Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Chapter 1 Tools of Geometry Exercise
Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Chapter 1 Tools Of Geometry Exercise Answers Page 1 Exercise 1 Problem 1
Given: 112
To simplify the above equation.
Using the method of the geometry.
The simplified equation is 112 = 121
Page 1 Exercise 2 Problem 2
Given: 2(7.5) + 2(11)
To simplify the above expression.
Using the method of geometry.
2(7.5) + 2(11) = 2(7.5) + 2(11)
2(7.5) + 2(11) = 15 + 22
2(7.5) + 2(11) = 37.
The simplified expression is 2.7.5 + 2.11 = 37.
Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Chapter 1 Tools of Geometry Page 1 Exercise 3 Problem 3
Given: π(5)2
To simplify the above expression.
Using the method of geometry.
= π(5)2
π = 3.14
π(5)2 = 3.14(5) 2
π(5)2 = 3.14(25)
π(5)2 = 78.5
The simplified expression is π(5)2 = 78.5.
Read and Learn More Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Solutions
Page 1 Exercise 4 Problem 4
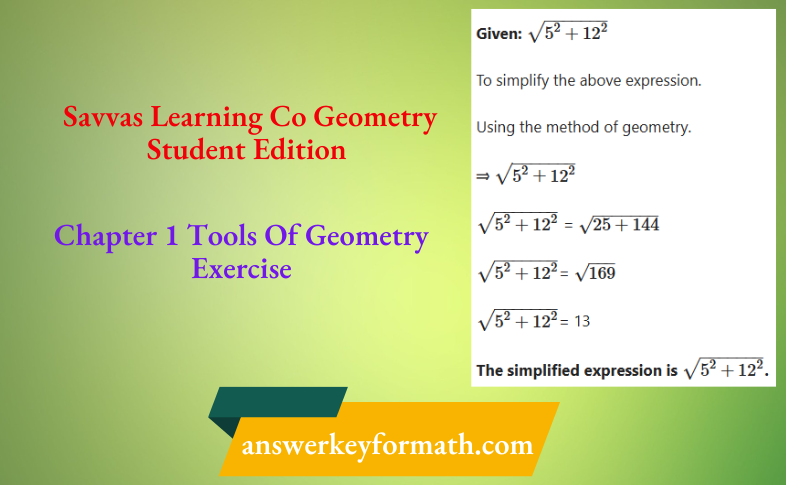
Chapter 1 Tools Of Geometry Exercise Solutions Savvas Learning Co Geometry Page 1 Exercise 5 Problem 5
Given: a = 4, b = −2
To find \(\frac{a−7}{3−b}\)
Using the method of geometry.
⇒ \(\frac{a−7}{3−b}\)
a = 4, b = −2
\(=\frac{4-7}{3-(-2)}\)
= \(\frac{-3}{5}\)
The evaluated expression is \(\frac{a−7}{3−b}\) = \(\frac{-3}{5}\)
Page 1 Exercise 6 Problem 6
Given: a = 4,b = −2
To find \(\sqrt{(7-a)^2+(2-b)^2}\)
Using the method of geometry
⇒ \(\sqrt{(7-a)^2+(2-b)^2}\)
= \(\sqrt{(7-4)^2+(2+2)^2}\)
= \(\sqrt{3^2+4^2}\)
= \(\sqrt{9+16}\)
= \(\sqrt{25}\)
= 5
The evaluated expression is \(\sqrt{(7-a)^2+(2-b)^2}\) = 5.
Savvas Geometry Student Edition Chapter 1 Solutions Tools of Geometry Page 1 Exercise 7 Problem 7
Given: ∣−8∣
To find the absolute value expression.
Using the method of geometry.
⇒ ∣−8∣
= 8
The absolute value is 8.
The absolute value of ∣−8∣ = 8.
Page 1 Exercise 8 Problem 8
Given: ∣2−6∣
To find the absolute value expression.
Using the method of geometry.
⇒ |2-6|
|2-6| = |− 4|
|2-6| = 4
The absolute value is 4
The absolute value of ∣2−6∣ = 4.
Tools Of Geometry Savvas Learning Co Chapter 1 Explanation Page 1 Exercise 9 Problem 9
Given: 2x + 7 = 13
To solve the equation.
Using the method of algebra.
2x = 6
x = \(\frac{6}{2}\)
x = 3
The solution of the equation is x = 3.
Page 1 Exercise 10 Problem 10
Given: 5x − 12 = 2x + 6
To solve the equation.
Using the method of algebra.
5x − 12 = 2x + 6
5x − 2x = 6 + 12
3x = 18
x = \(\frac{18}{3}\)
x = 6
The solution of the equation is x = 6.
Savvas Learning Co Geometry Chapter 1 Tools Of Geometry Explanation Guide Page 1 Exercise 11 Problem 11
Given: 2(x + 3) − 1 = 7x
To solve the equation.
Using the method of algebra.
2(x + 3)−1 = 7x
2x + 6 − 1 = 7x
2x + 5 = 7x
5 = 7x − 2x
5 = 5x
x = 1
The solution of the equation is x = 1.
Page 1 Exercise 12 Problem 12
Given: A child can construct models of buildings by stacking and arranging colored blocks.
To find the term construction mean in geometry.
Using the method of geometry.
Construction in Geometry means to draw shapes, angles, or lines accurately.
Construction in Geometry means to draw shapes, angles, or lines accurately.
Savvas Geometry Chapter 1 Answers For Tools Of Geometry Page 1 Exercise 13 Problem 13
Given: Artists often use long streaks to show rays of light coming from the sun.
To find the properties of a ray .
Using the method of geometry.
A ray is a line with a single endpoint (or point of origin) that extends infinitely in one direction.
A ray is a line with a single endpoint (or point of origin) that extends infinitely in one direction.
