Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Chapter 2 Reasoning And Proof Exercise
Page 79 Exercise 1 Problem 1
Given: An expression, 9x − 13
To find: The value of the expression at x = 7
Let, p(x) = 9x − 13
Now,p(7) = 9 × 7 − 13
⇒ p(7) = 63 − 13
⇒ p(7) = 50
The value of the given expression at x = 7 is 50.
Page 79 Exercise 2 Problem 2
Given: An expression, 90 − 3x
To find: The value of the expression at x = 31
Let,p(x) = 90 − 3x
Now, p(31) = 90 − 3 × 31
⇒ p(31) = 90 − 93
⇒ p(31) = −3
The value of the given expression at x = 31 is−3.
Read and Learn More Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Solutions
Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Chapter 2 Page 79 Exercise 3 Problem 3

Page 79 Exercise 4 Problem 4
Given: An algebraic equation, 2x − 17 = 4
To find: The value of x
We have
⇒ 2x − 17 = 4
⇒ 2x = 4 + 17
⇒ 2x = 21
⇒ x = \(\frac{21}{2}\)
The solution of the given algebraic equation is x = \(\frac{21}{2}\).
Page 79 Exercise 5 Problem 5
Given: An algebraic equation,(10x + 5) + (6x − 1) = 180
To find: The value of x.
We have
⇒ (10x + 5) + (6x − 1) = 180
⇒ 16x + 5 − 1 = 180
⇒ 16x + 4 = 180
⇒ 16x = 176
⇒ x = 11
The solution of the given algebraic equation is x = 11.
Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Chapter 2 Page 79 Exercise 6 Problem 6
Given: An algebraic equation,14x = 2(5x + 14)
To find: The value of x.
We have
⇒ 14x = 2(5x + 14)
⇒ 14x = 10x + 28
⇒ 4x = 28
⇒ x = 7
The solution of the given algebraic equation is x = 7.
Page 79 Exercise 7 Problem 7
Given: An algebraic equation,2(x + 4) = x + 13
To find: The value of x.
We have
⇒ 2(x + 4) = x + 13
⇒ 2x + 8 = x + 13
⇒ x = 13 − 8
⇒ x = 5
The solution of the given algebraic equation is x = 5.
Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Chapter 2 Page 79 Exercise 8 Problem 8
Given: An algebraic equation,7x + 5 = 5x + 17
To find: The value of x
We have
⇒ 7x + 5 = 5x + 17
⇒ 7x − 5x = 17 − 5
⇒ 2x = 12
⇒ x = 6
The solution of the given algebraic equation is x = 6.
Page 79 Exercise 9 Problem 9
Given: An algebraic equation,(x + 21) + (2x + 9) = 90
To find: The value of x
We have
⇒ (x + 21) + (2x + 9) = 90
⇒ x + 2x + 21 + 9 =90
⇒ 3x + 30 = 90
⇒ 3x = 60
⇒ x = 20
The solution of the given algebraic equation is x = 20.
Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Chapter 2 Page 79 Exercise 10 Problem 10
Given: An algebraic equation,2(3x − 4) + 10 = 5(x + 4)
To find: The value of x
We have
⇒ 2(3x − 4) + 10 = 5(x + 4)
⇒ 6x − 8 + 10 = 5x + 20
⇒ 6x − 5x = 20 + 8 − 10
⇒ x = 18
The solution of the given algebraic equation is x = 18.
Page 79 Exercise 11 Problem 11
Given: m∠1 = 4y and m∠2 = 2y + 18
To find: m∠1&m∠2.
We have ∠ACB = 90 (since∠ACB is a right angle)
⇒ m∠1 + m∠2 = 90
⇒ 4y + 2y + 18 = 90
⇒ 6y = 72
⇒ y = 12
Now,m∠1 = 4 × 12
⇒ m∠1 = 48° and m∠2 = 2 × 12 + 18
⇒ m∠2 = 42°
The value of m∠1 = 48° and that of m∠2 = 42°.
Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Chapter 2 Page 79 Exercise 12 Problem 12
Given: A figure.
To find: Linear pairs.
According to the definition of linear pair, we can only find one linear pair in the given figure and i.e., ∠ADC & ∠BDC.
The pair of angles that form a linear pair is ∠ADC & ∠BDC.
Page 79 Exercise 13 Problem 13
Given: A figure.
To find: A pair of adjacent angles that are not supplementary.
Clearly, ∠1 & ∠2 form a pair of adjacent angles that are not supplementary.
A pair of adjacent angles that are not supplementary is ∠1 & ∠2
Page 79 Exercise 14 Problem 14
Given: m∠ADC + m∠BDC = 180.
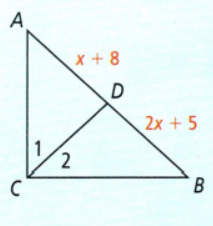
To find: Straight angle form.
The straight angle form has a measure 180° and is the sum of m∠ADC + m∠BDC is ∠ADB.
The required straight angle is ∠ADB.
Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Chapter 2 Page 79 Exercise 15 Problem 15
Given: The conclusion of a novel answers questions raised by the story.
To find: How do you think the term conclusion applies in geometryHypotheses are the answer you think you’ll find.
Prediction is your specific belief about the scientific idea: If my hypothesis is true, then I predict we will discover this.
The conclusion is the answer that the experiment gives.
The part of a conditional statement after then.
For example, the conclusion of “If a line is horizontal then the line has slope 0 ” is “the line has a slope 0”.
The term conclusion applies in geometry is that it gives the final value of the question.
Page 79 Exercise 16 Problem 16
Given: A detective uses deductive reasoning to solve a case by gathering, combining, and analyzing clues.
To find: How might you use deductive reasoning in geometryDeductive geometry is the art of deriving new geometric facts from previously-known facts by using logical reasoning.
In elementary school, many geometric facts are introduced by folding, cutting, or measuring exercises, not by logical deduction. In geometry, a written logical argument is called proof.
Deductive reasoning in geometry is much like the situation described above, except it relates to geometric terms. For example, given that a certain quadrilateral is a rectangle, and that all rectangles have equal diagonals, what can you deduce about the diagonals of this specific rectangle. They are equal.
