Pre-Calculus 11 Student Edition Chapter 1 Sequences and Series
McGraw Hill Pre Calculus 11 Chapter 1 Review Solutions Page 66 Problem 1 Answer
First determine 36,40,44,48,……. sequence is in arithmetic or not. If in arithmetic, find the common difference.
The given sequence is
36,40,44,48,……..
Here,
First term(t1)=36
Second term(t2)=40
Third term (t3)=44
fourth term(t4)=48
Now,
t2−t1 =40−36=4
t3−t2=44−40=4
t4−t3=48−44=4
Sequence has the constant common difference. So, the given sequence is in arithmetic progression. The common difference is 4.
The sequence 36,40,44,48 is in arithmetic and common difference is 4.
Precalculus Textbook Mcgraw Hill Answers
McGraw Hill Pre Calculus 11 Chapter 1 Review Solutions Page 66 Problem 2 Answer
Given: −35,−40,−45,−50,…..
To find: To check whether the given sequence is arithmetic or not
Consider the sequence −35,−40,−45,−50
The above sequence will be arithmetic sequence if the difference between the consecutive terms is equal hence we have
−40+35=−5
−45+40=−5
−50+45=−5
The common difference of consecutive terms is equal
Hence the given sequence is arithmetic sequence
The given sequence is an arithmetic sequence.
Read and Learn More Precalculus Textbook Mcgraw Hill Answers
McGraw Hill Pre Calculus 11 Chapter 1 Review Solutions Page 66 Problem 3 Answer

Pre Calculus 11 Chapter 1 Review Sequences And Series Answers Page 66 Problem 4 Answer
Given: 8.3,4.3,0.3,−3.7
To find: To check whether the given sequence is arithmetic or not
Consider the sequence 8.3,4.3,0.3,−3.7
The above sequence will be arithmetic sequence if the difference between the consecutive terms is equal
hence we have
4.3−8.3=−4
0.3−4.3=−4
−3.7−0.3=4
The common difference of consecutive terms is equal
Hence the given sequence is arithmetic sequence
Hence the given sequence is a arithmetic sequence
Precalculus Textbook Mcgraw Hill Answers
Pre Calculus 11 Chapter 1 Review Sequences And Series Answers Page 66 Problem 5 Answer
Given: a)18,30,42,54,66,…
b)7,12,17,22,….
c)2,4,6,8,…
d)−8,−12,−16,−20,…
e)4,7,10,13,….
A)tn=3n+1
B)tn=−4(n+1)
C)tn=12n+6
D)tn=5n+2
E)tn=2n
To find: match the sequence to its nth terms.
Consider the sequence 18,30,42,54,66
These are arithmetic sequence
Hence they have equal common difference
Hence the common difference-30−18=12
And the first term(a)=18
The nth terms of sequence is- a+(n−1)d
a+(n−1)d =18+(n−1)12
=18+12n−12
=12n+6
Consider the sequence 7,12,17,22,…
These are arithmetic sequence
Hence they have equal common difference
Hence the common difference-12−7=5
The first term of the sequence (a)=7
The nth of the sequence is=a+(n−1)d
=7+(n−1)5
=7+5n−5
=5n+2
Consider the sequence 2,4,6,8,…
These are arithmetic sequence
Hence they have equal common difference
Hence the common difference-4−2=2
The first term of the sequence is (a)=2
The nth term of the sequence is=a+(n−1)d
=2+(n−1)2
=2+2n−2
=2n
Precalculus Textbook Mcgraw Hill Answers
Consider the sequence −8,−12,−16,−20,….
These are arithmetic sequence
Hence they have equal common difference
Hence the common difference-=−12+8=−4
The first term of the sequence (a)=−8
The nth term of the sequence is=a+(n−1)d
=−8+(n−1)(−4)
=−8−4n+4
=−4n−4
Consider the sequence 4,7,10,13,….
These are arithmetic sequence
Hence they have equal common difference
Hence the common difference-7−4=3
The first term of the sequence is (a)=7
The nth term of the sequence is=a+(n−1)d
=7+(n−1)3
=7+3n−3
=3n+4
Hence the correct match of sequence and their nth term is
a)18,30,42,54,66,…
b)7,12,17,22,….
c)2,4,6,8,…
d)−8,−12,−16,−20,…
e)4,7,10,13,….
C)tn=12n+6
D)tn=5n+2
E)tn=2n
B)tn=−4(n+1)
A)tn=3n+1
Precalculus Textbook Mcgraw Hill Answers
Pre Calculus 11 Chapter 1 Review Solved Problems Page 66 Problem 6 Answer
Given: 98 and a sequence 7,14,21,28,…
To find: Whether the given number belongs to the given sequence and if it does find the corresponding value of n.
Consider the sequence 7,14,21,28
This is an arithmetic sequence hence it has equal common difference
Hence the common difference is 14−7=7
The first term of the sequence is (a)=7
Hence the nth term of the sequence is =a+(n−1)d
=7+(n−1)7
=7+7n−7
=7n
Consider tn=98
Hence 98=7n
∴n=14
Hence 98 does belong to the given sequence and the value of n=14.
Pre Calculus 11 Chapter 1 Review Solved Problems Page 66 Problem 7 Answer
Given: 110 and a sequence 7,14,21,…
To find : whether the given number belongs to the sequence and if it does find the corresponding value of n
Given: Consider the sequence 7,14,21,…
t1=7
t2=14
Common difference:t2−t1
=14−7
=7
The general term of the arithmetic sequence is tn=t1+(n−1)d…(1)
Substitute the values t1=7,d=7 in equation (1)
tn=7+(n−1)7…(2)
Substitute tn=110 in equation(2)
110=7+7n−7
110=7n
n=110/7
n=15.71
Therefore, 110 does not belong to the given sequence.
Therefore, 110 does not belong to the given sequence.
Mcgraw Hill Precalculus Textbook Answers
Pre Calculus 11 Chapter 1 Review Solved Problems Page 66 Problem 8 Answer
Given: tn=378 and the sequence 7,14,21,…
To find: whether the given number belongs to the sequence and if it does find the corresponding value of n
Given: Consider the sequence 7,14,21,…
The given sequence is arithmetic sequence.
t1=7 , t2=14
Common difference: t2−t1
=t2−t1
=14−7
The general term of an arithmetic sequence is tn=t1+(n−1)d…(1)
Putting these values d=7,t1=7,tn=378 in equation (1)
378=7+(n−1)7
378=7+7n−7
378=7n
n=378/7
n=54
Therefore, 378 does belong to the given sequence and the value of n is 54
Therefore, 378 does belong to the given sequence and the value of n is 54
Solutions For Chapter 1 Review Pre Calculus 11 McGraw Hill Page 66 Problem 9 Answer
Given: tn=575 and the sequence is 7,14,21,…
To find: whether the given number belongs to the sequence and if it does find the corresponding value of n
Given: Consider the sequence 7,14,21,…
The given sequence is arithmetic sequence.
t1=7,t2=14
Common difference:t2−t1
=14−7
=7
The general term of an arithmetic sequence is
tn=t1+(n−1)d…(1)
Putting these values d=7,t1=7,tn=575 in equation (1)
Mcgraw Hill Precalculus Textbook Answers
575=7+(n−1)7
575=7+7n−7
575=7n
n=575/7
n=82.14
Therefore, 575 does not belong to the given sequence.
Therefore, 575 does not belong to the given sequence.
Solutions For Chapter 1 Review Pre Calculus 11 McGraw Hill Page 66 Problem 10 Answer
Given: Sequence 1: 2,9,16,23
t1=2,t2=9
Common difference: d=t2−t1
=9−2
=7
General term of an arithmetic sequence is tn=t1+(n−1)d…(1)
Putting these values d=7,t1=2,n=17 in equation (1)
t17=2+(17−1)7
t17=2+16×7
t17=2+112
t17=114
Sequence2: 4,10,16,22
t1=4,t2=10
Common difference:d=t2−t1
=10−4
=6
General term of an arithmetic sequence is tn=t1+(n−1)d….(2)
Putting the values n=17,d=6,t1=4 in equation(2)
t17=4+(17−1)6
t17 =4+16×6
t17 =4+96
t17=100
Since, 114>110
t17 is greater in sequence 1
Solutions For Chapter 1 Review Pre Calculus 11 McGraw Hill Mcgraw Hill Precalculus Textbook Answers
So, the option A is correct.
114>100
t17 is greater in sequence 2
So, the option B is not correct .
114>100
t17 is equal in sequences.
So, the option C is not correct.
The option A is correct.
t17 is greater in sequence 1.
Solutions For Chapter 1 Review Pre Calculus 11 McGraw Hill Page 66 Problem 11 Answer
In the graph , sequence 1 has a larger positive slope than sequence 2.
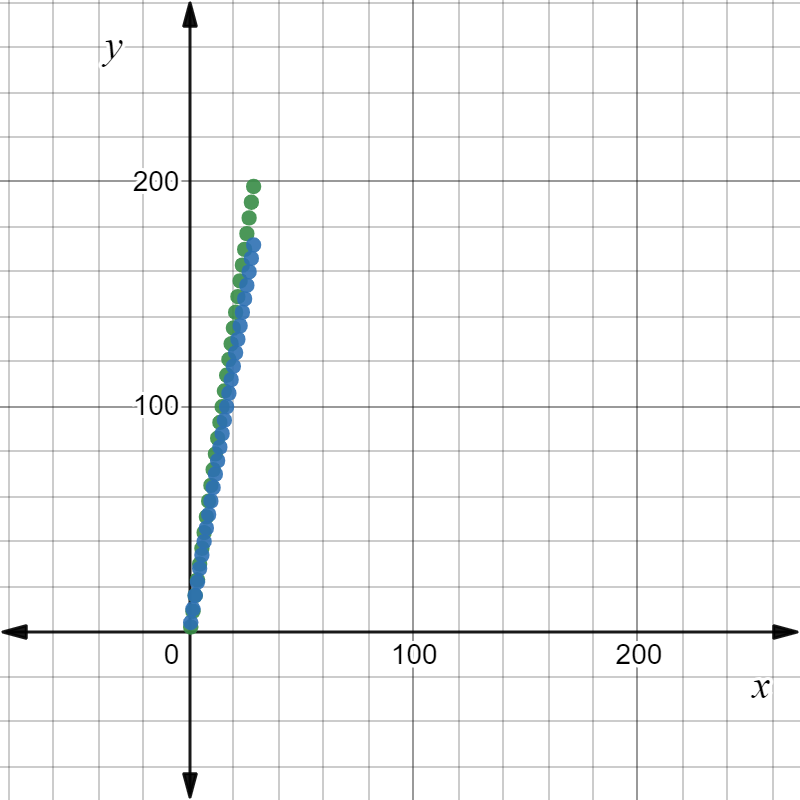
The value of term 17 is greater in sequence 1 than in sequence 2.
So, the option A is correct.
The value of term 17 is greater in sequence 1 than not in sequence 2
So, the option B is not correct.
The value of term 17 is not equal to both the sequences1 and sequence2.
So, the option C is not correct.
In the graph, sequence 1 has a larger positive slope than the sequence 2.
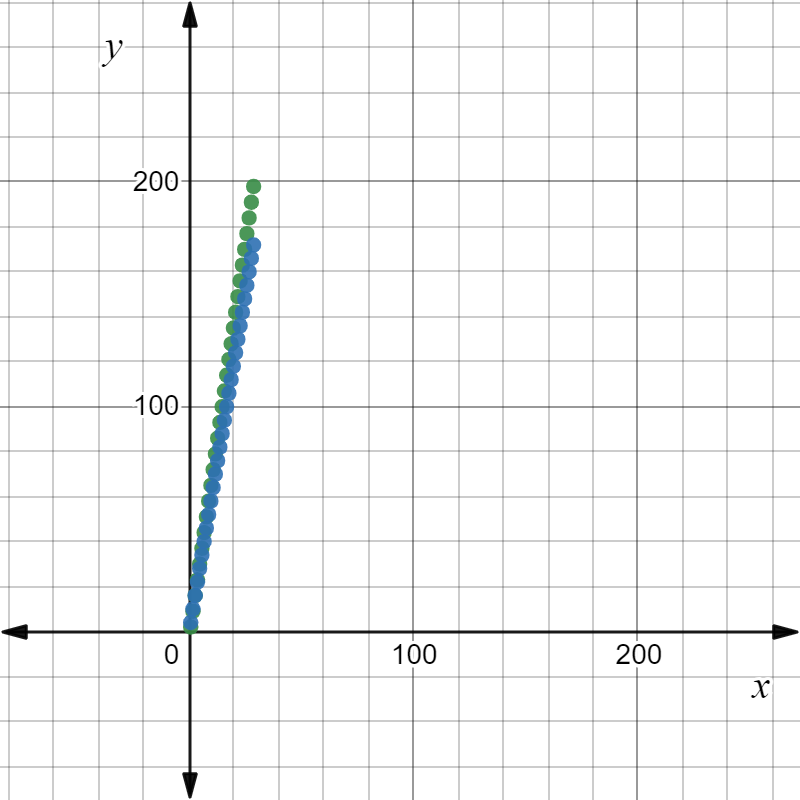
The value of term 17 is greater in sequence 1 than in sequence 2.
So, the option A is correct.
McGraw Hill Pre Calculus 11 Review Exercise Detailed Solutions Page 66 Problem 12 Answer
Given : The first term of the A.P. is 5.
The fourth term of the A.P. is 17.
At first , we have to assume the common difference of the A.P. be d.
Then we have to find the fourth term in terms of the first term and d and after that we have to equate this fourth term to the given fourth term to find d.
Lastly , after finding the value of d, we will be able to find the tenth term.
First term of the A.P. = 5
Let the common difference of the A.P. be d.
Then the fourth term of the A.P. is
5+(4−1)d=17
=>5+3d=17
=>3d=17−5
=>3d=12
=>d=12/3
=>d=4
Then , the tenth term is 5+(10−1)4=5+36=41
Hence, the tenth term of the Arithmetic sequence is 41.
Mcgraw Hill Precalculus Textbook Answers
McGraw Hill Pre Calculus 11 Review Exercise Detailed Solutions Page 66 Problem 13 Answer
The given arithmetic series is 6+9+12+⋯(S10).
We have to find out the sum of the series for 10th term.
Here t1=6
n=10
d=3
Using the above formula we will calculate the sum of the series.
Sn =n/2 [2t1 + (n − 1)d]
⇒ S10 =10/2 [2(6) + (10 − 1)3] [∵ t1 = 6, n = 10, d = 3]
⇒ S10 = 5[12 + 27]
⇒ S10 = 195
The indicated sum 6+9+12+⋯(S10 ) is 195.
McGraw Hill Pre Calculus 11 Review Exercise Detailed Solutions Page 66 Problem 14 Answer
The given arithmetic series is 4.5+8+11.5+⋯(S12).
We have to find out the sum of the series for 12th term.
Here t1=4.5
n=12
d=3.5
Using the above formula we will calculate the sum of the series.
Sn =n/2[2t1 + (n − 1)d]
⇒ S12 =12/2 [2(4.5) + (12 − 1)3.5] [∵ t1 = 4.5, n = 12, d = 3.5]
⇒ S12 = 6[9 + 38.5]
⇒ S12 = 285
The indicated sum of 4.5+8+11.5+⋯(S12 ) is 285.
McGraw Hill Pre Calculus 11 Review Exercise Detailed Solutions Page 66 Problem 15 Answer
The given arithmetic series is 6+3+0+⋯(S10 ).
We have to find out the sum of the series for 10th term.
Here t1=6
n=10
d=−3
Using the above formula we will calculate the sum of the series.
Sn =n/2[2t1 + (n − 1)d]
⇒ S10 =10/2[2(6) + (10 − 1)(−3)] [∵ t1 = 6, n = 10, d = −3]
⇒ S10 = 5[12 − 27]
⇒ S10 = −75
The indicated sum 6+3+0+⋯(S10 ). is −75.
Mcgraw Hill Precalculus Textbook Answers
Understanding Chapter 1 Review Exercise In McGraw Hill Pre Calculus Page 66 Problem 16 Answer
The given arithmetic series is 60+70+80+⋯(S20).
We have to find out the sum of the series for 20th term.
Here t1=60
n=20
d=10
Using the above formula we will calculate the sum of the series.
Sn =n/2 [2t1 + (n − 1)d]
⇒ S20 =20/2 [2(60) + (20 − 1)10] [∵ t1= 60, n = 20, d = 10]
⇒ S20 = 10[120 + 190]
⇒ S20 = 3100
The sum of the given series for 20th term is 3100.
Understanding Chapter 1 Review Exercise In McGraw Hill Pre Calculus Page 66 Problem 17 Answer
Given : The sum of first 12 terms of an arithmetic series is 186.
The 20th term is 83.
To find the sum of first 40 terms , at first we have to find the first term a1 and the common differenced with the given information.
Lastly , by putting the values of n,a1,d in the given formula, we will get the required answer.
Since the 20th term is 83,we have :
a1+(20−1)d=83=>a1+19d=83
∴a1=83−19d
Sum of 1st 12 terms is 186, so :186=(12/2)[2(83−19d)+(12−1)d]
=>186=6[2(83−19d)+11d]
=>186/6
=166−38d+11d
=>31=166−27d
=>27d=166−31
=>27d=135
=>d=135/27
=>d=5
a1 = 83 − 19(5) = 83 − 95 = −12
a40 = −12 + (40 − 1)(5)
=> a40 = −12 + 39(5)
=> a40 = −12 + 195
∴ a40 = 183
S40 = (40/2)[2(−12) + (40 − 1)(5)]
S40 = 20[−24 + 195]
S40 = 20(171)
S40 = 3420
Hence, the indicated sum is 3420.
Understanding Chapter 1 Review Exercise In McGraw Hill Pre Calculus Page 66 Problem 18 Answer
Here on the first day, I am able to contact only one person.
So a1=1
As each day progresses, I am able to contact two more people than the previous day.
So, the common difference d=2
To find the number of people I would contact on the 15th day, we have to find a15
We know
a15=a1+(15−1)d
as a1=1 and d=2,
a15=1+(15−1)2
⇒a15=1+14.2
⇒a15=1+28
⇒a15=29
If You have taken a job that requires being in contact with all the people in your neighbourhood.
On the first day, you are able to contact only one person.
On the second day, you contact two more people than you did on the first day.
On day three, you contact two more people than you did on the previous day.
Assume that the pattern continues then you would contact 29 people on 15 th day.
Understanding Chapter 1 Review Exercise In McGraw Hill Pre Calculus Page 66 Problem 19 Answer
Here on the first day, I am able to contact only one person. So a1=1
As each day progresses, I am able to contact two more people than the previous day. So, the common difference d=2
To find the total number of people I would have been in contact with by the end of the 15th day, we have to find S15.
Here n=15
We know,
S15=(15/2)(2a1+(15−1)d) as a1=1,d=2,
S15=(15/2)(2.1+(15−1)2)⇒S15
=(15/2)(2+14.2)⇒S15
=(15/2)(2+28)⇒S15
=(15/2).30⇒S15
=15.15⇒S15
S15 =225
You have taken a job that requires being in contact with all the people in you neighbourhood.
On the first day, you are able to contact only one person.
On the second day, you contact two more people than you did on the first day.
On day three, you contact two more people than you did on the previous day.
Assume that the pattern continues then the total number of people you would be in contact with by the end of the 15th day is 225
Understanding Chapter 1 Review Exercise In McGraw Hill Pre Calculus Page 66 Problem 20 Answer
We consider the number of people I am able to meet every day as the individual term of the series.
Given that, on the first day the man is able to contact with one person, so the first term of the series, i.e. a=1.
We observe that as days pass, the number of people I am able to interact increases constantly by 2. Hence d=2
At the end, I am supposed to meet with a sum of 625 people. Hence Sn=625.
We need to find the number of days required to meet the sum of 625 people, i.e. n.
We know that,
Sn=n/2{2a+(n−1)d}⇒625=n/2
{2.1+(n−1).2}
(Given)
⇒625=n/2.2(1+n−1)
⇒625=n.n
⇒625=n2
⇒n=25
Hence it will take 25days to know 625 people.
It will take 25 days to know 625 people in the neighbourhood.
Understanding Chapter 1 Review Exercise In McGraw Hill Pre Calculus Page 67 Problem 21 Answer
The objective of the problem is to find the number of seats in the entire concert hall.
Given: The first row has 10 seats
The second row has 12 seats
Total 30 rows of seats.
Here, the first row has 10 seats and the second row has 12 seats.
Also, each row has 2 seats more than the previous row.
Therefore,
a=10
d=2
n=30
By using the formula of the sum of the first n terms of A.P.:
S30=30/2[2(10)+(30−1)2]
S30=15[20+(29)2]
S30=15[78]
S30=1170
So, a total 1170 seats are there in concert hall.
Hence, a total 1170 seats are there in a concert hall.
Page 67 Problem 22 Answer
The objective of the problem is to check whether the given series is geometric or not.
If yes, then find the first term, common ratio, and general term of a sequence.
Given:3,6,10,15,…
Taking common ratio between terms,
6/3=2
10/6
=1.67
As the ratio between the consecutive terms is not constant, the given series is not geometric.
Hence, given series is not geometric as consecutive term ratio is not constant.
Page 67 Problem 23 Answer
Given:
1,−2,4,−8,…
The objective of the problem is to check whether the given series is geometric or not.
If yes, then find the first term, common ratio, and general term of a sequence
Taking the common ratio of consecutive terms,−2/1=−2/4
−2=−2/−8
4=−2
As this ratio is the same, the given sequence is geometric series.
As seen common ratio is −2, i.e., r=2.
By analyzing the given sequence, the first term is t1=1
Nth term of a geometric sequence is:tn=t1/rn−1
Therefore, the general term of a sequence,
tn=1⋅(−2)n−1
tn=(−2)n−1
Hence, the given sequence is a geometric sequence.
The first term is t1=1
Common ratio is r=−2
General term is tn=(−2)n−1
Page 67 Problem 24 Answer
Given sequence: 1,1/2,1/4,1/8,………..
Determine whether each of the following sequences is geometric.
If it is geometric, determine the common ratio, r, the first term, t1, and the general term of the sequence.
Determine ratio between consecutive terms
t2/t1=1/2
1→r=1/2
t3/t2=1/4
1/2→r=1/2
t4/t3=1/8
1/4→r=1/2
Ratio is same between consecutive terms
So, sequence is geometric.
common ratio: r=1/2
The first term: t1=1
General term of the sequence: tn=t1/rn−1
tn=1(1/2)n−1
tn=1/2n−1
common ratio: r=1/2
The first term: t1=1
General term of the sequence: tn=1/2n−1
Page 67 Problem 25 Answer
Given sequence: 16/9,−3/4,1,………..
Determine whether each of the following sequences is geometric.
If it is geometric, determine the common ratio, r, the first term, t1, and the general term of the sequence.
Determine ratio between consecutive terms
t2/t1=−3/4
16/9→r=−27/4
t3/t2=1−3/4
→r=−4/3
Ratio is not same between consecutive terms
So, the sequence is not geometric.
The sequence 16/9,−3/4,1,……….. is not geometric.
Page 67 Problem 26 Answer
Given: Initial number of bacteria:
P0=5000
Growth rate r=8%
r=0.08
To find number of bacteria at end of n=5 hours.
P = P0(1 + r)n
P = 5000(1 + 0.08)5
P = 5000(1.08)5
P = 5000(1.4693280768)
P = 7346
Number of bacteria present at end of 5 hours is 7346
Page 67 Problem 27 Answer
Given: Initial number of bacteria: P0=5000
Growth rate r=8%
r=0.08
Determine a formula for the number of bacteria present after n hours.
P=P0/(1+r)n
P=5000(1+0.08)n
P=5000(1.08)n
Formula for the number of bacteria present after n hours:
P=5000(1.08)n
Page 67 Problem 28 Answer
Given: Radius of circle in original diagram 81cm
To find circumference of the smallest circle in the 4th stage.
Original radius: 81
Smallest circle radius in stage1:1/3
(81)=27
Smallest circle radius in stage 2:1/3
(27)=9
Smallest circle radius in stage 3:1/3
(9)=3
Smallest circle radius in stage 4:1/3
(3)=1
Circumference of the smallest circle in the 4th
stage is: =2πr
=2π(1)
=2π
Circumference of the smallest circle in the 4th stage is: 2πcm
Page 67 Problem 29 Answer
Arithmetic Sequence
Definition: The difference between two consecutive terms in an arithmetic sequence is constant.
This difference is known as a common difference.
Formula: The formula to find the general term of an arithmetic sequence is:
tn=t1/+(n−1)d
Here, n is the number of terms, d is a common difference, tn is the general term and t1 is the first term.
Example: Consider the sequence: 4,8,12,16,20,…
We can observe that the difference between two consecutive terms in the above sequence is constant, 4.
Geometric Sequence
Definition: The ratio of consecutive terms in a geometric sequence is constant.
Formula: The formula to find the general term of a geometric sequence is:
tn=t1/rn−1
Here, n is the number of terms, r is the common ratio, t1 is the first term and tn is the general term.
Example: Consider the sequence: 3,9,27,81,…
We can observe that the ratio of consecutive terms in the above sequence is constant, 3.
Therefore, the definition, formula and example of arithmetic and geometric sequence are explained as;
Arithmetic Sequence
Definition: The difference between two consecutive terms in an arithmetic sequence is constant. This difference is known as a common difference.
Geometric Sequence
Definition: The ratio of consecutive terms in a geometric sequence is constant.
