Geometry Homework Practice Workbook 1st Edition Chapter 1 Points Lines and Planes
Geometry Homework Practice Workbook 1st Edition Chapter 1 Exercise 1.7 Solution Page 13 Problem 1 Answer
The given shape is
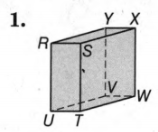
We must determine the figure and which category it belongs to.
If all the sides are straight line then the figure is stated to be polyhedron.
The given figure is
Clearly, we can observe that the figure is a cuboid which is nothing but a three-dimensional projection of a rectangle.
As a result, the shape is a polyhedron in nature.
The following bases, edges, and vertices are as follows:
1 Vertex-
2 Edges-
Read and Learn More Geometry, Homework Practice Workbook 1st Edition Solutions
The shape is proved as polyhedron and it is identified as cuboid with :
1 Vertex- U, T, S, R, Y, X, W, V.
2 Edges-UT, TS, SR, RU, SX, XY, YR, YV, VW, WX, WT, VU.
Solutions For Points, Lines, And Planes Exercise 1.7 Page 13 Problem 2 Answer
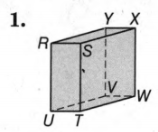
The given shape is
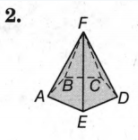
We must determine the figure and which category it belongs to.
If all the sides are straight line then the figure is stated to be polyhedrons.
The given figure is

Geometry Homework Practice Workbook Chapter 1 Page 13 Problem 3 Answer
The given figure is
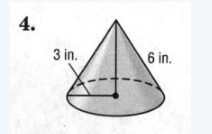
We must find the slant height and radius in order to find the surface area.
After we find the slant height, we can calculate the surface area.
Given, l=6;r=3
Therefore,s=πr(l+r)
⇒ s=3.14×3×9
⇒ s=84.78 inches
The surface area is found to be 84.78≈84.8inches
Page 13 Problem 4 Answer
The given figure is
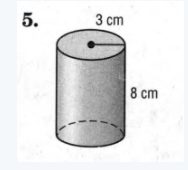
We must find the height and radius in order to find the surface area.
After we find the height and radius, we can calculate the surface area.
Given,r=3;h=8
Therefore,s=2πr(h+r)
⇒ s=2×3.14×3×11
⇒ s=207.24
The surface area is found to be 207.24≈and 207.2cm.
Geometry Workbook 1st Edition Exercise 1.7 Solutions Page 13 Problem 5 Answer
The given figure is
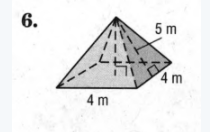
We must find the slant height and radius in order to find the surface area.
After we find the slant height, we can calculate the surface area.
Given, b = 4; h = 5
∴ s = b(b+4h)
⇒ s=4(4+20)
⇒ s=4×24
⇒ s=96m
The surface area is found to be 96m.
Points, Lines, And Planes Solutions Chapter 1 Exercise 1.7 Geometry Workbook Page 13 Problem 6 Answer
Given
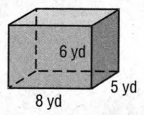
To find the volume of the solid.
The given solid is a cuboid and its volume is calculated by the formula Length(l)×Width(w)×Height(h).
Length(l) = 8yd.
Width(w) = 5yd.
Height(h) = 6yd.
The volume of the cuboid is Length(l) × Width(w) × Height(h) = 8 × 5 × 6= 240yd .
Hence we can conclude that the volume of the cuboid is 240y d3.
Step-By-Step Solutions for Geometry Homework Practice Workbook Chapter 1 Exercise 1.7 Page 13 Problem 7 Answer
Given
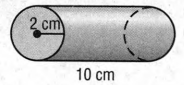
To find the volume of the solid.
The given diagram is of a cylinder and its volume is calculated by the formula V=Π×r2×h.
(where are the radius and height of the cylinder respectively)
Radius(r) = 2cm.
Height(h) = 10 cm.
The volume of the cylinder is Π × r × h = Π × 2 × 10 2 2
= 3.14 × 40
= 125.6cm.
Hence we can conclude that the volume of the cylinder is 125.6 cm2.
Page 14 Problem 8 Answer
Given
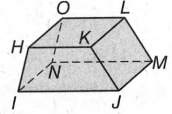
To determine whether the solid is a polyhedron.
Then identify the solid.
This solid is a trapezoid.
A polyhedron is a 3D shape that has flat faces, straight edges, and sharp vertices or corners.
The trapezoid has flat faces, straight edges, and sharp vertices; hence it is a polyhedron.
There are 8 vertices of the trapezoid and they are H,I,J,K,L,M,N,O.
There are 6 faces of the trapezoid and they are KLOH,JMNI,JKHI,MLON,ONIH,JKLM.
There are 12 edges of the trapezoid and they are, JK, KH, HI, OH, NI, KL, JM, LO, LM, MN, NO.
Hence we can conclude that the given solid is a polyhedron. The polyhedron is a trapezoid.
Geometry Chapter 1 Exercise 1.7 Free Solutions Page 14 Problem 9 Answer
Given
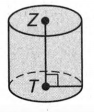
To determine whether the solid is a polyhedron.
Then identify the solid.
This solid is a cylinder.
A polyhedron is a 3D shape that has flat faces, straight edges, and sharp vertices or corners.
A cylinder has a curved surface hence it is not a polyhedron.
Hence we can finally conclude that the given solid is not a polyhedron. The given solid is a cylinder.
Geometry Homework Practice Workbook Chapter 1 Page 14 Problem 10 Answer
Here given a cone that is
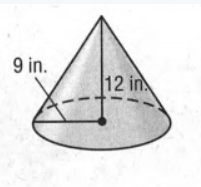
From the given solid we have to calculate the surface area and volume of this cone.
To calculate the Surface Area we will use the formula of surface area that is Surface Area=πrl+πr2 and to calculate the Volume the formula is Volume=1/3πr2h wherer=radius,l=Slant Height,h=height.
Given that from the above cone of the diagram, we can say radius(r)=9in.
And height(h)=12in.
So, we have to calculate the slant height of the cone by using the Pythagoras theorem
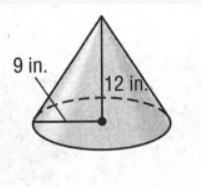
Slant Height(l)=√r2+h2
=√92+122in.
=√81+144in.
=√225in.
=15in.
Now to calculate the surface area of the cone we will replace the value of the radius, height, and slant height in the formula that is Surface Area=πrl+πr2.
So, Surface Area=(π×9×15+π×92)in2.
=216 πin2
=678.58 in2
And the volume of the cone will be Volume=1/3πr2h. Replacing the value of radius and height we will get
Volume=(1/3×π×92×12)in3.
=1017.876in3.
Hence, the surface area of the cone is 678.58 in 2 and the volume of the cone is 1017.876 in 3.
Geometry Homework Practice Workbook Exercise 1.7 Student Solutions Page 14 Problem 11 Answer
Given that,
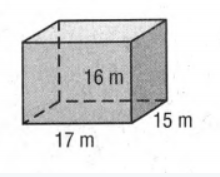
Here the given solid is a cube and we have to calculate the Surface Area and Volume of the cuboid solid.
To calculate the Surface Area and Volume at first, we will calculate the perimeter of any side of the cube here the formula is Perimeter=2×(length+breadth) and the area of any side of the cube is Base = length × breadth Now the formula of Surface Area is Surface Area=Perimeter×height+2×Base and the formula of volume that is Volume=Base×Height.
Here given a cuboid-shaped solid
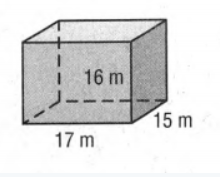
Now if we take a closer look at the diagram we can say that length=17m,breadth=15m,height=16m.
So if we replace the value of length and breadth in the formula that is Perimeter=2×(length+breadth) to calculate the perimeter of one side of the cube we will get
Perimeter=2×(17+15)m
=64m
And to calculate the area of one side the formula isBase=length×breadth
Base=(17×15)m2
=255m2
Now the perimeter base and height will be replaced by their value in the formula of Surface Area=Perimeter×height+2×Base
Surface Area=(64×16+2×255)m2
=1534m2
Replace base and height by their value in the formula Volume=Base×Height to calculate the volume of the cuboid and we will get
Volume=(255×16)m3
=4080m3.
Hence, the surface area of the cubic solid is 1534m2, and the volume of the cubic solid is 4080m3.
Points, Lines, and Planes Exercise 1.7 Geometry Workbook answers Page 14 Problem 12 Answer
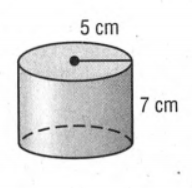
Given that,
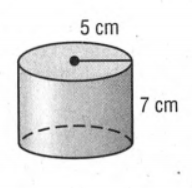
Here the given solid is a cylinder and we have to calculate the Surface Area and volume of the solid.
To calculate the surface Area
we will use2πrh+2πr2 and forVolume
we will useπr2h where r is the radius and h is the height of the solid cylinder.
Here given a cylindrical solid
If we give a closer look at the solid we can say the radius (r) is 5cm and height(h) is 7cm.
Now if we replace the value of r and h to calculate the surface area of the solid in the formula surface area(S)=2πrh+2πr2
we will get
S=(2×π×5×7+2×π×52)cm2
=376.99cm2
≈377.0cm2
And if we replace the value of r and h to calculate the volume of the solid in the formula Volume(V)=πr2h
we will get
V=(π×52×7)cm3
=549.77cm3
≈549.8cm3.
Hence, the surface area and volume of the cylindrical solid are 377.0 cm2 and 549.8 cm3 respectively.
Geometry Homework Practice Workbook Chapter 1 Page 14 Problem 13 Answer
Given that, boxes to hold a stack of 8.5inch by 11inch papers and volume of the box to be 500 Cubic inches.
Now we have to find out the height of the boxes.
The box is in cuboid shape so the box’s volume will be length × breadth × height.
Given that, boxes to hold a stack of 8.5inch by11 inch papers.
so the length of the box is 8.5 inches and the breadth of the box is 11 inches.
Now given that the volume of the box is 500 Cubic inches.
So to calculate the height of the cuboid, we will replace the above information in the formula Volume of the Cuboid=length×breadth×height
500=8.5×11×height or,height=8.5×11 /500inch
=5.34759358inch
≈5.35inch.
Hence, the height of the box should be 5.35 inches.
