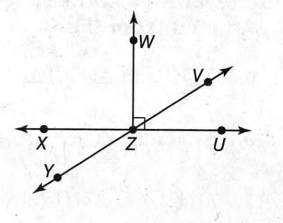
In the figure, it is clear that∠YZU &∠UZV forms a straight angle when they are put together.
That means∠YZV=180°.
Yes, ∠YUZ & ∠UZV are supplementary.
Page 10 Problem 10 Answer
The given diagram is,
In the picture, ∠GFH & ∠CFE angles that are both vertical and obtuse, which means both angles are less than a right angle but less than a straight angle and both angles are lying on opposite sides of two intersecting lines.
Therefore, two obtuse vertical angles are ∠GFH & ∠CFE.
Geometry Homework Practice Workbook Chapter 1 Page 10 Problem 11 Answer
The given diagram is,
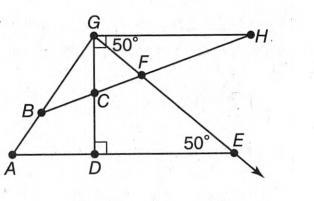
In the figure, there are only two angles with vertex B that is ∠ABC & ∠GBC And we can see that, ∠ABC +∠GBC=180°, So these are the linear pair with vertex B.
Therefore, ∠ABC & ∠GBC is a linear pair with vertex B.
Step-By-Step Solutions For Geometry Homework Practice Workbook Chapter 1 Exercise 1.5 Page 10 Problem 12 Answer
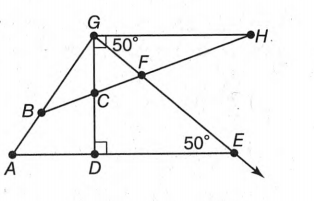
The given diagram is,
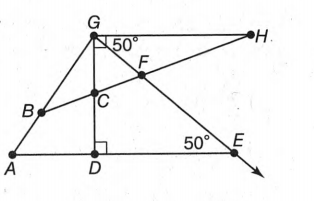
In the figure, the angle ∠FED=50° and ∠FGH=50°.Then, ∠CGF=90°−50°=40°[∵∠CGH=90°].
∠FED is not an adjacent point to∠FGC because there is no common vertex, But complementary to ∠FGC Because ∠FGC+∠FED=50°+40°=90°.
Therefore, ∠FED is not adjacent to, but complementary to ∠FGC.
Geometry Homework Practice Workbook Chapter 1 Page 10 Problem 13 Answer
We need to find an angle adjacent and supplementary to∠DCB.
This can be found by using the definition of adjacent angles and supplementary angles
A figure is given
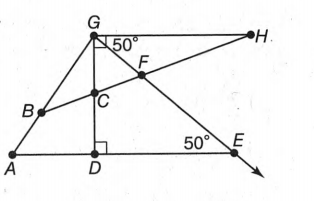
We know that the angles on a straight line add up to180o.
∠DCB and∠DCF lie on the straight line BCF.
Hence, ∠DCB+∠DCF=180o
∠DCB and∠DCF also lie beside each other.
Hence, ∠DCF is the angle adjacent and supplementary to∠DCB.
∠DCF is an angle adjacent and supplementary to∠DCB.
Geometry Chapter 1 Exercise 1.5 Free Solutions Page 10 Problem 14 Answer
We are given two angles that are complementary.
It is also given that the measure of one angle is 21 more than twice the measure of the other angle.
We need to find the measures of these angles.
Consider the required angles as variables and construct a mathematical equation with the definition of complementary angles.
Let,x and y be the values of the two angles.
It is given that the measure of one angle is 21 more than twice the measure of the other angle.
Hence, we get,
y=21+2x……………………(1)
We know that complementary angles add up to 90o.
It is given that x and y are complementary to each other.
Therefore,
x+y=90o
⇒ x+(21+2x)=90o
[From (1), y=21+x]
⇒ x+21+2x=90o
⇒ 21+3x=90o
⇒ 3x=69
⇒ x=69/3
⇒ x=23
From (1), y=21+2x
⇒ y=21+2(23)
⇒ y=67
The measurements of the required angles are 34.5o and 55.5o.
Geometry Homework Practice Workbook Chapter 1 Page 10 Problem 15 Answer
It is given that the supplement of an angle has a measure78 less than the measure of the angle.
We need to find the measure of the angle.
This can be found by considering the required angles as variables and constructing a mathematical equation with the definition of supplementary angles.
Let,x and y be the values of two angles.
It is given that the supplement of an angle has a measure78 less than the measure of the angle.
Hence, y=x−78………….(1)
The two angles are a supplement to each other.
Therefore,
x+y=180o
⇒ x+(x−78)=180
[From (1), y=x−78]
⇒ x+x−78=180
⇒ 2x−78=180
⇒ 2x=258
⇒ x=258/2
⇒ x=129
From (1), y=x−78
⇒ y=129−78
⇒ y=51
The measures of the required angles are 129o and 51o.
Geometry Homework Practice Workbook Exercise 1.5 Student Solutions Page 10 Problem 16 Answer
It is also given that m∠BGC=16x−4 and m∠CGD=2x+13.
We need to find the value of x, so that∠BGD is a right angle.
This can be found by adding up the given angle expressions to 90o.
A figure is given
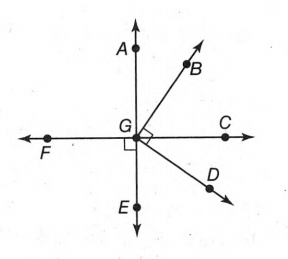
From the given figure, we can say that ∠BGC+∠CGD=∠BGD
m∠BGC=16x−4,m∠CGD=2x+13
It is said that∠BGD is a right angle which is equal to 90o.
Hence, m∠BGC+m∠CGD=90o
⇒(16x−4)+(2x+13)=90
⇒16x−4+2x+13=90
⇒18x+9=90
⇒18x=81
⇒ x=81/18
⇒ x=4.5
The value of x so that∠BGD is a right angle is 2.4.
Points, Lines, And Planes Exercise 1.5 Geometry Workbook Answers Page 10 Problem 17 Answer
A figure is given,
We need to explain the correctness of the given statement.
This can be explained based on the statement that two angles are said to be complementary when they add up to 90o.
We see in the figure that ∠NQP is a right angle, i.e, ∠NQP=90o…………………(1)
We see that ∠NQP is made up of two angles, namely ∠NQO and ∠OQP, i.e, ∠NQP=∠NQO+∠OQP………………..(2)
From (1) and (2), we get,∠NQO+∠OQP=90o
Hence, these two angles are complimentary as they add up to give 90o.
The given statement can be assumed from the figure given.
Page 10 Problem 18 Answer
A figure is given,
We need to explain the correctness of the given statement.
This can be explained with the help of the statement that vertical angles refer to each of the pairs of opposite angles made by two intersecting lines.
We see that the lines NR and MP intersect each other at point Q.
The angles ∠MQN,∠MQR lie on the line NR.
Hence, ∠MQN+∠MQR=180o and they are a pair of opposite angles.
Therefore, these two angles are vertical angles
∠MQN and∠MQR are vertical angles.
Geometry Homework Practice Workbook Chapter 1 Page 10 Problem 19 Answer
It is given that Darren sketched a map of the cross streets nearest to his home for his friend Miguel.
We need to describe two different angle relationships between the streets.
This can be found by using the angle definitions and the fact that the angles on a straight line add up to 180o.
A figure is given
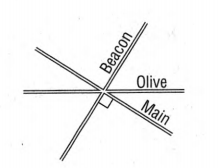
We see that Olive and Main add up to give 90o.
We see that Bacon and Main are perpendicular to each other.
The two different angle relationships between the streets are
Olive and Main are complementary and
Bacon and Main are perpendicular to each other.
