HMH Middle School Grade 7 Practice Fluency Workbook 1st Edition Chapter 3 Rational Numbers
HMH Grade 7 Practice Fluency Workbook Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 Solutions Page 15 Problem 1 Answer
A rational number is given as,19/20.
A rational number is required to write the given rational number as a terminating decimal.
To write the given rational number as a terminating decimal, it is necessary to convert the given rational number into a decimal fraction.
Multiply the numerator and denominator of the given rational number 19/20 by 5 to obtain a decimal fraction.
19⋅5/20⋅5
19⋅5/20⋅5 =95/100
The decimal fraction 95/100 can be written as 0.95.
The required terminating decimal is 0.95.
The terminating decimal of the given rational number 19/20 is 0.95.
Read and Learn More HMH Middle School Grade 7 Practice Fluency Workbook 1st Edition Solutions
HMH Middle School Grade 7 Chapter 3 Page 15 Problem 2 Answer
A rational number is given as, −1/8.
A rational number is required to write the given rational number as a terminating decimal.
To write the given rational number as a terminating decimal, it is necessary to convert the given rational number into a decimal fraction.
Multiply the numerator and denominator of the given rational number −1/8 by 125 to obtain a decimal fraction.
−1⋅125/8⋅125
−1⋅125/8⋅125 =−125/1000
The decimal fraction −125/1000 can be written as,−0.125.
The required terminating decimal is −0.125.
The terminating decimal of the given rational number −1/8 is −0.125.
HMH Middle School Grade 7 Chapter 3 Page 15 Problem 3 Answer

Rational Numbers Exercise 3.1 Chapter 3 Answers HMH Grade 7 Workbook Page 15 Problem 4 Answer
A rational number is given as, −7/9.
A rational number is required to write the given rational number as a terminating decimal.
To write the given rational number as a terminating decimal, it is necessary to convert the given rational number into a decimal fraction.
Ignore the negative sign, and divide 7 by 9.
Here, 7 will be the dividend and 9 will be the divisor.
Since, 9 is larger than 7, the first number of the quotient will be 0 and the remainder 7.
As the division continues to go forever, the quotient and the remainder always gives the value 7.
Hence, −7/9=−0.7777777.
The value −0.7777777 can be written as−0.7.
Hence, the required repeating decimal is −0.7.
The repeating decimal of the given rational number −7/9 is −0.7.
HMH Middle School Grade 7 Chapter 3 Page 15 Problem 5 Answer
A rational number is given as,11/15.
A rational number is required to write the given rational number as a terminating decimal.
To write the given rational number as a terminating decimal, it is necessary to convert the given rational number into a decimal fraction.
Divide 11 by 5.
Here, 11 will be the dividend and 5 will be the divisor.
Since 11 is larger than 5, the first number of the quotient will be 0 and the remainder 11.
The next number of the quotient will be 7 and the remainder 5.
Similarly, the third number of the quotient will be 3 and the remainder 5.
As the division continues to go forever, the quotient always gives the value 3 and the remainder always gives the value 5.
Hence, 11/15
11/15 =0.733333.
The value 0.733333 can be written as 0.73.
Hence, the required repeating decimal is 0.73.
The repeating decimal of the given rational number 11/15 is 0.73.
Step-By-Step Solutions For Exercise 3.1 Rational Numbers HMH Grade 7 Practice Workbook Page 15 Problem 6 Answer
A rational number is given as, 8/3.
A rational number is required to write the given rational number as a terminating decimal.
To write the given rational number as a terminating decimal, it is necessary to convert the given rational number into a decimal fraction.
Divide 8 by 3.
Here, 8 will be the dividend and 3 will be the divisor.
Here, 8 is larger than 3. When 3 is multiplied by 2, it gives results 6. The value 6 is smaller than 8.
Hence, the first number of the quotient will be 2 and the remainder 2.
The next number of the quotient will be 6 and the remainder 2.
As the division continues to go forever, the quotient always gives the value 6
and the remainder always gives the value 2.
Hence, 8/3=2.666666.
The value 2.666666 can be written as 2.6.
Hence, the required repeating decimal is 2.6.
The repeating decimal of the given rational number 8/3 is 2.6.
HMH Middle School Grade 7 Chapter 3 Page 15 Problem 7 Answer
Three digits 2,3 and 4 are given.
A rational number is required to write a mixed number that has a terminating decimal, and write the decimal.
A rational number is also required to write a mixed number that has a repeating decimal, and write the decimal.
Form fractions using the given numbers and then find whether they terminating or repeating.
Form possible improper fractions that can be formed with the use of the given numbers.
First, take 2 as the denominator.
Hence, two improper fractions are formed as, 4×3/2 and 3×4/2.
Take 3 as the denominator.
Hence, two improper fractions are formed as, 4×2/3 and 2×4/3.
Take 4 as the denominator.
Hence, two improper fractions are formed as, 3×2/4 and 2×3/4.
The required improper fractions are 4×3/2,3×4/2,4×2/3,2×4/3,3×2/4 and 2×3/4.
Solve the improper fractions one by one.
For 4×3/2,4×3/2=1×1/2
4×3/2=5.5
Now, for 3×4/2,3×4/2=10/2
3×4/2=5
Hence, 3×4/2=5.
For 4×2/3,
4×2/3=1×4/3
4×2/3=4.6
Now, for 2×4/3,
2×4/3=10/3
2×4/3=3.3
Hence, 2×4/3=3.3.
For 3×2/4,
3×2/4=14/4
3×2/4=3.5
Now, for 2×3/4,
2×3/4=11/4
2×3/4=2.75
Hence, mixed numbers with terminating decimals are 4×2/3 and 2×4/3.
And, mixed numbers with repeating decimals are 4×3/2,3×4/2,3×2/4 and 2×3/4.
The mixed numbers that have terminating decimals are 4×2/3 and 2×4/3.
The mixed numbers that have repeating decimals are 4×3/2,3×4/2,3×2/4 and 2×3/4.
HMH Middle School Grade 7 Chapter 3 Page 15 Problem 8 Answer
A rational number is given that a ruler is marked at every 1/16 inch.
A rational number is required to convert the improper fraction into decimal and tell whether it is terminating or repeating.
Simplify the given fraction and then find whether it is terminating or repeating.
Given,
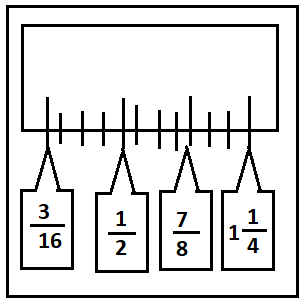
Simplify the given improper fractions.
For 3/16,
3/16=0.1875
As 0.1875 is not repeating, it shows that it is a terminating decimal.
For 1/2,
1/2=0.5
As 0.5 is not repeating, it shows that it is a terminating decimal.
For 7/8,
7/8=0.875
As 0.875 is not repeating, it shows that it is a terminating decimal.
For 11/4,
11/4=5/4
11/4=1.25
As, 1.25 is not repeating, it shows that it is a terminating decimal.
All the given improper fractions are not repeating, so, they are terminating decimals.
Exercise 3.1 Rational Numbers Solutions For HMH Middle School Grade 7 Workbook Page 16 Problem 9 Answer
An improper fraction is given as, 11×5/6.
A rational number is required to find the decimal for the fraction part and then write the whole improper number as a decimal.
Simplify the improper fraction and convert it into decimal form.
First, separate the whole number part and the fraction part, that is, 11 and 5/6 respectively.
Solve the value for 5/6.
5/6=0.83.
Now, add up the whole number part with the decimal value.
Hence, 11+0.83
11+0.83 =11.83.
The decimal value of the given improper fraction is 11.83.
HMH Middle School Grade 7 Chapter 3 Page 16 Problem 10 Answer
An improper fraction is given as,9×2/9.
A rational number is required to find the decimal for the fraction part and then write the whole improper number as a decimal.
Simplify the improper fraction and convert it into decimal form.
First, separate the whole number part and the fraction part, that is, 9 and 2/9respectively.
Solve the value for 2/9.
2/9=0.2
Now, add up the whole number part with the decimal value.
Hence, 9+0.2=9.2.
Use direct method to solve 9×2/9.
9×2/9=8×3/9
9×2/9=9.2
Hence, 9×2/9=9.2.
The decimal value of the given improper fraction is 9.2.
Examples Of Problems From Exercise 3.1 Rational Numbers In HMH Grade 7 Workbook Page 16 Problem 11 Answer
A mixed number is given as, 9×2/9.
A rational number is required to use two methods to write the given mixed number as a decimal.
To write the given mixed number as a decimal, in first method rewrite the number and then find decimal for fraction part, in second part write the number as improper fraction and then write the given mixed number as a decimal.
Rewrite the number.
21×5/8=21+5/8
Find decimal for the fraction part.
5/8=5⋅125/8⋅125
5/8=625/1000
5/8=0.625
Hence, 5/8=0.625.
Now,
21×5/8=21+5/8
21×5/8=21+0.625
21×5/8=21.625
Hence, 21×5/8=21.625.
Write the number as an improper fraction.
21×5/8=17×3/8
Write the given mixed number as a decimal.
17×3/8=173⋅125/8⋅125
17×3/8=21625/1000
17×3/8=21.625
Hence, 17×3/8=21.625.
The mixed number 9×2/9 as a decimal is 21.625.
