Go Math Grade 8 Texas 1st Edition Solutions Chapter 1 Real Numbers Exercise
Go Math Grade 8 Texas 1st Edition Chapter 1 Real Numbers Solutions Page 2 Exercise 1 Problem 1
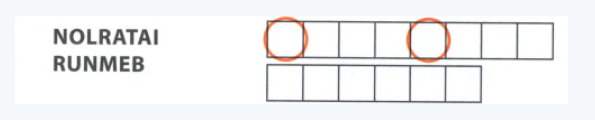
The puzzle is given as
To find a puzzle solution.
By using number concepts, preview key vocabulary.
The given puzzle is
NOLRATAI
RUNMEB
The given statement is
Any number that can be written as a ratio of two integers.
The above statement give hint as the number related to rational value.
So, the solution is “Rational Number”.
The key vocabulary from this unit is “RATIONAL NUMBER”.
Page 2 Exercise 2 Problem 2
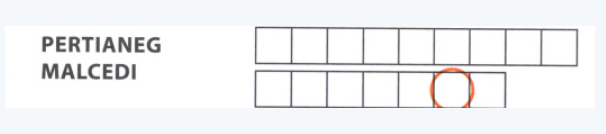
The puzzle is given as
To find a puzzle solution.
Method: To preview key vocabulary by using number concepts.
The given puzzle is
PERTIANEG
MALCEDI
The given statement is
A decimal in which one or more digits repeat infinitely.
The infinitely repeat of number is known as repeating.
The number can be integer and non-integer so the second one is decimal.
So, the answer we get is “Repeating Decimal”.
The key vocabulary from this unit is “REPEATING DECIMAL”.
Solutions For Real Numbers Exercise In Go Math Grade 8 Texas Page 2 Exercise 3 Problem 3
The given statement is the set of rational and the set of irrational numbers.
To find a puzzle solution.
By using number concepts, preview key vocabulary.
The given puzzle is
LAER
SEBMNUR
To find a puzzle solution.
By using number concepts, preview key vocabulary
From the definition of real numbers
Real numbers are numbers that include both rational and irrational numbers.
So, the definition of a real number matches the given statement.
Also, rearrange the alphabets in the puzzle.
LAER which is unscrambled to REAL.
The next word is SEBMNUR which is unscrambled to NUMBERS.
So, the answer is “Real Numbers”
The key vocabulary from this unit is “REAL NUMBERS”.
Page 2 Exercise 4 Problem 4
Given: A method of writing very large or very small numbers by using powers of 10.
To find a puzzle solution.
By using number concepts, preview key vocabulary.
The given puzzle is
NIISICFTCE
OITANTON
As we have statement
A method of writing very large or very small numbers by using powers of 10 .
The statement talk about some notation concept as we know.
Scientific notation is a way to express numbers in a form that makes numbers that are too small or too large more convenient to write.
So, the answer is “Scientific Notation”
The key vocabulary from this unit is “SCIENTIFIC NOTATION”.
Go Math Grade 8 Chapter 1 Real Numbers Exercise Solutions Page 3 Exercise 5 Problem 5
Use real numbers to solve real-world problems.
We have to finding real world problems.
The set of real numbers is the combination of rational and irrational numbers.
The entire number line from ±∞ represents the set of all real numbers.
Real numbers are used in a multitude of real-world scenarios.
For example, they are used to describe distances, weights, area, volume, and price.
Real numbers are used in a multitude of real-world scenarios. They are used to describe distances, weights, area, volume, and price.
Page 4 Exercise 6 Problem 6
Given number: 7
To find out the square of the 7
Method – For finding square multiplying the number by itself.
It is given that,7
We have to find the square of 7
To get a square of a given number multiplies the number by itself, we get
So, Multiplying 7 by itself, we will get
Square of the 7 = 7 × 7
= 49
The square of a given number 7 will be 49.
Real Numbers Solutions Chapter 1 Go Math Grade 8 Texas Page 4 Exercise 7 Problem 7
Given: 21.
To find the square of 21.
Method – For finding square multiplying the number by itself.
It is given, 21
We have to find the square of 21
To get a square of a given number multiplies the number by itself.
By itself, we will get
So, Multiplying 21 by itself, we will get
Square of 21 = 21 × 21
= 441
The square of a given number 21 will be 441.
Page 4 Exercise 8 Problem 8
Given: −3.
To find the square of −3
Method – For finding the square of the given number multiply the number by itself.
It is given,−3.
We have to find the square of −3.
To get a square of a given number multiplies the number by itself.
So, Multiplying −3 by itself, we will get
Square of −3 = −3 × −3
= 9
The square of a given number −3 will be 9.
Step-By-Step Solutions For Go Math Grade 8 Chapter 1 Real Numbers Page 4 Exercise 9 Problem 9
Given: 2.7.
To find the square of 2.7.
Method – For finding the square of a given number multiply the number by itself.
It is given,2.7.
We have to find the square of 2.7.
To get a square of a given number multiplies the number by itself.
So, multiplying by 2.7 itself, we will get.
Square of 2.7. = 2.7 × 2.7
= 7.29
The square of given numbers 2.7 will be 7.29.
Page 4 Exercise 10 Problem 10
Given: \(\frac{−1}{4}\).
To find the square of \(\frac{−1}{4}\).
Method – for finding the square of a given number multiply the number by itself.
It is given \(\frac{−1}{4}\).
We have to find the square of \(\frac{−1}{4}\).
To get a square of a given number multiplies the number by itself.
So, multiplying by \(\frac{−1}{4}\) itself, we will get.
The square of \(\frac{−1}{4}\) = \(\frac{−1}{4}\) × \(\frac{−1}{4}\)
= \(\frac{1}{16}\).
The square of given numbers\(\frac{−1}{4}\) will be \(\frac{1}{16}\).
Go Math Grade 8 Real Numbers Free Solutions Page 4 Exercise 11 Problem 11
Given:−5.7.
To find the square of −5.7.
Method – for finding the square of a given number multiply the number by itself.
It is given,−5.7
We have to find the square of−5.7
To get a square of a given number multiplies the number by itself.
So, Multiplying by 5.7 itself, we will get
The square of −5.7= −5.7 × −5.7
= 32.49.
The square of given numbers 5.7 will be 32.49.
Page 4 Exercise 12 Problem 12
Given: 1\(\frac{1}{2}\)
To find the square of 1\(\frac{1}{2}\).
Method – For finding the square of a given number multiply the number by itself.
It is given 1\(\frac{1}{2}\)
We have to find the square of 1\(\frac{1}{2}\).
To get a square of a given number multiplies the number by itself.
But first, we have to convert mixed fractions into fractions.
= 1\(\frac{1}{2}\)
= \(\frac{5×1+2}{5}\)
= \(\frac{7}{5}\)
Further, we have to find the square of \(\frac{7}{5}\).
So, Multiplying by \(\frac{7}{5}\) itself, we will get
The square of 1\(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{7}{5}\) × \(\frac{7}{5}\)
= \(\frac{49}{25}\).
The square of a given number \(\frac{7}{5}\) will be \(\frac{49}{25}\).
Go Math Grade 8 Texas Exercise Solutions For Real Numbers Page 4 Exercise 13 Problem 13
Given: 92.
To find the square of 92.
Method – For finding the square of a given number multiply the number by itself.
It is given, 92.
We have to find the square of 92.
To get a square of a given number multiplies the number by itself.
So, multiplying by 9 itself, we will get
Square of 92 = 9 × 9
= 81.
The square of a given numbers 92 will be 81.
Page 4 Exercise 14 Problem 14
Given: 24
To simplify exponential expression of 24.
Method – For finding the value of a given number multiply 4 times the number by itself.
It is given, 24.
We have to simplify the exponential expression of 24.
To simplify the exponential expression of a given number multiplies four times itself.
So, multiplying, we will get
24 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2
= 16
Simplified value of the exponential expression 24 will be 16.
Real Numbers Exercise Go Math Grade 8 Texas 1st Edition Answers Page 4 Exercise 15 Problem 15
Given: (\(\frac{1}{3}\))2
To simplify the exponential expression of (\(\frac{1}{3}\))2.
Method – For finding the square of a given number multiply the number by itself.
It is given, (\(\frac{1}{3}\))2
We have to simplify exponential expression of (\(\frac{1}{3}\))2.
To get a square of a given number multiplies the number by itself.
So, multiplying by \(\frac{1}{3}\) itself, we will get
(\(\frac{1}{3}\))2 = \(\frac{1}{3}\) × \(\frac{1}{3}\)
= \(\frac{1}{9}\)
The simplified exponential expression of (\(\frac{1}{3}\))2 will be \(\frac{1}{9}\).
Page 4 Exercise 16 Problem 16
Given: (−7)2.
To simplify the exponential expression of (−7)2.
Method – For finding the square of a given number multiply the number by itself.
It is given, (−7)2.
We have to simplify the exponential expression of(−7)2.
To get a square of a given number multiplies the number by itself.
So, multiplying by −7 itself, we will get
(−7)2. = −7 × −7
= 49.
The simplified exponential expression of (−7)2 will be 49.
Page 4 Exercise 17 Problem 17
Given: 43.
To simplify the exponential expression of 43.
Method -For finding the cube of a number, multiply that number itself, then multiply the product obtained with the original number again.
It is given,43.
Four multiply by itself three times.
We will get
43 = 4 × 4 × 4
= 64.
The simplified exponential expression of 43 will be 64.
Page 4 Exercise 18 Problem 18
Given: 105.
To simplify the exponential expression of 105.
Method- To simplify the exponential expression, we will use exponent rules.
It is given,105.
We have to simplify the exponential expression of 105.
To get a simplified expression of a given number multiplies the number five times by itself.
So, multiply 10 to itself at five times.
We will get
105 = 10 × 10 × 10 × 10 × 10
= 100000
The simplified exponential expression of 105 will be 100000.
Page 4 Exercise 19 Problem 19
Given: 3\(\frac{1}{3}\).
To convert a mixed fraction into an improper fraction.
Method- To convert a mixed fraction into an improper fraction, we multiply the denominator of the fraction by the whole number and then add the product to the numerator.
Like, for converting the mixed fraction x \(\frac{a}{b}\) we will write the same as \(\frac{(b×x)+a}{b}\).
It is given 3\(\frac{1}{3}\).
We have to convert mixed fractions into improper fractions.
Multiply 3 by 3, the product will be 9.
= 3 × 3
= 9
Then, We will add the product with the numerator We will get
= 9 + 1
= 10
After that Writing 10 over 3.
We will get improper fraction as \(\frac{10}{3}\).
The mixed fraction 3\(\frac{1}{3}\) will be \(\frac{10}{3}\) in improper fraction.
Page 4 Exercise 20 Problem 20
Given: 5 \(\frac{5}{6}\).
To convert a mixed fraction into an improper fraction.
Method- To convert a mixed fraction into an improper fraction, we multiply the denominator of the fraction by the whole number and then add the product to the numerator.Like, for converting the mixed fraction x \(\frac{a}{b}\) we will write the same as \(\frac{(b×x)+a}{b}\).
It is given 5 \(\frac{5}{6}\).
We have to convert mixed fractions into improper fractions.
Multiply 6 by 5, the product will be 30.
= 6 × 5
= 30
Then, We will add the product with the numerator We will get
= 30 + 5
= 35.
After that Writing 35 over 6.
We will get an improper fraction as \(\frac{35}{6}\).
The mixed fraction 5 \(\frac{5}{6}\) will be \(\frac{35}{6}\) in improper fraction.
Page 4 Exercise 21 Problem 21
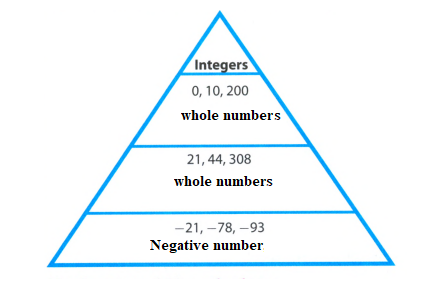
The whole number and positive number is 0,10,200.
The whole number and positive number is 21, 44, 308.
The integer and a negative number are -21,-78, -93.
Hence , the answer is
Page 5 Exercise 22 Problem 22
Prime factors that, themselves, have only factors of 1 and themselves. Non-prime numbers, like 10, have prime factors.
Note that 1 is a factor of all integers.
If the two factors are equal (the same), like 4 × 4 = 16 , then each of them is called a “square root.“
One of the two equal factors of a number is a square root.
Hence, One of the two equal factors of a number is a square root.
Page 5 Exercise 23 Problem 23
The square root of a non-negative number, is a non-negative number that when multiplied by itself results in the original number.
The square root of a negative number does not exist in the real numbers.
Example: Since 25 is a non-negative number, there is a non-negative number 5, such that 52 = 25.
The real number is the non negative square root of a number.
Hence, the real number is the non negative square root of a number.
