Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Chapter 1 Tools of Geometry Exercise 1.3 Measuring Segments
Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Chapter 1 Exercise 1.3 Measuring Segments Solutions Page 23 Exercise 1 Problem 1
Given: The point on \(\overrightarrow{D A}\) that is 2 units from D.
To name each of the following.By using geometry theory.
The ray moves in the direction of A therefore the only point 2 units away from D is point B, because we have to move 2 units toward A.
Solving the question, we found that it is B.
Page 23 Exercise 2 Problem 2
Given:
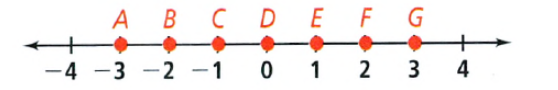
The coordinate of the midpoint of AG
Using properties of line.
Midpoint of \(\overrightarrow{A G}\)
= \(\frac{A+G}{2}\)
Midpoint of \(\overrightarrow{A G}\)
= \(\frac{3−3}{2}\)
Midpoint \(\overrightarrow{A G}\) = 0
The coordinate of the midpoint of \(\overrightarrow{A G}\) = 0 whcich is at D.
Read and Learn More Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Solutions
Exercise 1.3 Measuring Segments Savvas Geometry Answers Page 23 Exercise 3 Problem 3

Solving the question, we found point Q and line ℓ.
Page 23 Exercise 4 Problem 4
Given: Two segments are congruent and saying that two segments have equal length.
To find When would you use each phrase.
Using theoretical method.
If two segments are equal in length, then they are congruent and if they are congruent then they are equal in length.
But the word equal is used to compare numbers; we can not say that two numbers are congruent, we say that two numbers are equal.
And the word congruent is used to compare shapes; we can not say that two triangles are equal, we say that two triangles are congruent.
The word equal is used to compare numbers. and the word congruent is used to compare shapes.
Chapter 1 Exercise 1.3 Measuring Segments Savvas Learning Co Geometry Explanation Page 24 Exercise 5 Problem 5
Given: You and your friend live 5 mi apart. He says that it is 5 mi from his house to your house and −5 mi from your house to his house.
To find What is the error in his argument.
Using the theoretical method.
The error is that the distance is never negative.
He applied the rule that the distance between two points on the number line is the absolute value of the difference between the two points, but he did not apply the absolute value which gives only positive numbers.
For example, if we calculate the distance on the number line between the point 7 and the point 2, it should be
∣7 − 2∣ = ∣2 − 7∣ = 5 ≠ −5
The error is that the distance is never negative.
Solutions For Measuring Segments Exercise 1.3 In Savvas Geometry Chapter 1 Student Edition Page 24 Exercise 6 Problem 6
Given:
To Find the length of BD
Using addition.
Length of BD = 6 + 3
BD = 9 units
Length of BD = 9 units
Page 24 Exercise 7 Problem 7
Given:
To Find the length of AD
Using addition.
Length of AD = 3 + 8
AD = 11
Length of AD = 11
Exercise 1.3 Measuring Segments Savvas Learning Co Geometry Detailed Answers Page 24 Exercise 8 Problem 8
Given:
To Find the length CE
Using subtraction.
Length of CE = 7 − 1
CE = 6 units.
Length of CE = 6 units.
Page 24 Exercise 9 Problem 9
Given: RS = 15
ST = 9
To find RT
Using addition.
RT = RS + ST
RT = 15 + 9
RT = 24
Value of RT = 24.
Geometry Chapter 1 Measuring Segments Savvas Learning Co Explanation Guide Page 24 Exercise 10 Problem 10
Given:

To find value of y
Using RT = RS + ST
RT = RS + ST
15y−9 = 4y + 8 + 8y + 4
15y − 9 = 12y + 12
15y − 12y = 12 + 9
3y = 21
y = \(\frac{3}{21}\)
y = 7
Value of y = 7.
Page 24 Exercise 10 Problem 11
Given:

To find RS,ST, and RT
Using simple calculation
15y − 9 = 4y + 8 + 8y + 4
15y − 9 = 12y + 12
15y − 12y = 12 + 9
3y = 21
y =\(\frac{3}{21}\)
y = 7
ST = 4y + 8
ST = 4.7 + 8
ST = 28 + 8
ST = 36
RS = 8y + 4
RS = 8.7 + 4
RS = 60
RT = RS + ST
RT = 60 + 36
RT = 96
Value of ST = 36, RT = 96,RS = 60
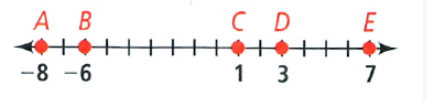
Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Chapter 1 Tools of Geometry Exercise 1.3 Measuring Segments Page 24 Exercise 11 Problem 12
Given:
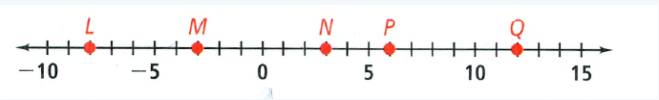
To Tell whether the segments \(\overline{M N}\) and \(\overline{P Q}\) are congruent.
Using properties of line.
\(\overline{M N}\) = |−3 − 3| = 6 units
\(\overline{P Q}\) = |6 − 12| = 6 units
Since distance between \(\overline{M N}\) and \(\overline{P Q}\) are equal so they are congruent.
\(\overline{M N}\) and \(\overline{P Q}\) are congurent.
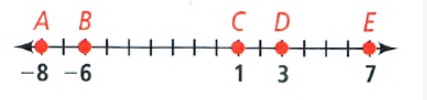
Page 24 Exercise 12 Problem 13
Given:
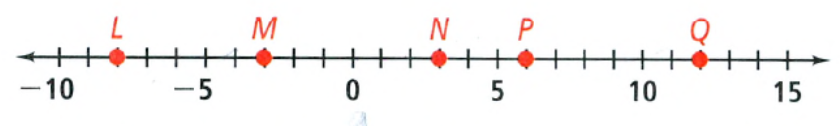
Tell whether the segments \(\overline{L P}\) and \(\overline{M Q}\) are congruent.
Using properties of line.
From the above figure we have
\(\overline{L P}\) = ∣−8−6∣ = 14 units
\(\overline{M Q}\) =∣−3−12∣ = 15 units.
So, distance between these two lines are not equal.
So, \(\overline{L P}\) and \(\overline{M Q}\) are not congruent \(\overline{L P}\) and \(\overline{M Q}\) are not congurent.
Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Chapter 1 Tools of Geometry Exercise 1.3 Measuring Segments Page 24 Exercise 13 Problem 14
Given: A is the midpoint of \(\overline{X Y}\)
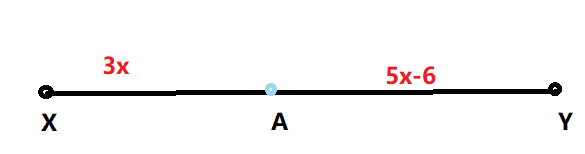
To find XA
Using the midpoint of the line segment method.
From the given figure, XA = 3x.
So, it is must to solve x, first.
It is also given that A is the midpoint of a line segment XY
So, XA = AY
Substitute the given expression
3x = 5x − 6
⇒ −2x = −6
⇒ x =\(\frac{−6}{-2}\)
⇒ x = 3
Value of XA is 3
Page 24 Exercise 13 Problem 15
Given: A is the midpoint of \(\overline{X Y}\)
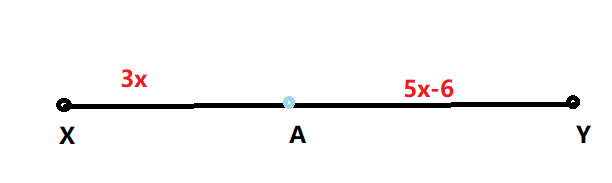
To find AY and XY.
Using the midpoint of line segment method
A is mid point of XY.
Therefore, value of XA and AY are equal.
⇒ 3x = 5 x− 6
⇒ 5x − 3x = 6
⇒ 2x = 6
⇒ x = 3
AY = 5x − 6
Substitute the value of x in equation for AY
AY = 5(3) − 6
⇒ 15 − 6
⇒ 9
By segment addition postulate
XA + AY = XY
⇒ 9 + 9 = 18
Value of AY is 9 and XY is 18.
Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Chapter 1 Tools of Geometry Exercise 1.3 Measuring Segments Page 24 Exercise 14 Problem 16
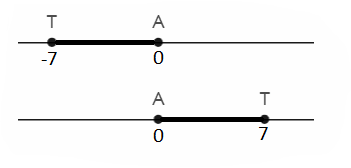
Given: PT = 5x + 3 ,TQ = 7x − 9
To find the value of PT
Using the midpoint of a line segment method
PT = 5x + 3
TQ = 7x − 9
Since T is the midpoint of a line segment PQ.
PT = TQ
5x + 3 = 7x − 9
Subtract 5x from both sides
3 = 2x − 9
Add 9 both sides
12 = 2x
x = \(\frac{12}{2}\)
6 = x or x = 6
Substitute value of x in PT = 5x + 3.
Then it results in PT = 5(6) + 3
⇒ 33
The value of PT n is 33
Page 24 Exercise 15 Problem 17
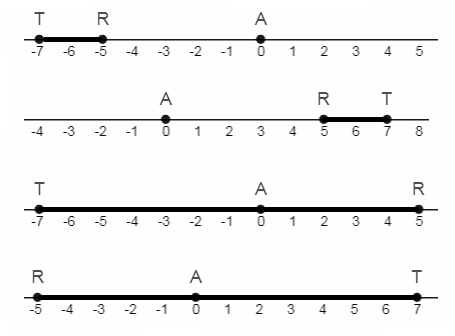
Given: PT = 4x − 6 , TQ = 3x + 4
To find the value of PT.
Using the midpoint of line segment method.
Given that
PT = 4x−6
So it is required to solve x first
PT = TQ
Substituting the expression
4x − 6 = 3x + 4
Solve for x
4x = 3x + 10
⇒ x = 10
Substituting value of x in PT
⇒ 4(10) − 6
⇒ 40 − 6
⇒ 34
Value of PT is 34.
Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Chapter 1 Tools of Geometry Exercise 1.3 Measuring Segments Page 24 Exercise 16 Problem 18
Given: X = −7, Y = −3,Z = 1 and W = 5
To find the length of the two-segmentUsing the formula distance between two points
Given the following coordinates:
X = −7,Y = −3, Z = 1 , and W = 5
The length of the segments:
ZX = ∣1−(−7)∣
ZX = ∣8∣
ZX = 8, and
WY = ∣5−(−3)∣
WY = ∣8∣
WY = 8
Since, ZX = WY ,then
\(\overline{Z X}\)= \(\overline{W Y}\).
The length of the two segments are 8 and 8 respectively and also they are congruent
Page 24 Exercise 17 Problem 19
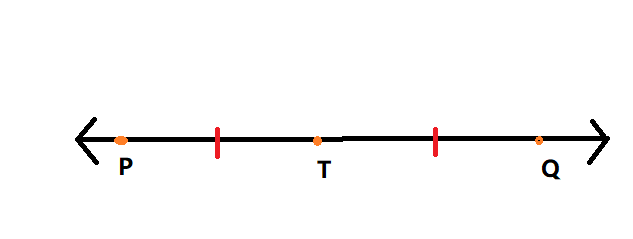
Given: The coordinate of A is 0, AR = 5, and AT = 7.
To find the possible coordinates of the midpoint of the \(\overline{A T}\).
Using the properties of geometry.
Let M be the midpoint of \(\overline{A T}\) , given that A = 0 so T may be located to the left or to the right of A as shown.
If T is to the left of A, then T = −7 so the midpoint is,
M = \(\frac{A+T}{2}\)
= \(\frac{0+(-7)}{2}\)
= \(\frac{-7}{2}\)
M = − 3.5
If T is to the right of A, then T = 7 so the midpoint is
M = \(\frac{A+T}{2}\)
M = \(\frac{0+(7)}{2}\)
M = \(\frac{7}{2}\)
M = 3.5
The possible coordinates of the segment is M = −3.5 or M = 3.5
Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Chapter 1 Tools of Geometry Exercise 1.3 Measuring Segments Page 24 Exercise 18 Problem 20
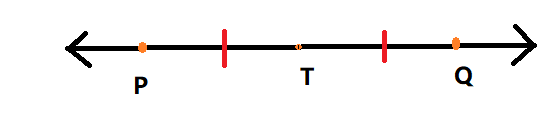
Given: The coordinate of A is 0, and AR = 5 and AT = 7.
To find the possible coordinates of the midpoint of the RT
Using the properties of geometry.
Let M be the midpoint o \(\overline{R T}\)
We are given that A = 0 so R and T may be located to the left or to the right of A as shown
If both R and T is to the left of A ,the mid point is
M = \(\frac{R+T}{2}\)
M = \(\frac{-5+(-7)}{2}\)
M = \(\frac{-12}{2}\)
Therefore M = −6.
If both R and T is to the right of A ,the mid point is
M = \(\frac{R+T}{2}\)
M = \(\frac{5+(7)}{2}\)
M = \(\frac{12}{2}\)
Therefore M = 6.
If T is left of A and R is to the right of A ,the midpoint is
M = \(\frac{R+T}{2}\)
M = \(\frac{5+(-7)}{2}\)
M = \(\frac{-2}{2}\)
M = − 1
Therefore M = −1
If R is left of A and T is to the right of A , the midpoint is
M = \(\frac{R+T}{2}\)
M = \(\frac{-5+(7)}{2}\)
M = \(\frac{2}{2}\)
M = 1
Therefore M = 1
The possible coordinates of the segment is M = −6 or M = 6 or M = −1 or M = 1.
Page 25 Exercise 19 Problem 21
Given: To sketch a segment without using a ruler.
To sketch a segment of 3 in.
Using geometrical method.
Sketch the segment with 3 in

The segment of 3 in is

Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Chapter 1 Tools of Geometry Exercise 1.3 Measuring Segments Page 25 Exercise 20 Problem 22
Given: To sketch a segment without using a ruler.
To sketch a segment of 6 in.
Using geometrical method.
The segment with 6 in is
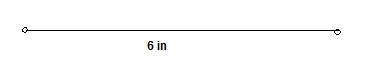
Segment with 6 in is
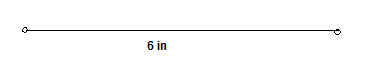
Page 25 Exercise 21 Problem 23
Given: To sketch a segment without using a ruler.
To sketch a segment of 10 cm.
Using geometrical method.
The segment with 10 cm is
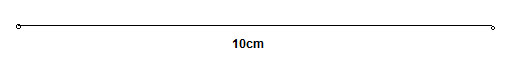
Segment with 10 cm is
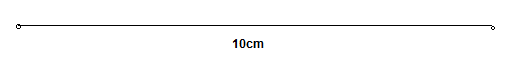
Page 26 Exercise 22 Problem 24
Given: To sketch a segment without using a ruler.
To sketch a segment of 65 mm.
Using geometrical method.
The segment with 65 mm is
![]()
Segment with 65 mm is
![]()
Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Chapter 1 Tools of Geometry Exercise 1.3 Measuring Segments Page 25 Exercise 23 Problem 25
Given: A map of Florida and assuming that the route 10 between Quincy and Jacksonville is straight.
If you drive an average speed of 55 mi/h ,how long it will take to get from Lake Oak to Jacksonville.
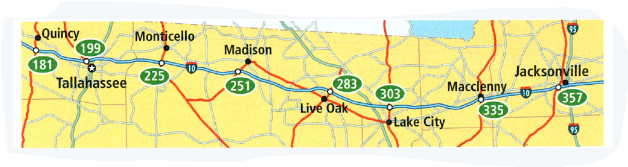
To find out how can you use mile markers to find distances between points.
o find how average speed, distance, and time all relate to each other.Using average speed formula.
From the figure we can see that:
Live Oak is marked as 283
Jacksonville is marked as 357
Therefore the distance between the two places is 357 − 283 = 74
Average speed = distance traveled/time taken
Substitute average speed = 55 and distance = 74
To get 55 = ( 74 /Time taken)
Time taken =\(\frac{74}{55}\) ≈ 1.35 Hours.
The average speed, distance, and time all relate to each other asb Time taken =\(\frac{74}{55}\) ≈ 1.35 Hours.
