Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Chapter 6 Polygons And Quadrilaterals Exercise 6.2 Properties of Parallelograms
Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Chapter 6 Exercise 6.2 Properties Of Parallelograms Solutions Page 363 Exercise 1 Problem 1
Given: The parallelogram as
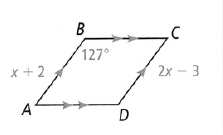
To find – The value of m∠A.
We will be using the properties of the parallelogram to find the above asked.
From the figure, we have ∠B = 127°.
Now as the opposite angles of the parallelogram are equal so we have
⇒ ∠B = ∠D
⇒ ∠A = ∠C
By angle sum property we have
⇒ ∠A + ∠B + ∠C + ∠D = 360°
⇒ ∠A + 127o + ∠A + 127°
= 360°
⇒ 2∠A + 254° = 360°
⇒ 2∠A = 106°
⇒ ∠A = \(\frac{63}{2}\)
⇒ ∠A = 53°
The value of m∠A is 53°.
Read and Learn More Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Solutions
Exercise 6.2 Properties Of Parallelograms Savvas Geometry Answers Page 363 Exercise 2 Problem 2
Given: The parallelogram as
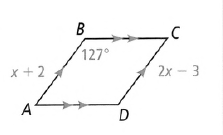
To find – The value of m∠D.
We will be using the properties of the parallelogram to find the above asked.
From the given figure we have ∠B = 127°.
Now as the opposite angles of the parallelogram are equal so, we have
⇒ ∠B = ∠D
⇒ ∠D = 127°
The value of m∠D is 127°.
Exercise 6.2 Properties Of Parallelograms Savvas Geometry Answers Page 363 Exercise 3 Problem 3
Given: The parallelogram as
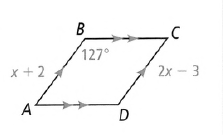
To find – The value of x.
We will be using the properties of the parallelogram to find the above asked.
From the given figure, we have AB = x + 2
⇒ CD = 2x − 3.
Mow in a parallelogram the opposite sides are equal so, we have
⇒ AB = CD
⇒ x + 2 = 2x − 3
⇒ 2x − x = 3 + 2
⇒ x = 5
The value of x is 5.
Properties Of Parallelograms Solutions Chapter 6 Exercise 6.2 Savvas Geometry Page 363 Exercise 4 Problem 4
Given: The parallelogram as
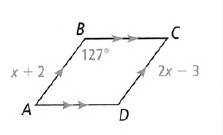
To find – The value of AB.
We will be using the properties of the parallelogram to find the above asked.
Now as we have that ABCD is a parallelogram, so the opposite sides are parallel and equal, that is AB = CD.
So, we have :
⇒ x + 2 = 2x − 3
⇒ 2x − x = 3 + 2
⇒ x = 5
From the given figure, we have AB = x + 2.
And we have x = 5, which gives
⇒ AB = x + 2
⇒ AB = 5 + 2
⇒ AB = 7
The value of AB is 7.
Properties Of Parallelograms Solutions Chapter 6 Exercise 6.2 Savvas Geometry Page 363 Exercise 5 Problem 5
Given: The figure as

Since, AB = BC so we know by theorem 6−7 that is three or more parallel lines cut off congruent segments on one transversal then they cut off congruent segments on every transversal.
So we have
⇒ FE = ED
⇒ ED = 12
⇒ FD = FE + ED
= 12 + 12
= 24
The value of ED = 12 and FD = 24.
Chapter 6 Exercise 6.2 Properties Of Parallelograms Savvas Learning Co Geometry Explanation Page 363 Exercise 6 Problem 6
If we know one measure of angle, we can find the other three angles by using the angle sum property of a quadrilateral, which says that the sum of all the angles is 360o
Also, in the parallelogram the opposite angles are equal so, we can easily find the measure of three angles if we have the measure of one angle.
For example if in a parallelogram one angle is x , then the opposite angle will also be x and suppose the adjacent angle to x is y , so the opposite angle will also be y.
So by angle sum property we have x + x + y + y = 360°.
So if we have one known value of angle of a parallelogram, then we can find the other three by using angle sum property of the quadrilateral and by using the property of parallelogram that opposite angles are equal.
Chapter 6 Exercise 6.2 Properties Of Parallelograms Savvas Learning Co Geometry Explanation Page 363 Exercise 7 Problem 7
We may have the difference between quadrilateral and parallelogram written as -Quadrilaterals are polygons with four sides while parallelogram is a special type of a quadrilateral that has some special properties.
The four sides of quadrilateral cannot be equal or parallel but in a parallelogram the opposite sides are equal and parallel.
The angles in a Quadrilateral may vary and may not be all equal but in a parallelogram the opposite angles are equal.
The diagonals of a parallelogram divides the parallelogram into two congruent triangles, but this may not be necessary in a quadrilateral.
The diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other but this is not necessary in a quadrilateral.
The difference between quadrilateral and parallelogram is given below :
⇒ Quadrilaterals are polygons with four sides while parallelogram is a special type of a quadrilateral that has some special properties.
⇒ The four sides of quadrilateral cannot be equal or parallel but in a parallelogram the opposite sides are equal and parallel.
⇒ The angles in a Quadrilateral may vary and may not be all equal but in a parallelogram the opposite angles are equal.
⇒ The diagonals of a parallelogram divides the parallelogram into two congruent triangles, but this may not be necessary in a quadrilateral.
⇒ The diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other but this is not necessary in a quadrilateral.
Chapter 6 Exercise 6.2 Properties Of Parallelograms Savvas Learning Co Geometry Explanation Page 363 Exercise 8 Problem 8
Consider the figure given to us as
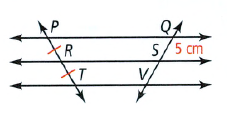
Now we are given that
PR ≅ RT
QS = 5cm
PT and QV ae transversals of the lines PQ, RS,TV.
The classmate has applied the following theorem
Theorem: If three ( or more) parallel lines cut off congruent segments on one transversal, then they cut off congruent segments on every transversal.
Since, the lines PQ,RS and TV are not given to be parallel, therefore, the statement QV = 10 may not be correct.
The statement given by our classmate that is QV = 10 may not be correct because we are not given any lines to be parallel.
Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Chapter 6 Page 364 Exercise 9 Problem 9
Given: We have the parallelogram with one angle as 53° and one as x°
The figure for the same is given below
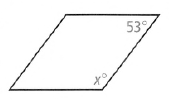
To find – The value of x.
We will be using the properties of parallelogram to find the value of the given variable.
We have one angle of parallelogram as 53° as the opposite angles are equal in a parallelogram so the opposite angle will also be 53°.
Similarly, we have two angles measuring as x°.
By angle sum property of a quadrilateral we have
⇒ 53 + x + 53 + x = 360
⇒ 2x + 106 = 360
⇒ 2x = 360 − 106
⇒ 2x = 254
⇒ x = \(\frac{254}{2}\)
⇒ x = 127°
The value of x is given as 127°.
Solutions For Properties Of Parallelograms Exercise 6.2 In Savvas Geometry Chapter 6 Student Edition Page 364 Exercise 10 Problem 10
Given: We have the parallelogram with two angles given as 113° and x°.
The figure for the same is given below
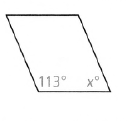
To find – The value of x.
We will be using the concept of properties of parallelogram to find the value of the unknown variable.
We are given one angle as 113°.
As opposite angles in parallelogram are equal to the other opposite angle will be 113°
Similarly, we have two angles as x°.
By angle sum property of quadrilateral, we have
⇒ 113 + x + 113 + x = 360
⇒ 2x + 226 = 360
⇒ 2x = 134
⇒ x = \(\frac{134}{2}\)
⇒ x = 67°
The value of x is given as 67°.
Solutions For Properties Of Parallelograms Exercise 6.2 In Savvas Geometry Chapter 6 Student Edition Page 364 Exercise 11 Problem 11
Given: The figure of the parallelogram is
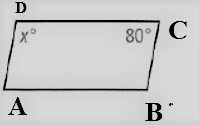
To find – We have to find the value of x.
We will analyze the given data and then apply the condition to solve the problem.
Given, The figure of the parallelogram is
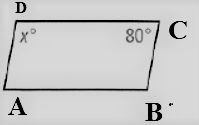
As we now that, the opposite angles of a parallelogram are equal.
Thus , ∠D = ∠B , ∠A = ∠B
The angle sum property of a parallelogram tells that
⇒ ∠A + ∠B ∠C + ∠D = 180°
⇒ 80° + x°+ 80° + x° = 180°
⇒ 2x = 180° − 160°
⇒ x =\(\frac{20^{\circ}}{2}\)
⇒ x = 10°
Hence, the value of x = 10°.
The value of x in given parallelogram is 10°.
Exercise 6.2 Properties Of Parallelograms Savvas Learning Co Geometry Detailed Answers Page 364 Exercise 12 Problem 12
Given: The figure of the parallelogram is
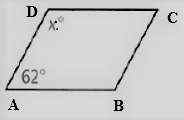
To find – We have to find the value of x.
We will analyze the given data and then apply the condition to solve the problem.
Given, The figure of the parallelogram is
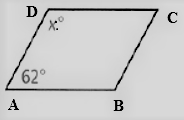
As we now that, the opposite angles of a parallelogram are equal.
Thus , ∠D = ∠B , ∠A = ∠C
The angle sum property of a parallelogram tells that
⇒ ∠A + ∠B + ∠C + ∠D = 180°
⇒ 62° + x + 62° + x = 180°
⇒ 2x = 180° − 124°
⇒ x = \(\frac{56^{\circ}}{2}\)
⇒ x = 28°
Hence, the value of x = 28°.
The value of x in given parallelogram is 28°.
Exercise 6.2 Properties Of Parallelograms Savvas Learning Co Geometry Detailed Answers Page 364 Exercise 13 Problem 13
Given: The figure of the parallelogram is

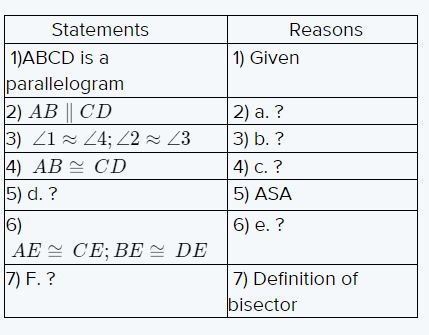
To find – We have to complete the given table.
We will analyze the given data and then apply the condition to solve the problem.
Given, The figure of the parallelogram is
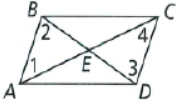
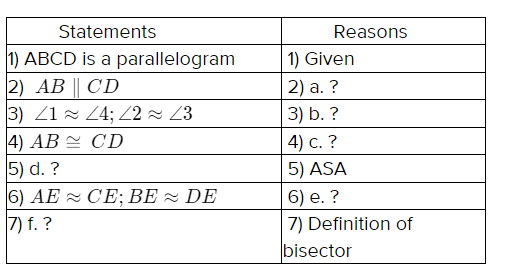
Since, ABCD is a parallelogram, which means.
Its opposite sides are parallel
Thus, AB ∥ CD
And ∠1 = ∠4 (Alternate Interior angle Property)
Similarly ∠2 = ∠3
Since, opposite sides of a parallelogram are equal.
Thus, AB ≈ CD
In triangle AED & BEC
∠1 = ∠4 (Alternate Interior Angle Property)
AD = BC (Opposite Sides of a parallelogram are equal)
∠AED = ∠BEC (Vertically Opposite Angle Property)
Hence, by ASA Congruency ΔAED ≅ ΔBEC.
The diagonals of a parallelogram bisects each other.
Thus, AE = CE, BE = DE
The bisector is a ray or a segment which divides the geometry in two identical halves.
In the parallelogram ABCD ,AC and BD bisects each other at E.
Exercise 6.2 Properties Of Parallelograms Savvas Learning Co Geometry Detailed Answers Page 364 Exercise 14 Problem 14
Given: The side lengths given are
⇒ PT = 2x
⇒ TR = y + 4
⇒ QT = x + 2
⇒ TS = y
The figure of the parallelogram is
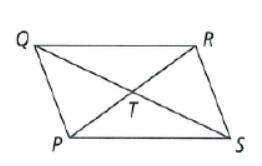
To find – We have to find the value of x and y.
We will analyze the given data and then apply the condition to solve the problem.
Given, The side lengths given are
⇒ PT = 2x
⇒ TR = y + 4
⇒ QT = x + 2
⇒ TS = y
The figure of the parallelogram is
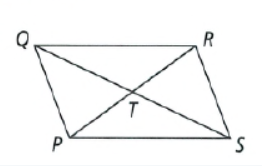
Since, the diagonals of a parallelogram bisects each other.
So, PT = TR , QT = TS
Thus, the equation obtained are
⇒ 2x = y + 4 and x + 2 = y
On solving the above equations, we get
⇒ 2x = (x + 2) + 4
⇒ 2x − x = 4 + 2
⇒ x = 6
⇒ y = 6 + 2
⇒ y = 8
Hence, the value of x = 6 and y = 8.
The value of x and y in given parallelogram is 6 and 8.
Geometry Chapter 6 Properties Of Parallelograms Savvas Learning Co Explanation Guide Page 364 Exercise 15 Problem 15
Given: The given sides are
⇒ PT = x + 2
⇒ TR = y
⇒ QT = 2x
⇒ TS = y + 3
The figure of the parallelogram is
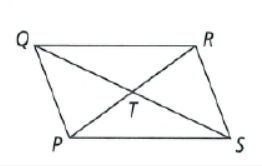
To find – We have to find the value of x and y.
We will analyze the given data and then apply the condition to solve the problem.
Given, The given side lengths are
⇒ PT = x + 2
⇒ TR = y
⇒ QT = 2x
⇒ TS = y + 3
The figure of the parallelogram is
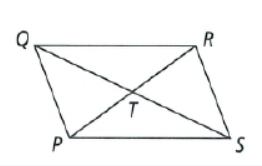
Since, the diagonals of a parallelogram bisects each other.
⇒ PT = TR
⇒ QT = TS
So, the equations obtained are x + 2 = y and 2x = y + 3
On solving the above equations, we get
⇒ 2x = (x + 2) + 3
⇒ 2x − x = 2 + 3
⇒ x = 5
⇒ y = 5 + 2
⇒ y = 7
Hence, the value of x = 5 and y = 7.
The value of x and y in given parallelogram is 5 and 7.
Geometry Chapter 6 Properties Of Parallelograms Savvas Learning Co Explanation Guide Page 364 Exercise 16 Problem 16
Given: The relation between the segments are PQ = QR = RS
The diagram given is
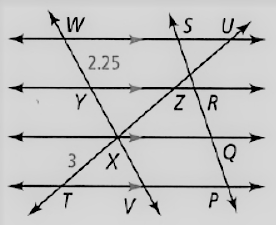
To find – We have to find the length of XZ.
We will analyze the given data and then apply the condition to solve the problem.
Given, The side length given are
PQ = QR = RS
The diagram given is
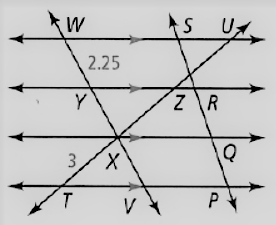
Since, the if a line cuts the parallel lines of pair of three or more, then
Those parallel lines will divide the cutting lines in equal segments.
So, XT = XZ = ZU
As it is given that, the length of the segment is
XT = 3
Thus , XT = XZ
⇒ XZ = 3
Hence, the value of XZ = 3.
The value of XZ in the given figure is 3.
Exercise 6.2 Properties Of Parallelograms Savvas Geometry Answers Page 364 Exercise 17 Problem 17
Given: The relation given is PQ = QR = RS
The diagram given is
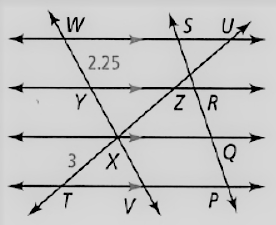
To find – We have to find the length of TU.
We will analyze the given data and then apply the condition to solve the problem.
Given, The relation given is
PQ = QR = RS
The diagram given is
Since, the if a line cuts the parallel lines of pair of three or more, then
Those parallel lines will divide the cutting lines in equal segments.
So , XT = XZ = ZU
As it known that, the length of the segment XT = 3
Thus, TU = XT + ZX + ZU
⇒ TU = 3(XT)
⇒ TU = 3(3)
⇒ TU = 9
Hence, the value of TU = 9.
The value of TU in the given figure is 9.
Exercise 6.2 Properties Of Parallelograms Savvas Geometry Answers Page 364 Exercise 18 Problem 18
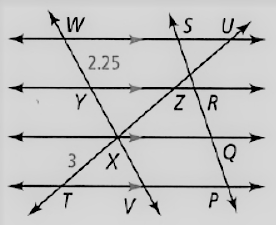
Given: The relation given is PQ = QR = RS
The diagram given is
To find – We have to find the length of XV.
We will analyze the given data and then apply the condition to solve the problem.
Given, The relation given is
PQ = QR = RS
The diagram given is
Since, the if a line cuts the parallel lines of pair of three or more, then
Those parallel lines will divide the cutting lines in equal segments.
So, WY = YX = XV
As we know that, the length of the segment is
⇒ WY = 2.25
Thus ,WY = XV
⇒ XV = 2.25
Hence, the value of XV = 2.25.
The value of XV in the given figure is 2.25.
Properties Of Parallelograms Solutions Chapter 6 Exercise 6.2 Savvas Geometry Page 364 Exercise 19 Problem 19
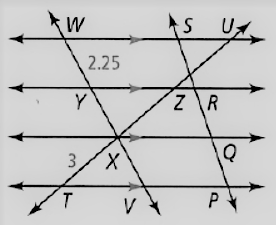
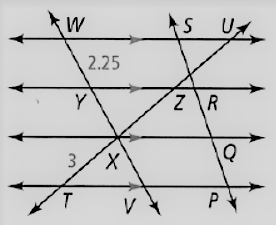
Given: The given relation is PQ = QR = RS
The diagram given is
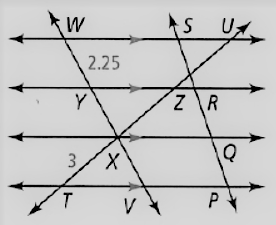
To find – We have to find the length of YV.
We will analyze the given data and then apply the condition to solve the problem.
Given, The given relation is, PQ = QR = RS
The diagram given is
Since, the if a line cuts the parallel lines of pair of three or more, then
Those parallel lines will divide the cutting lines in equal segments.
So , WY = YX = XV
As we know that, the length of the segment is
WY = 2.25
Thus , YV = YX + XV
⇒ YV = 2XV
⇒ YV = 2WY
⇒ YV = 2(2.25)
⇒ YV = 4.5
Hence, the value of YV = 4.5.
The value of YV in the give figure is 4.5.
Properties Of Parallelograms Solutions Chapter 6 Exercise 6.2 Savvas Geometry Page 364 Exercise 20 Problem 20
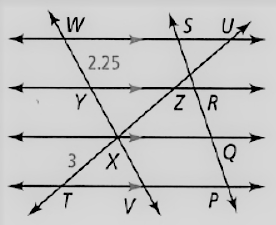
Given: The given relation is PQ = QR = RS
The diagram given is
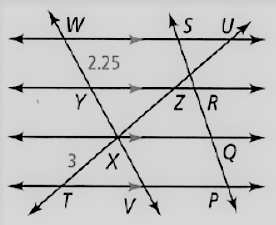
To find – We have to find the length of WV.
We will analyze the given data and then apply the condition to solve the problem.
Given, The given relation is, PQ = QR = RS
The diagram given is
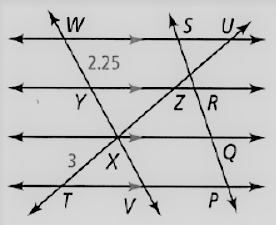
Since, the if a line cuts the parallel lines of pair of three or more, then
Those parallel lines will divide the cutting lines in equal segments.
So, WY = YX = XV
As we know that, the length of the segment is
⇒ WY = 2.25
Thus , WV = WY + YX + XV
⇒ WV = 3WY
⇒ WV = 3(2.25)
⇒ WV = 6.75
Hence, the value of WV = 6.75.
The value of WV in the given figure is 6.75.
Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Chapter 6 Page 364 Exercise 21 Problem 21
Given: The parallelogram given is
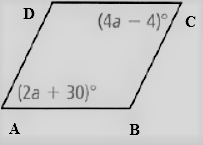
To find – We have to find the values of each variables in the given parallelogram.
We will analyze the given data and then apply the condition to solve the problem.
Given, The parallelogram given is
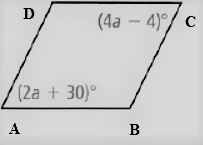
As we now that, the opposite angles of a parallelogram are equal.
Thus , ∠A = ∠C
So, the angles are related as
⇒ 4a − 4 = 2a + 30
⇒ 4a − 2a = 30 + 4
⇒ 2a = 34
⇒ a = \(\frac{34}{2}\)
⇒ a = 17
Hence, the value of a = 17.
The value of a in the given parallelogram is 17.
Properties Of Parallelograms Solutions Chapter 6 Exercise 6.2 Savvas Geometry Page 365 Exercise 22 Problem 22
Given: The parallelogram given is
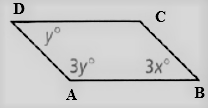
To find – We have to find the values of x and y and we have to find the relation between the angles.
We will analyze the given data and then apply the condition to solve the problem.
Given, The parallelogram given is
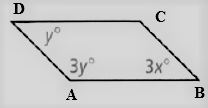
As we now that, the opposite angles of a parallelogram are equal.
So, ∠D = ∠B, ∠A = ∠C
Thus, the angles are related as y = 3x, ∠C = 3y
As we know the angle sum property of a parallelogram
⇒ ∠A + ∠B + ∠C + ∠D = 360°
⇒ 3y + 3x + 3y + y = 360°
⇒ 3y + y + 3y + y = 360°
⇒ 8y = 360°
⇒ y = \(\frac{360^{\circ}}{8}\)
⇒ y = 45°
⇒ x = \(\frac{45^{\circ}}{3}\)
⇒ x = 15°
Hence, the value of x = 15° and y = 45°.
The relation between angles in the given parallelogram is y = 3x and ∠C = 3y and the values of x andy are 15° and 45°.
Chapter 6 Exercise 6.2 Properties Of Parallelograms Savvas Learning Co Geometry Explanation Page 365 Exercise 22 Problem 23
Given: The parallelogram given is
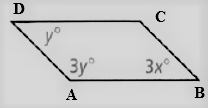
To find – We have to find the values of x and y and also have to tell which variable is going to be solved first.
We will analyze the given data and then apply the condition to solve the problem
Given, The parallelogram given is
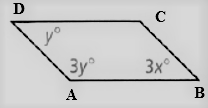
As we now that, the opposite angles of a parallelogram are equal.
So, ∠D = ∠B , ∠A = ∠C
Thus, the angles are related as y = 3x, ∠C = 3y
As we know the angle sum property of a parallelogram
⇒ ∠A + ∠B + ∠C + ∠D = 360°
⇒ 3y + 3x + 3y + y = 360°
⇒ 3y + y + 3y + y = 360°
⇒ 8y = 360°
⇒ y = \(\frac{360^{\circ}}{8}\)
⇒ y = 45°
⇒ x = \(\frac{45^{\circ}}{3}\)
⇒ x = 15°
Hence, the value of x = 15° and y = 45°.
The variable first going to be solve is y m and the values of x and y are 15° and 45°.
Chapter 6 Exercise 6.2 Properties Of Parallelograms Savvas Learning Co Geometry Explanation Page 365 Exercise 23 Problem 24
Given: The parallelogram given is
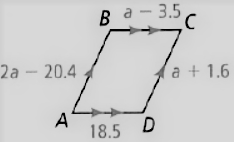
To find – We have to find the length of given parallelogram.
We will analyze the given data and then apply the condition to solve the problem.
Given, The parallelogram given is
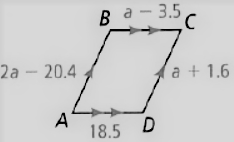
Since, the length of opposite sides of parallelogram are equal.
So, AD = BC , AB = CD
Thus, the sides are related as
⇒ 18.5 = a − 3.5
⇒ a = 18.5 + 3.5
⇒ a = 22
The length of sides are
⇒ CD = a + 1.6
⇒ 22 + 16
⇒ 38
BC = a − 3.5
⇒ 22.0 − 3.5
⇒ 18.5
AB = 2a − 20.4
⇒ 2(22.0) − 20.4
⇒ 44.0 − 20.4
⇒ 23.6
Hence, the length of sides are
CD = 38
BC = 18.5
AB = 23.6
AD 18.5.
The length of sides of the given parallelogram are CD = 38, BC = 18.5, AB = 23.6, AD = 18.5.
Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Chapter 6 Page 365 Exercise 24 Problem 25
Given: The parallelogram given is
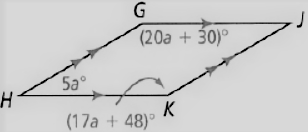
To find – We have to find the value of a angle measure of given parallelogram.
We will analyze the given data and then apply the condition to solve the problem.
Given, The parallelogram given is
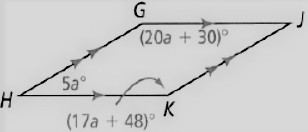
As we now that, the opposite angles of a parallelogram are equal.
So, ∠G = ∠K ∠H = ∠J
Thus, the angles are related as
⇒ 20a + 30 = 17a + 48
⇒ 20a − 17a = 48 − 30
⇒ 3a = 18
⇒ a = 6
The angle measures are
∠G = (20a + 30)°
⇒ (20(6) + 30)°
⇒ 150°
∠H = 5a°
⇒ 5(6)°
⇒ 30°
∠J = ∠H
⇒ ∠J = 30°
∠K = ∠G
⇒ ∠K = 150°
Chapter 6 Exercise 6.2 Properties Of Parallelograms Savvas Learning Co Geometry Explanation
Hence, the angle measure are
⇒ ∠G = 150°
⇒ ∠H = 30°
⇒ ∠J = 30°
⇒ ∠K = 150°.
The values of angle measure of given parallelogram is ∠G = 150°, ∠H = 30°, ∠J = 30°, ∠K = 150°.
