Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Chapter 7 Similarity Exercise
Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Chapter 7 Similarity Exercise Solutions Page 429 Exercise 1 Problem 1
In this question, we have been given a diagram and an angle ∠1.
We need to find the measure of an angle.
By using Supplementary angles, we will calculate the result.
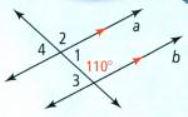
When two angles add up to 180 degrees, they are considered to be supplementary angles.
A straight line is formed by the intersection of two angles, but the angles do not have to be the same.
So, we find the angle by subtracting 110 to the 180 degrees
⇒ ∠1 + 110° = 180°
⇒ ∠1 = 180° − 110°
⇒ ∠1 = 70°
By using Supplementary angles, the measure of the given angle ∠1 is 70°
Chapter 7 Similarity Exercise Savvas Geometry Answers Page 429 Exercise 2 Problem 2
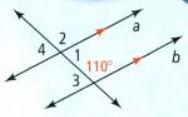
In this question, we have been given a diagram and an angle ∠2.
We need to find the measure of an angle.
By using Supplementary angles, we will calculate the result.
Read and Learn More Savvas Learning Co Geometry Student Edition Solutions
When two angles add up to 180 degrees, they are considered to be supplementary angles.
A straight line is formed by the intersection of two angles, but the angles do not have to be the same.
Since the previous exercise 1 , we have the value ∠1=70°.
So, we find the angle by subtracting 70 to the 180 degrees
⇒ ∠2+70° = 180°
⇒ ∠2 = 180° − 70°
⇒ ∠2 = 110°
By using Supplementary angles, the measure of the given angle ∠2 is 110°.
Chapter 7 Similarity Exercise Savvas Geometry Answers Page 429 Exercise 3 Problem 3
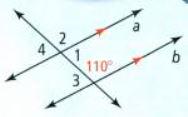
In this question, we have been given a diagram and an angle ∠3.
We need to find the measure of an angle.
By using Supplementary angles, we will calculate the result.
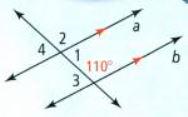
When two angles add up to 180 degrees, they are considered to be supplementary angles.
A straight line is formed by the intersection of two angles, but the angles do not have to be the same.
So, we find the angle by subtracting 110 to the 180 degrees
⇒ ∠3 + 110° = 180°
⇒ ∠3 = 180°− 110°
⇒ ∠3 = 70°
By using Supplementary angles, the measure of the given angle ∠3 is 70°.
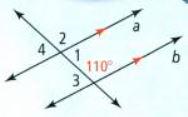
Similarity Exercises Solutions Chapter 7 Savvas Geometry Page 429 Exercise 4 Problem 4
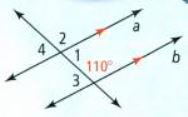
In this question, we have been given a diagram and an angle ∠4.
We need to find the measure of an angle.
By using Supplementary angles, we will calculate the result.
By using Supplementary angles, the measure of the given angle∠4 is 70°.
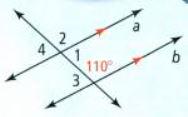
Similarity Exercises Solutions Chapter 7 Savvas Geometry Page 429 Exercise 5 Problem 5
In this question, we have been given ΔPAC ≅ ΔDHL.
We need to complete the congruence statement.
By using the properties of Congruence of Triangles, we will calculate the result.
We have given the two congruent triangles ΔPAC and ΔDHL.
The two triangles are said to be congruent if all three sides of one triangle are comparable to the corresponding three sides of the second triangle by SSS using rule
⇒ PA = DH
⇒ AC = HL
⇒ PC = DL
Therefore, \(\overline{P C} \cong \overline{D L}\).
By using the properties of Congruence of Triangles, the complete congruence statement is \(\overline{P C} \cong \overline{D L}\).
Chapter 7 Similarity Savvas Learning Co Geometry Explanation Page 429 Exercise 6 Problem 6
In this question, we have been given ΔPAC ≅ ΔDHL.
We need to complete the congruence statement.
By using the properties of Congruence of Triangles, we will calculate the result.
The two triangles are said to be congruent if any two sides and the angle included between the sides of one triangle are equivalent to the corresponding two sides and the angle between the sides of the second triangle by using SAS rule.
⇒ PA = DH
⇒ AC = HL
Therefore, ∠H ≅ ∠A
By using the properties of Congruence of Triangles, the complete congruence statement is ∠H≅∠A
Chapter 7 Similarity Savvas Learning Co Geometry Explanation Page 429 Exercise 7 Problem 7
In this question, we have been given ΔPAC ≅ ΔDHL.
We need to complete the congruence statement.
By using the properties of Congruence of Triangles, we will calculate the result.
We have given the two congruent triangles ΔPAC and ΔDHL
The two triangles are said to be congruent if any two angles and the side included between the angles of one triangle are comparable to the corresponding two angles and sides included between the angles of the second triangle by using ASA rule.
From the previous Page 429 Exercise 6 Problem 6 we have the angle ∠A ≅ ∠H, PC ≅ DL
Therefore, ∠PCA ≅ DLH
By using the properties of Congruence of Triangles, the complete congruence statement is ∠PCA ≅ DLH.
Solutions For Similarity Exercises In Savvas Geometry Chapter 7 Student Edition Page 429 Exercise 8 Problem 8
In this question, we have been given ΔPAC ≅ ΔDHL.
We need to complete the congruence statement.
By using the properties of Congruence of
Triangles, we will calculate the result.
Since all the sides of the ΔDHL when we find the congruence for ΔHDL so, the triangles are congruent by SSS rule.
The two triangles are said to be congruent if all three sides of one triangle are comparable to the corresponding three sides of the second triangle.
Therefore, ΔHDL ≅ ΔAPC
By using the properties of Congruence of Triangles, the complete congruence statement is ΔHDL ≅ ΔAPC.
Solutions For Similarity Exercises In Savvas Geometry Chapter 7 Student Edition Page 429 Exercise 9 Problem 9
In this question, we have been given a triangle.We need to write a congruence statement for each pair of triangles.
By using the SSS rule, we will calculate the result.
The two triangles are said to be congruent if all three sides of one triangle are comparable to the corresponding three sides of the second triangle.
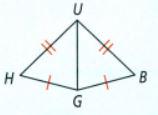
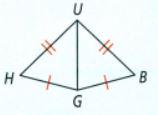
We have given the two triangles ΔHUG and ΔBUG in which we have given three equal sides
⇒ HU = BU
⇒ HG = BG
⇒ UG=UG(sameside)
Therefore, ΔHUG ≅ ΔBUG by SSS rule
A congruence statement for the pair of triangles is “The two triangles are said to be congruent if all three sides of one triangle are comparable to the corresponding three sides of the second triangle”. by SSS rule the triangles are congruent ΔHUG ≅ ΔBUG.
Solutions For Similarity Exercises In Savvas Geometry Chapter 7 Student Edition Page 429 Exercise 10 Problem 10
In this question, we have been given a triangle, and the value of
⇒ BC = 12
⇒ EF = 4.7
We need to find the value of BF and DE.
By using the properties of the triangle, we will calculate the result.
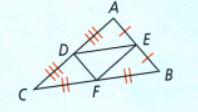
As we know from the triangle diagram the side BC = BF + CF and BF = CF so to calculate the value of BF we substitute the value
⇒ 12 = BF + BF
⇒ 12 = 2BF
\(\frac{12}{2}\)= BF
6 = BF or BF = 6
We know the value of EF which is equal to DE
By using the properties of the triangle, the value of BF is 6 . the value of EF is 4.7
Solutions For Similarity Exercises In Savvas Geometry Chapter 7 Student Edition Page 429 Exercise 11 Problem 11
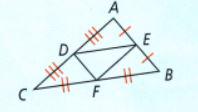
In this question, we have been given a triangle, and the value of
⇒ BC = 12
⇒ EF = 4.7
We need to find the value of AD and AC.
By using the properties of the triangle, we will calculate the result.
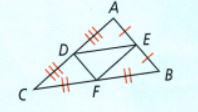
We can calculate the value of BE by Pythagoras theorem by substituting the values from the previous Page 429 Exercise 10 Problem 10 in triangle ΔBEF
⇒ BE2 = BF2 − EF2
⇒ BE2 = 62 − 4.72
⇒ BE2 = 13.91
⇒ BE = 3.72
Now, we calculate the value of AD by Pythagoras theorem by substituting the values from the previous Page 429 Exercise 10 Problem 10 in triangle ΔADE
⇒ AD2 = 4.72 − 3.72
⇒ AD2 = 4.72 − 3.72
⇒ AD = \(\sqrt{8.4}\)
⇒ AD = 2.9
By using the properties of the triangle, the value of BE is 3.72 the value of AD is 2.9.
Similarity Exercises Savvas Learning Co Geometry Detailed Answers Page 429 Exercise 12 Problem 12
In this question, we have been given an artist sketches a person.
She is careful to draw the different parts of the person’s body in proportion.
We need to find the meaning of proportion in this situation By using the proportion, we will calculate the result.
The meaning of proportion in this situation is the proper or suitable relationship between the size, shape, and orientation of different portions of anything
An artist creates a portrait of a person. She takes great care to draw the various sections of a person’s physique in proportion. The meaning of proportion in this situation is the proper or suitable relationship between the size, shape, and orientation of different portions of anything.
Similarity Exercises Savvas Learning Co Geometry Detailed Answers Page 429 Exercise 13 Problem 13
In this question, we have been given Siblings often look similar to each other.
We need to find the two geometric figures to be similarBy using the Geometric figures, we will calculate the result.
As we know Geometric figures are similar if they have the same shape but not necessarily the same size.
Siblings are frequently mistaken for one another. Geometric figures are similar if they have the same shape but not necessarily the same size.
Geometry Chapter 7 Similarity Savvas Learning Co Explanation Guide Page 429 Exercise 14 Problem 14
In this question, we have been given a road map that has a scale on it that tells us how many miles are equivalent to a distance of 1 inch on the map.
We need to estimate the distance between the two cities on the map.
By using the Distance, we will calculate the result.
We first measure the distance between the two cities in inches, then using the given scale, we convert the distance to miles.
On a road map, there is a scale that shows how many miles are comparable to 1 inch on the map. To measure the distance between the two cities in inches, then using the given scale, convert the distance to miles.
